There are lots of varieties of errors in Python. Irrespective of the place you’re in your Python journey, you’ve got more than likely confronted a number of of those errors. For some, it may be straightforward to know what’s unsuitable in your code. For others? Not a lot. That is why I am explaining what they imply.
5
IndentationError
When you’re an absolute newbie in Python or have moved from a language like C/C++ or Java, then this would be the most typical error you will encounter. In Python, we outline blocks utilizing indentation as an alternative of braces, as is frequent in lots of different languages. A “block” refers to a section of code that’s handled as a single unit. Take into consideration conditional blocks, a perform, or a loop.
In Python, all statements inside a block should have the identical degree of indentation. When the indentation degree modifications (both will increase or decreases), it signifies the beginning or finish of a block. Python depends closely on constant indentation. Inconsistent indentation will result in IndentationError.
A standard state of affairs when you might face this error is whenever you copy-paste code into your editor. Generally, as a result of distinction between how totally different editors format textual content, the indentation could break from one editor to a different.
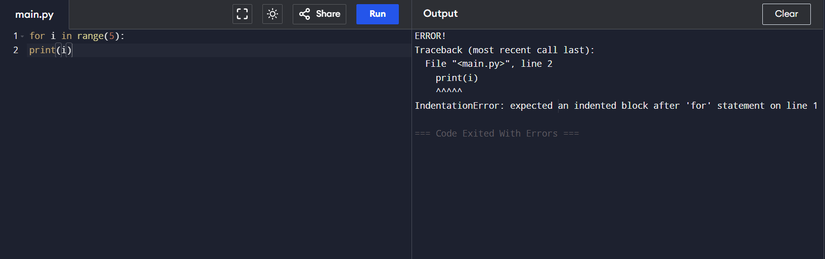
for i in vary(5):
print(i)
Whereas copying the above strains of code, the indentation broke. Making an attempt to run this code will produce IndentationError. To repair this, that you must indent the statements persistently underneath their block.
for i in vary(5):
print(i)
One other concern you might face associated to this error is utilizing tabs and areas. Some editors use tabs whereas others use 4 areas for indentation. When you combine them up in your code, you will get an error. This one is much more complicated as a result of it is arduous to see with the bare eye which line comprises tabs and which one comprises areas.
4
SyntaxError
Each programming language has a syntax. In different phrases, a algorithm that you must comply with in an effort to write code in that language. So, when you break any of these guidelines, the language does not know what you are making an attempt to do and offers you a syntax error.
In Python, a SyntaxError occurs when the interpreter finds code that doesn’t conform to the foundations of the Python language. This implies the code is structured in a approach that Python can not perceive or execute. A SyntaxError will forestall your program from even beginning. A number of the most typical syntax errors you will face in Python are:
- Lacking a punctuation (forgetting the colon (:) when beginning a code block, comparable to conditionals, loops, or features.)
-
Misspelling or misplacing a Python key phrase (writing
esleas an alternative ofelse, utilizing abreakassertion the place it isn’t imagined to happen.) - Utilizing reserved key phrases as variable names.
- Misusing operators (utilizing the project operator (=) the place you are supposed to make use of the equal operator (==) in an announcement.)
- Forgetting to finish a parenthesis or finish a quote. This typically occurs whenever you’re working with a number of expressions and they’re inside nested parentheses.
The excellent news is that the Python interpreter is sort of sensible sufficient to pinpoint what kind of syntax error you dedicated and level to the road quantity, and even the approximate place of the error. Though generally the error message could also be a bit bit ambiguous and never mirror the precise trigger. When you’re utilizing code editor or IDE, then it may recommend the error and potential fixes.
3
IndexError
Python affords a number of built-in information buildings comparable to lists, tuples, and units. We regularly must iterate by these information buildings and entry parts. Each information construction comprises one thing known as an index, which is the place of a selected ingredient in that construction.
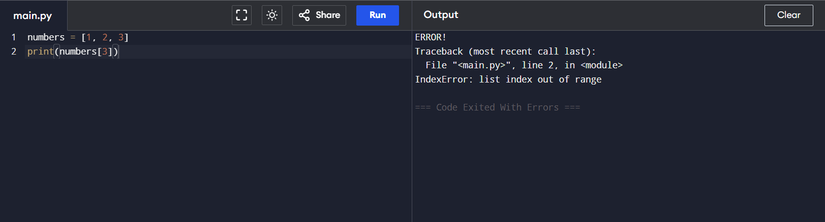
numbers = [1, 2, 3]
Right here, we’ve a listing known as numbers. The way in which we will entry the weather of the checklist is thru its indices, like this:
print(numbers[1])
IndexError generally occurs whenever you attempt to entry a component in an information construction (additionally known as a sequence) in an index that’s exterior the legitimate vary of indices for that information construction. In lots of programming languages, together with Python, the index begins from zero. So, if a sequence comprises N parts, the vary of indices is 0 to N-1.
Typically, programmers neglect to deal with this zero-based index case and fall into an off-by-one error, which causes an index error. To keep away from index errors, at all times measure the size of your sequence.
if index
When iterating by a sequence, a common Python mistake many programmers make is modifying it too. This additionally causes an index error. So, keep away from doing that.
2
ValueError
Python affords many information varieties. When working with totally different information varieties, we have to take care of totally different literal values. Generally, we use them as perform arguments. What we have to know is that each perform has an anticipated kind of knowledge as an argument. When receiving that information, the perform additionally checks whether or not the worth it acquired is legitimate.
And this brings the ValueError in Python. It is a built-in exception that’s raised when a perform or operation receives an argument that has the proper information kind however an inappropriate worth. This implies the kind of the argument is appropriate, however its particular worth isn’t legitimate for the operation being carried out.
A fairly frequent case for that is whenever you need to convert one information kind to a different.
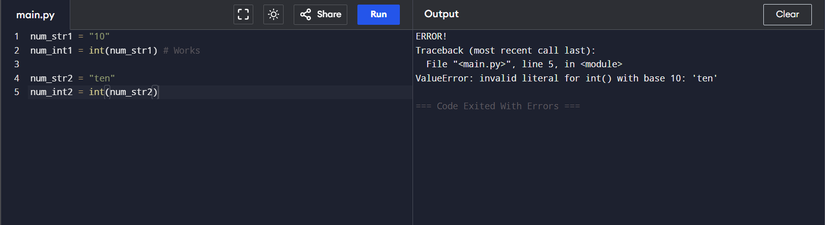
int('10')
This converts the string ’10’ to the integer 10. However, when you do that:
int('ten')
You get a worth error. That is as a result of the int() perform expects a string information kind argument. However that string worth must be made up of digits. That is the explanation ‘ten’ is an unacceptable worth. Equally, you might get this error when doing mathematical operations.
import math
math.sqrt(-5)
The sqrt() perform expects a constructive quantity. So, a damaging quantity as an argument will increase a worth error. One other frequent state of affairs of going through worth errors is whenever you take person enter. As a result of you have no management over what the person can enter, typing a unsuitable worth will end in an error.
One of the best ways to deal with ValueError is by utilizing try-except blocks.
strive:
num = enter("Enter a quantity: ")
num_int = int(num)
besides ValueError as e:
print(f"Caught a ValueError: {e}")
This manner, you may forestall program crashes even when the person inputs the unsuitable worth.
1
AttributeError
The AttributeError is a typical exception in Python that happens whenever you attempt to entry an attribute or methodology that doesn’t exist on a specific object. In easy phrases, it means you are asking an object to do one thing it isn’t designed to do.
Whether or not you are working with strings, lists, or customized lessons, it is simple to imagine an object has sure properties or capabilities, particularly when switching between totally different information varieties. Nonetheless, Python will increase an AttributeError the second you try to name an attribute that is not accessible.
textual content = "hiya world"
print(textual content.push())
Strings haven’t any push() methodology. So, within the above instance, you will get an attribute error. Here is one other instance:
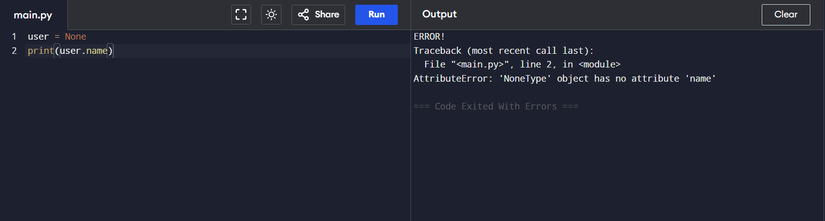
person = None
print(person.identify)
Making an attempt to entry the ‘identify’ attribute on a NoneType object will even end in that error. In all these circumstances, the item you are working with merely does not help the attribute you are making an attempt to entry. To forestall this error from interrupting your program, take into account verifying object varieties.
kind(obj)
isinstance()
The built-in dir() perform reveals all legitimate attributes and strategies accessible on an object. Utilizing it in your object will let you understand what attributes you should utilize.
Python being a simple language, it is fairly straightforward to learn the basics of the language. Now that you understand about among the frequent errors, you’ll debug them and write more Pythonic code with none worries.
Source link