Synthetic intelligence has did not persuade most Individuals that it’s going to make them higher at considering, deciding, or connecting with different people. New analysis launched December 1, 2025, reveals persistent skepticism about AI’s capability to reinforce core cognitive talents and interpersonal relationships, even among the many know-how’s heaviest customers.
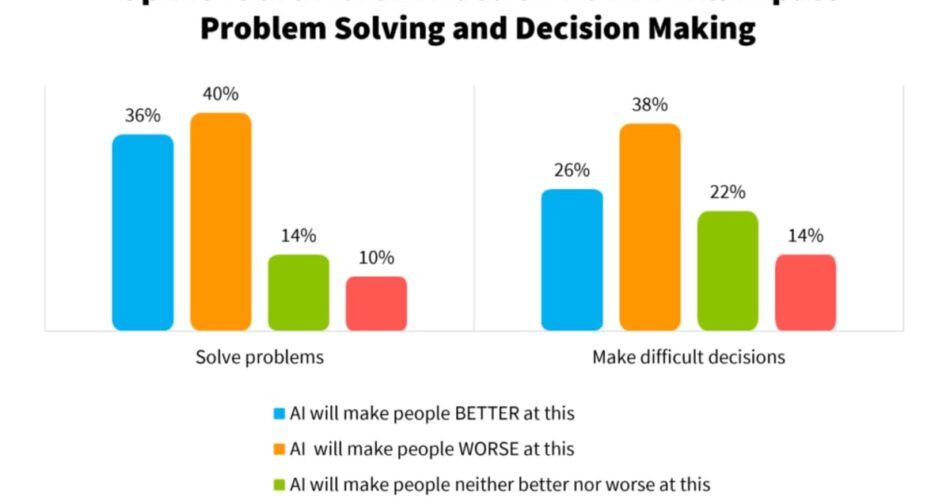
The survey data from SSRS and Challenge Liberty Institute reveals majorities of U.S. adults view AI’s influence negatively on talents to suppose creatively and kind significant human relationships. Opinions on problem-solving and decision-making capabilities lean detrimental as properly, although barely extra balanced than the overwhelming skepticism directed towards creativity and relationships.
These findings align with earlier analysis from Challenge Liberty Institute, Elon College’s Imagining the Digital Future Middle, and Pew Analysis Middle documenting typically detrimental public perceptions of AI’s results on uniquely human traits and cognitive expertise.
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one
Heavy customers stay unconvinced
4 p.c of U.S. adults report utilizing AI instruments “virtually continually,” representing the know-how’s most devoted person base. This group demonstrates extra optimism about AI’s potential than the overall inhabitants, but their enthusiasm has clear limits. Fewer than half of day by day customers—46 p.c—consider AI will make individuals higher at fixing issues. Solely 39 p.c suppose it is going to enhance decision-making talents.
The skepticism turns into extra pronounced when inspecting AI’s impact on human relationships. Among the many 37 p.c of U.S. adults who use AI day by day, greater than 4 instances as many say the know-how will make individuals worse at forming significant connections in comparison with those that count on enhancements. Fifty-three p.c anticipate deterioration in relationship-building talents, whereas simply 12 p.c foresee enhancement.
These patterns create challenges for product builders trying to construct shopper AI functions. The information suggests even in depth hands-on expertise with AI instruments doesn’t essentially convert customers into believers within the know-how’s capability to enhance basic human capabilities.
Youth skepticism poses advertising and marketing drawback
Youthful adults, usually the first audience for brand new AI-enabled instruments, show notably detrimental views about synthetic intelligence’s influence. The know-how reveals particularly weak efficiency amongst this demographic when measuring attitudes towards artistic considering and forming significant human relationships.
This skepticism amongst 18-to-29-year-olds carries strategic implications for advertising technology companies deploying agentic AI capabilities throughout 2025. Whereas platforms have rushed to combine autonomous AI methods into marketing campaign administration, the survey suggests youthful shoppers—who characterize essential long-term adoption prospects—harbor severe doubts about AI’s function in human-centric actions.
The findings problem assumptions that digital natives will naturally embrace AI integration throughout all elements of life. As a substitute, the info signifies this era approaches the know-how with discernment, weighing particular use circumstances in opposition to potential downsides.
Purchase advertisements on PPC Land. PPC Land has customary and native advert codecs by way of main DSPs and advert platforms like Google Advertisements. Through an public sale CPM, you may attain business professionals.
Considerate trade-offs, not reactionary worry
In-depth interviews performed with a subset of 18-to-29-year-old survey respondents reveal nuanced considering relatively than blanket resistance to synthetic intelligence. In accordance with the analysis, this era is “thoughtfully weighing the professionals and cons of AI throughout totally different settings, deliberating about which trade-offs they’re snug making in their very own lives.”
Most younger adults interviewed acknowledged advantages to AI-enabled instruments and platforms, notably for instrumental, fact-based duties. Nevertheless, additionally they acknowledged extra refined potential harms when AI replaces historically human-to-human interactions.
One 27-year-old respondent named Greg (names modified to guard privateness) articulated this balanced perspective: “What makes me enthusiastic about AI is that it isn’t executed but, it is a work in progress.”
The interviews revealed AI has prompted many younger adults to suppose extra intentionally about distinctive worth that human beings contribute to totally different interactions and settings. For some, publicity to AI-powered methods has made the “human aspect” in experiences like job functions, counseling, or inventive creation extra obvious than earlier than. This consciousness has led them to replicate on whether or not that human dimension represents one thing value preserving.
A number of younger adults raised issues extending past particular contexts to broader behavioral adjustments. They talked about normal impatience with duties and different individuals, unwillingness to be taught via trial and error, and prioritizing ends over means as potential penalties of accelerating AI reliance.

Sector-specific functions present promise
Whereas total sentiment tendencies detrimental, the analysis identifies contexts the place respondents see extra potential worth. Instrumental, fact-based duties characterize the strongest use case for AI adoption in public notion. These functions require knowledge processing, sample recognition, and computational evaluation relatively than creativity, empathy, or interpersonal sensitivity.
This distinction issues for marketing professionals managing AI-powered campaign optimization the place technical evaluation helps relatively than replaces human strategic judgment. The survey suggests shoppers differentiate between AI dealing with mechanical duties versus making choices requiring uniquely human qualities.
The promoting business has deployed AI extensively throughout technical infrastructure all through 2025. Amazon launched AI agents for automated campaign management in November. StackAdapt introduced its Ivy assistant in July for processing pure language queries in programmatic promoting. These implementations focus totally on knowledge evaluation and workflow automation relatively than artistic or relational features.
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one
Belief challenges compound adoption limitations
The SSRS findings doc skepticism extending past technical capabilities to basic questions on AI’s function in human society. This sample aligns with broader consumer trust challenges facing the advertising industry as AI integration accelerates.
Analysis launched in July 2025 confirmed 59 p.c of shoppers expressing discomfort with their knowledge getting used to coach AI methods. Two-thirds reported elevated issues about unauthorized knowledge entry, cybercrime threats, and identification theft. These privateness anxieties intersect with the potential skepticism documented within the SSRS survey to create a number of limitations to AI acceptance.
Media experts surveyed in December 2025 mirrored comparable warning, with 36 p.c indicating they’re cautious about promoting inside AI-generated content material and can take further precautions earlier than doing so. Forty-six p.c recognized growing ranges of AI-generated content material unsuitable for manufacturers as a severe risk to media high quality.
The mixture of functionality doubts and belief issues creates compound challenges for platforms trying to scale AI adoption. Customers should consider each that AI can carry out claimed features and that deployment serves their pursuits relatively than primarily benefiting know-how suppliers.
Measurement and transparency gaps
The skepticism documented within the SSRS analysis displays broader implementation challenges going through organizations deploying AI methods. Research published in November 2025 discovered most corporations stay in pilot mode regardless of govt claims of enterprise-ready AI applications, with insufficient knowledge governance frameworks undermining implementation high quality.
In accordance with Publicis Sapient evaluation, executives typically mistake generative AI experimentation or fundamental device utilization for full integration. One guide characterised the hole as “confidence with out measurement is perception, not certainty.” This disconnect between said AI readiness and precise functionality mirrors public skepticism about whether or not the know-how can ship claimed advantages.
Advertising and marketing organizations face specific measurement challenges. Survey data released in November 2025 confirmed 72 p.c of entrepreneurs plan to extend AI utilization over the following 12 months, but solely 45 p.c really feel assured of their skill to use it efficiently. Amongst these reporting low confidence, 40 p.c cited inadequate organizational understanding of AI or massive language fashions.
The shortcoming to trace outcomes in opposition to acceptable objectives ranked as a big barrier for 44 p.c of entrepreneurs surveyed. Many depend on proxy metrics like clicks or internet visitors that fail to seize AI’s broader enterprise influence, creating measurement gaps that might gas shopper skepticism about precise worth delivered.
Platform deployment outpaces person readiness
Main know-how corporations have accelerated AI characteristic releases all through 2025 regardless of persistent public skepticism. Google expanded AI Mode to all U.S. customers in Might 2025. The corporate’s AI Overviews now serve over 1.5 billion customers month-to-month, with enlargement to extra English-language nations scheduled for later within the 12 months.
Nevertheless, accuracy concerns shadow these deployments. Analysis printed in July 2025 testing AI instruments for pay-per-click promoting steering discovered 20 p.c of responses contained inaccurate info. Google AI Overviews demonstrated the poorest efficiency with 26 p.c incorrect solutions, doubtlessly exposing thousands and thousands of customers to flawed steering.
These reliability points compound the potential skepticism documented within the SSRS survey. If customers doubt AI can improve their considering, creativity, or relationships, accuracy issues present concrete proof supporting these issues relatively than proof to alter minds.
Industry analysis from October 2025 predicted one-third of corporations will erode model belief and buyer expertise via untimely deployment of generative AI chatbots and digital brokers in 2026. Forrester characterised the chance as strain to scale back operational prices driving organizations to implement customer-facing AI methods in contexts the place failure is probably going.
Human worth turns into extra seen
The SSRS analysis paperwork an sudden consequence of AI deployment: the know-how has made many individuals extra acutely aware of uniquely human contributions to interactions and outputs. A number of younger adults interviewed for the examine talked about that encountering AI methods highlighted the uncommon and sometimes difficult-to-measure worth people contribute to numerous actions.
This heightened consciousness of human distinctiveness represents each a problem and a possibility for AI builders. Customers who develop into extra acutely aware of what makes human interplay worthwhile might resist AI substitution in these domains whereas remaining open to deployment in areas the place human involvement provides much less distinctive worth.
For promoting functions, this means continued openness to AI-powered analytics and campaign management toolsthat increase relatively than exchange human strategic considering. Newton Analysis’s integration with Snowflake Cortex AI in November 2025 exemplifies this strategy, enabling manufacturers to run media combine modeling and incrementality evaluation whereas entrepreneurs retain decision-making authority.
The excellence between augmentation and alternative seems essential for public acceptance. In accordance with the SSRS findings, most respondents acknowledge AI’s utility for particular duties whereas desirous to protect human components in actions the place these contributions matter most.
Product growth implications
The nuanced reflections captured within the SSRS interviews recommend people are approaching AI adoption rationally relatively than emotionally. They check instruments, consider usefulness, and weigh integration choices earlier than absolutely incorporating AI into their lives. This measured strategy contradicts assumptions that resistance stems primarily from worry or misunderstanding.
Kristen Purcell, Jeb Bell, and Jessica Theodule authored the analysis, with particular due to Darby Steiger, Rachel Askew, Melissa Silesky, Hannah Ritz and the SSRS qualitative crew. The examine positions AI adoption as an ongoing analysis course of the place customers constantly assess whether or not particular functions ship ample worth to justify potential downsides.
For product builders, this implies profitable AI instruments should show clear utility in contexts customers already discover acceptable for technological help. Advertising and marketing AI as a common resolution for all human actions conflicts with public sentiment favoring selective deployment primarily based on cautious consideration of trade-offs.
The analysis additionally suggests transparency about AI’s limitations may construct belief extra successfully than overselling capabilities. If customers count on AI to wrestle with creativity, relationships, and sophisticated decision-making, merchandise that acknowledge these boundaries whereas excelling at knowledge processing and routine duties might obtain higher adoption than these promising complete cognitive enhancement.
Regulatory and coverage context
The skepticism documented within the SSRS survey arrives as regulators worldwide enhance scrutiny of AI deployment. European knowledge safety authorities adopted Pointers 3/2025 in September, establishing advanced compliance necessities the place Digital Companies Act and Common Information Safety Regulation obligations intersect.
Australia proposed dual-track privateness compliance frameworks in August, basically difficult present reform proposals by specializing in whether or not knowledge use serves particular person greatest pursuits relatively than mere consent mechanisms. These regulatory developments replicate official concern about AI’s influence on shopper welfare that aligns with public skepticism within the SSRS knowledge.
Privateness lawsuits focusing on AI functions have elevated all through 2025. Industry predictions released in Octoberforecast a 20 p.c surge in privateness litigation throughout 2026 as shoppers and legislation corporations broaden focus past monitoring pixels to embody AI functions themselves.
The mixture of public skepticism, regulatory strain, and authorized danger creates incentives for corporations to deploy AI extra cautiously than present adoption charges recommend. Advertising and marketing organizations face specific strain to show AI utilization serves shopper pursuits relatively than primarily decreasing operational prices or enhancing focusing on capabilities on the expense of privateness.
Trade adaptation patterns
Advertising and marketing know-how platforms have responded to AI skepticism with various methods. Some emphasize transparency and person management. Others deal with demonstrating concrete worth via pilot applications and measurable outcomes. Nonetheless others have slowed deployment pending higher understanding of shopper acceptance.
Survey data from media experts launched in December 2025 confirmed 52 p.c recognized social media as going through severe challenges throughout the business throughout the subsequent 12 months, with AI-generated content material issues contributing to this evaluation. Eighty-one p.c said growing ranges of AI-generated content material in retail media networks might be a big concern requiring monitoring.
These skilled issues mirror shopper skepticism within the SSRS knowledge. Each audiences query whether or not AI deployment in sure contexts serves real wants or creates new issues requiring extra oversight and intervention.
The advertising and marketing neighborhood faces choices about deployment tempo and transparency. Research from Raptive released in July 2025 confirmed reader belief dropping practically 50 p.c for content material perceived as AI-generated, with corresponding 14 p.c declines in model commercial effectiveness. These findings recommend aggressive AI deployment with out shopper acceptance dangers damaging present enterprise fashions.
Trying forward
The SSRS analysis paperwork public sentiment at a particular second in AI’s growth. Future surveys might reveal shifting attitudes as know-how improves and deployment patterns evolve. Nevertheless, the present snapshot reveals clear boundaries round the place Individuals at present see worth in AI help.
Builders hoping to develop AI’s function in human cognition, creativity, and relationships face the problem of adjusting minds already skeptical primarily based on precise utilization expertise. The discovering that even heavy customers doubt AI’s capability to reinforce artistic considering or interpersonal connections suggests easy publicity is not going to routinely generate acceptance.
Advertising and marketing professionals navigating this panorama should stability platform capabilities in opposition to shopper consolation. Industry analysis from McKinsey printed in July 2025 recognized agentic AI as probably the most vital rising development for advertising and marketing organizations, with $1.1 billion in fairness funding flowing into the know-how throughout 2024.
Nevertheless, funding momentum alone can’t overcome skepticism rooted in analysis of AI’s precise influence on human talents. The SSRS knowledge suggests profitable deployment requires demonstrating worth in domains customers already discover acceptable relatively than trying to develop AI into all elements of human exercise no matter public acceptance.
The analysis crew emphasised the human nature of present AI adoption patterns. Individuals are testing, evaluating, and making thought-about judgments about the place synthetic intelligence matches into their lives. This rational strategy means successful acceptance requires delivering real worth in contexts customers discover acceptable relatively than advertising and marketing AI as a common resolution disconnected from precise wants and preferences.
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one
Timeline
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one
Abstract
Who: SSRS and Challenge Liberty Institute performed the analysis, surveying U.S. adults and conducting in-depth interviews with 18-to-29-year-olds. Analysis authors embrace Kristen Purcell (SSRS), Jeb Bell (Challenge Liberty Institute), and Jessica Theodule (Challenge Liberty Institute).
What: Survey knowledge reveals majorities of Individuals view AI negatively for considering creatively and forming significant human relationships. Even among the many 37% who use AI day by day, skepticism persists—with solely 46% believing AI will enhance problem-solving and simply 39% anticipating higher decision-making. Qualitative interviews present younger adults thoughtfully weighing AI trade-offs relatively than displaying reactionary worry.
When: The findings had been launched December 1, 2025, constructing on earlier analysis from Challenge Liberty Institute, Elon College’s Imagining the Digital Future Middle, and Pew Analysis Middle displaying comparable patterns of public skepticism towards AI’s influence on uniquely human traits.
The place: The analysis examines attitudes throughout the U.S. grownup inhabitants, with particular deal with heavy AI customers (4% who use instruments “virtually continually”) and youthful adults aged 18-29 who characterize main goal audiences for AI-enabled merchandise however show notably detrimental views.
Why: The analysis issues as a result of it paperwork persistent skepticism about AI’s capability to reinforce core human talents even amongst heavy customers, creating challenges for product builders and advertising and marketing professionals deploying AI methods. The findings recommend public resistance stems from considerate analysis relatively than worry or misunderstanding, requiring corporations to show real worth in acceptable contexts relatively than advertising and marketing AI as a common resolution. This skepticism compounds with belief challenges, accuracy issues, and regulatory strain to create a number of limitations to AI acceptance throughout shopper {and professional} audiences.
Source link