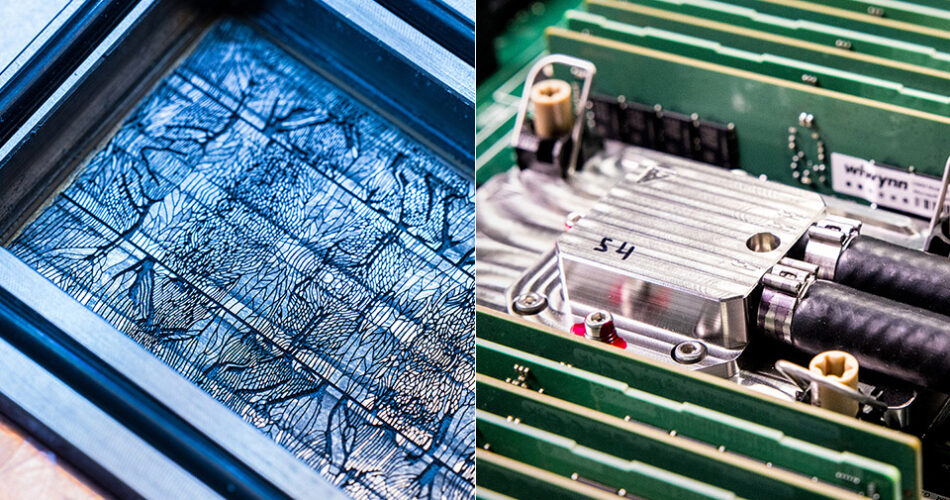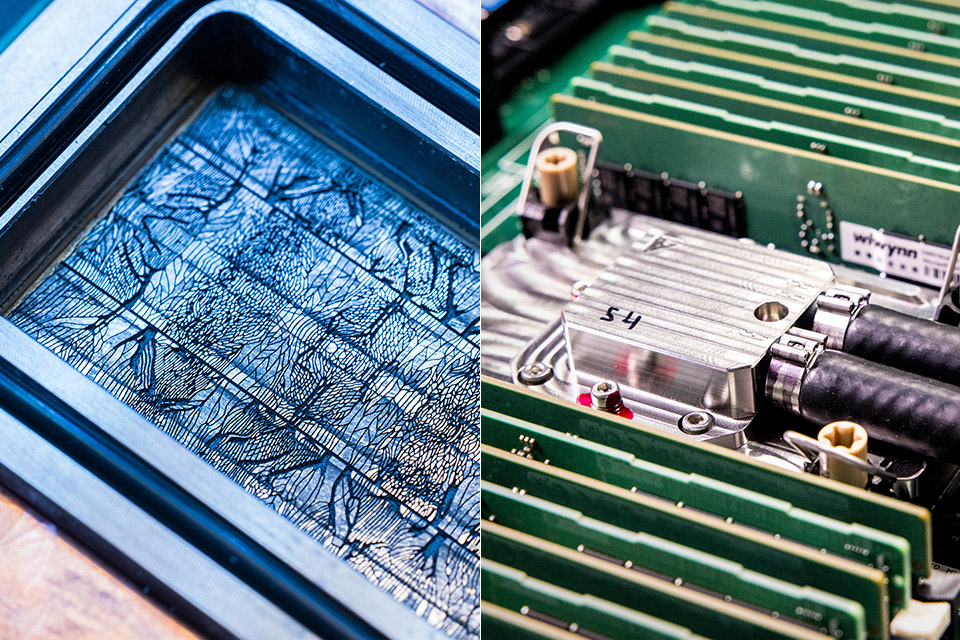
Photograph credit score: Dan DeLong for Microsoft
Cooling laptop chips is a quiet warfare within the tech world; as AI pushes silicon to the restrict, they’re hotter than ever and conventional cooling is failing to maintain up. Microsoft’s new discovery, microfluidics, can change the sport by cooling from inside.
Microfluidics works by carving microscopic grooves into the again of a silicon chip, so liquid cooling can move straight the place the warmth is generated. These grooves, in regards to the diameter of a human hair, are little rivers that take away warmth quicker than the copper plates utilized in many information facilities at the moment. Microsoft’s testing confirmed this could take away warmth as much as 3 times higher than these plates, decreasing the utmost temperature rise in a chip by 65%. This cooling resolution stored a server working a simulated Microsoft Groups assembly secure.
Designing these grooves is just not a simple process as they must be deep sufficient to switch sufficient liquid however not so deep the chip turns into unstable. Microsoft labored with a Swiss firm, Corintis, to refine the design, borrowing from nature. The grooves mirror the branching patterns of veins in a leaf, directing coolant to the most well liked elements of the chip. AI additionally performed a job, monitoring warmth patterns to see the place the liquid flows. It’s a fragile stability of engineering and artwork that retains the chip secure whereas the coolant does its job.
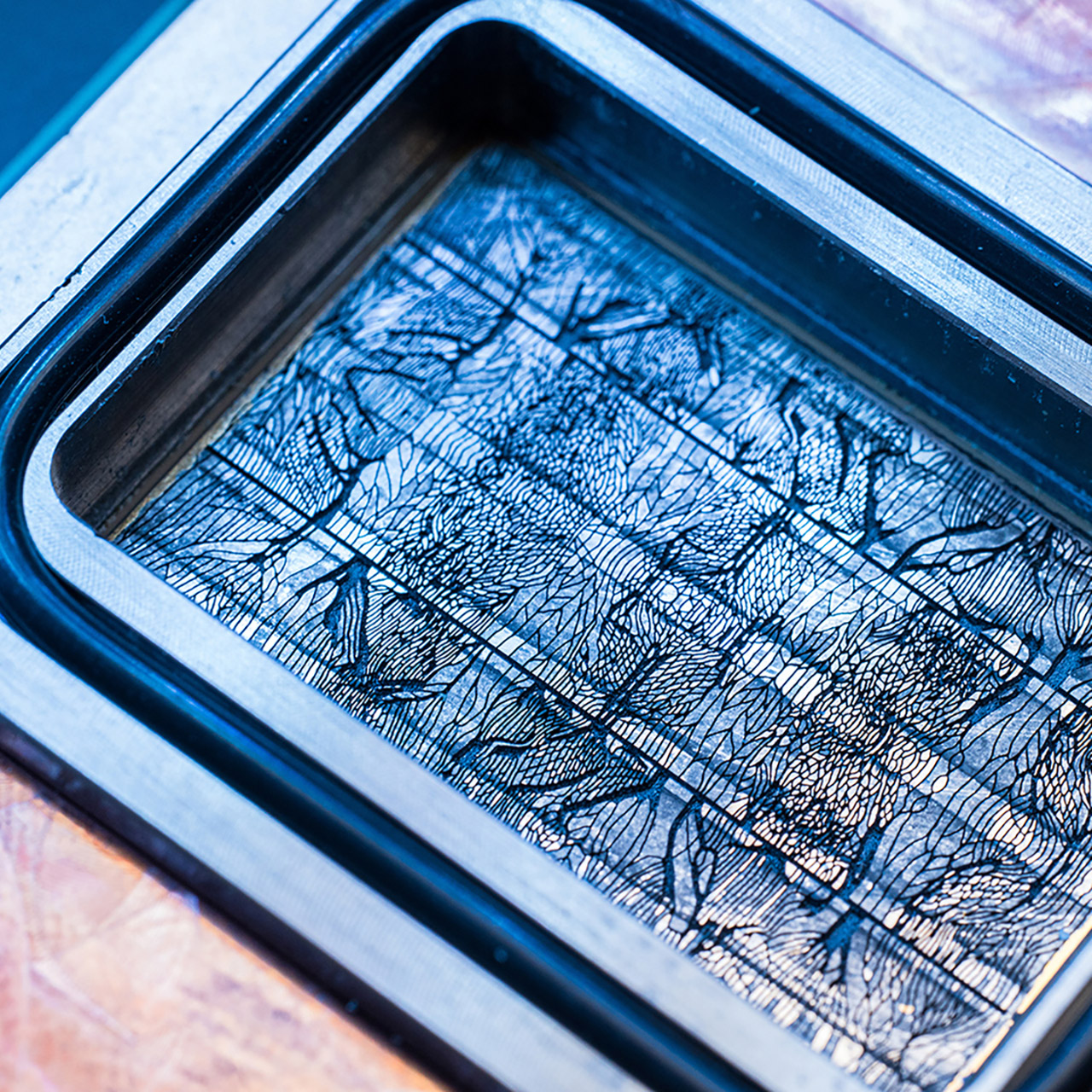

That is necessary as a result of present chips, particularly these utilized in AI, generate quite a lot of warmth as they course of enormous quantities of information. Conventional cooling strategies, like followers blowing air or copper plates with liquid flowing throughout them, can’t sustain. These applied sciences use layers of fabric between the chip and the coolant that act as blankets, trapping some warmth. Microfluidics removes these layers, so the coolant can contact the silicon straight. Which means the liquid doesn’t must be as chilly to work, saving the power that will in any other case go to chilling it.
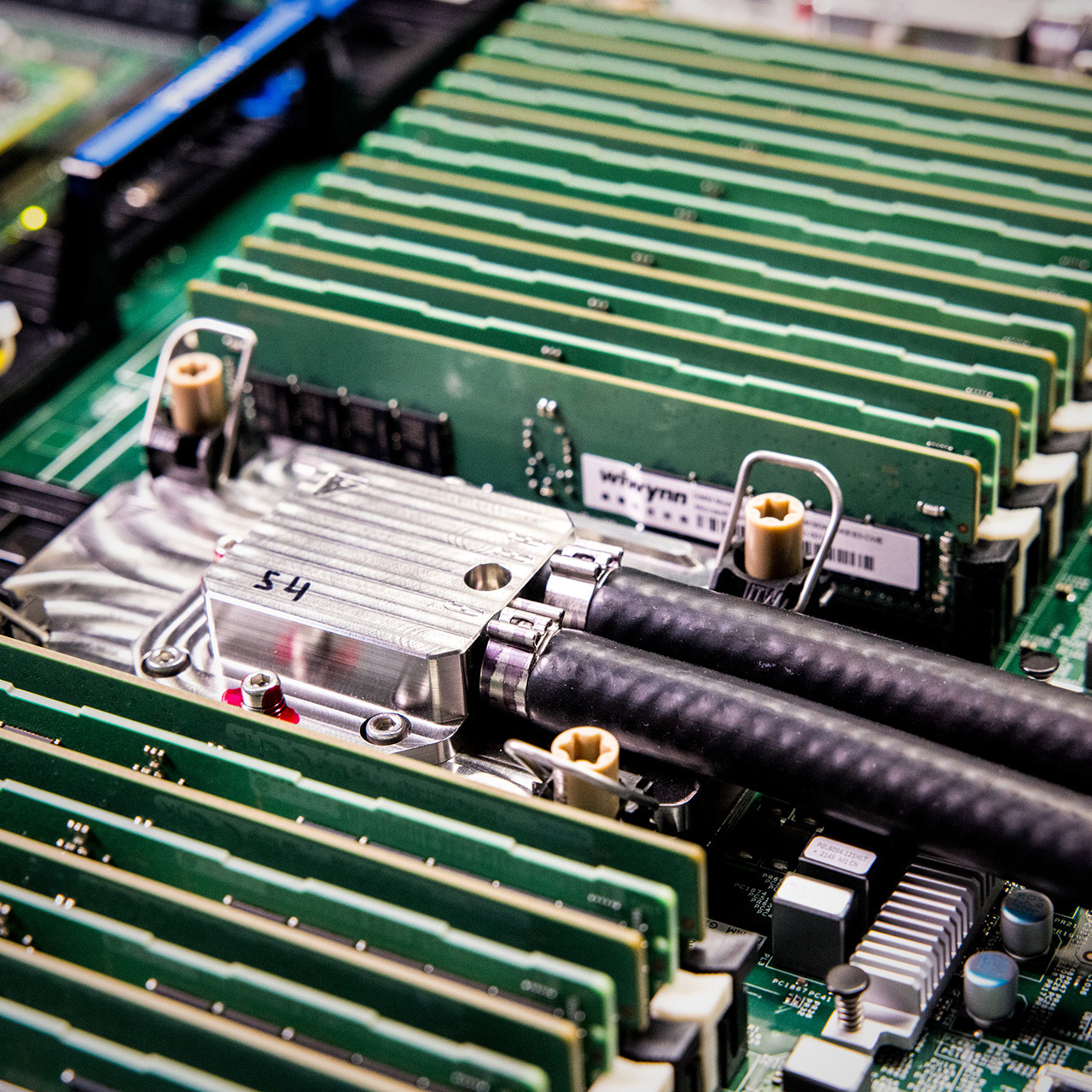
Knowledge facilities, the spine of companies like cloud computing and video calls, will profit huge time. Take a Microsoft Groups name for instance. A whole bunch of companies work collectively to attach individuals, host chats, mix audio and transcribe speech. These duties spike at predictable instances like the beginning of a gathering and servers get maxed out. To deal with these spikes, firms both add extra servers that are often idle or overclock present ones. Overclocking generates extra warmth which might injury the chip. Microfluidics might let servers run quicker with out overheating, scale back prices and enhance reliability.
Sooner or later, this know-how might fully change semiconductor structure. Stacking chips in 3D might make them quicker by decreasing the gap information travels, however warmth has been the barrier. Microfluidics might repair this by routing coolant by means of tiny pillars between stacked chips, like pipes in a skyscraper. This might result in smaller, extra highly effective information facilities and push the bounds of computing.
Source link