You may not realize it, however a few of the main work within the cybersecurity area is being accomplished in Burnaby, B.C.
That’s as a result of the Decrease Mainland metropolis is house to the Canadian headquarters of Fortinet, one of many world’s largest cybersecurity firms. Whereas Fortinet has workplaces and operations in additional than 150 nations and territories, its international “FortiGuard Labs” R&D campus is definitely primarily based in Burnaby. It’s maybe a stunning reality contemplating the corporate’s huge buyer base of almost 900,000 that features such clientele as Interpol, the World Financial Discussion board, NATO and MIT. In complete, over 2,600 staff out of Fortinet’s 14,000-plus international workforce are unfold throughout Canada.
However Fortinet’s Canadian ties prolong to co-founder, president and chief expertise officer Michael Xie’s youth. Within the 90s, the Chinese language native moved to North America and studied engineering on the College of Manitoba. Whereas Fortinet would later be based in Sunnyvale, California in 2000, Xie was truly dwelling in Burnaby when he prototyped what would change into the corporate’s first product.
“It actually allowed us to begin the group right here. So though headquartered in Sunnyvale, I say [we’re] ‘heartquartered’ right here. It simply grew right here and grew right here as a result of we had a expertise pool,” says Gordon Phillips, regional vp of gross sales for Western Canada at Fortinet. “It’s such an vital half, as a result of each product is touching right here. The largest risk analysis lab is right here. Every bit of our enterprise touches Burnaby.”
Throughout a media tour of a part of the Burnaby campus, Fortinet supplied a glimpse at a few of the work that goes on there. Giant screens containing an virtually overwhelming quantity of information are hung prominently all through. Rows and rows of desks and computer systems are aligned, with staff typing away diligently. In an adjoining windowed room, analysts, with the assistance of synthetic intelligence and machine studying instruments, are actively responding to threats that are available, represented on-screen by purple dots that circulate in a pool of protected inexperienced ones that pour like a miniature Niagara Falls.
As we transfer by means of the ability, we come to a large room containing the entire servers. It appears to be like as high-tech as you’d anticipate, and there’s one thing oddly stress-free about imagining the extreme Tron-like cyber warfare these machines are participating in as they quietly hum in a nondescript room. On the similar time, it’s good to know that they’re fairly sustainable, too. Utilizing a dry cooler system, the lab is ready to take Canada’s naturally cooler air in 9 months of the yr to maintain the machines from overheating at 98 per cent effectivity.
All of that is little doubt vital contemplating that Fortinet’s community of human and machine employees are labouring 24/7 to course of a couple of trillion safety occasions every day. It’s a staggering quantity to even attempt to comprehend. And naturally, risk ranges are solely growing over time with the development of expertise. Throughout our tour, Fortinet defined that the monetary affect of cybercrime is estimated to be round US$10 billion (about C$13.8 billion) this yr. As Phillips explains, that’s a major enhance in simply a few years.
“Development has been phenomenal, and it’s getting larger and larger,” says Phillips. “I do suppose AI will play into that and make it much more important over the subsequent few minutes.”
On the similar time, Phillips cites latest feedback about operational expertise (OT) from Fortinet CEO Ken Xie about there being “ten instances extra” gadgets than folks, which can solely exacerbate these threats. They’re not essentially as mature as IT cybersecurity, so there’s undoubtedly loads of work to do there,” he says.
In fact, it wasn’t all the time that method.
“After we first began doing safety, actually, it was perimeter safety and defending your endpoint system with some antivirus. Now, we’ve 60-plus options that prospects can get from us, options and providers, and it may be each piece of it. It comes from mail, it comes from the endpoints. It comes from the cloud. It comes from the purposes. It comes from cell gadgets. There’s so many items now,” he says. “Safety began off, ‘if we shield the perimeter and run some safety on the desktop, we’re fairly safe.’ Now, we’re so open, and we’re such a excessive speaking society that there’s simply so many locations that they’ll hit us from. In order that’s actually been the most important change — staying forward of it.”
He particularly singles out cell gadgets as one thing that individuals have to regulate.
“I feel each one in every of us now could be coping with these loopy SMSes coming in the place they’re simply in search of a reply, or they’re seeing you’ve a package deal being delivered, or couldn’t be delivered, and, ‘click on on this hyperlink.’ We will’t click on on these hyperlinks. However it does really feel like Amazon or UPS or whoever it’s. So it’s an actual problem as a result of individuals are making selections each day, ‘Is {that a} protected hyperlink or not? Is that my financial institution or not? Is that an actual alert or not?’” he says.
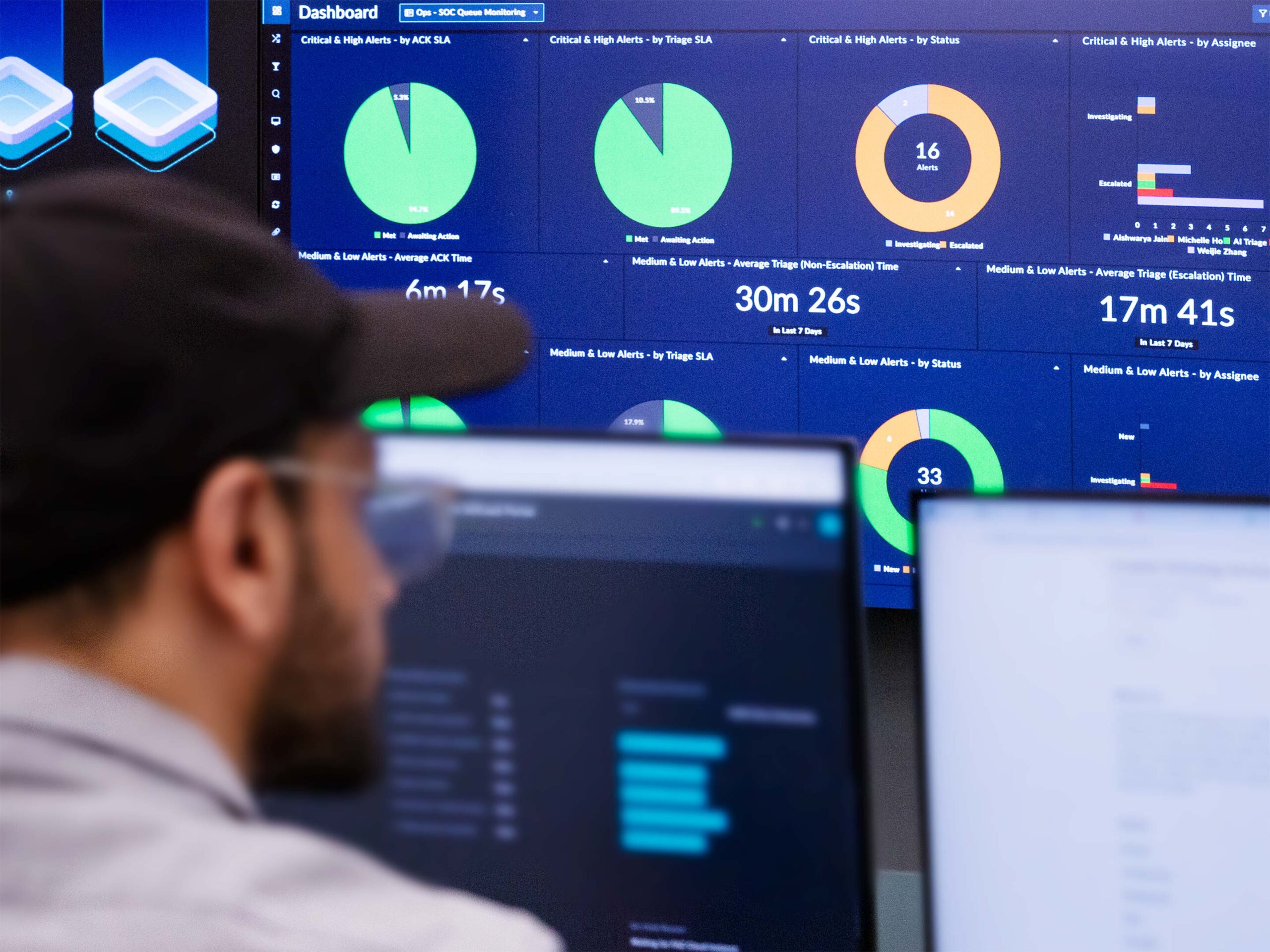

“And all people has not less than one [device]. Typically, individuals are carrying a cellphone, they’re carrying a pill, they’re carrying a number of gadgets. Whereas earlier than, your laptop at your workplace was considerably straightforward to safe. Now, the merchandise or the gadgets we’ve to safe are at house, they’re in our pockets, they’re in our vehicles — they’re in all places.”
In its latest Threat Landscape Report, Fortinet additionally supplied perception into the evolving habits of dangerous actors around the globe. Most notably, Canada positioned third (5 per cent) general by way of the very best variety of cyberattacks final yr, behind solely the U.S. (61 per cent) and U.Okay. (6 per cent).
“A whole lot of instances, cybercriminals are attempting to instil discomfort and terror, and in a beautiful free nation like Canada, it has a much bigger affect if they aim this atmosphere,” says Phillips. “The quantity of essential infrastructure we do right here due to energy technology, due to the power sector and people type of organizations — and the truth that we’ve very sturdy well being care in Canada.” He added that Canada’s shut relationship with the U.S. can also be a contributing issue.
When it comes to what’s truly being focused, Fortinet notes that industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and monetary providers have been going through a “surge” in tailor-made cyberattacks. With respect to that final market, Phillips notes that “we’ve very massive banks in Canada in comparison with lots of the different geographies on the market on the earth,” which makes them of explicit curiosity to hackers. “Now we have very sturdy cyber safety resilience in our banks, which is nice. Now we have a really safe infrastructure there, however they’re focused as a result of the affect is important.”

Naturally, people can’t reply to each one in every of these threats, particularly when there are a couple of trillion per day. Phillips says that’s the place AI can are available. “We’re triaging trillions of threats a day, in search of these patterns. Creating that layer of defence the place we will logically go in and see what’s occurring is essential,” he says. “The opposite piece of it that’s tremendous cool, although, is the agentic AI, the place you possibly can take a much less expert analyst and have your playbooks information them by means of.”
He proposes an instance of a plant operator who’s “not an IT man” however will get an alert on a Friday night that any individual is making an attempt to get into the system and suspects it’s fraudulent due to the timing.
“He can actually simply say, ‘What is going on?’ and it’ll give a reply saying, ‘That is the behaviour we’re seeing.’ What are you recommending we do?’ ‘Properly, I like to recommend you name the IT safety group, or I like to recommend you unplug this system,’ or no matter it will get advised. However it’s primarily based on the playbooks and one of the best practices that our FortiGuard Labs group has put in,” says Phillips. “So I feel that’s going to be the most important impact of AI — we’ll be capable to repel the assaults extra successfully. As a result of we virtually have a reserve military now. We virtually have a complete group of individuals that may be extra expert cyberprofessionals by leveraging AI to upskill them on the time of an assault.”
However finally, Phillips says it’s vital that we, the common folks, keep vigilant as a result of we’re the “first line of defence” towards cybercrime. “We’re those which can be going to see far more of these makes an attempt, as a result of it’s a numbers recreation to that risk actor. If I ship out one million textual content messages, I solely want a pair to click on on it, as a result of that turns into cash for me,” he says. (Throughout our tour, Fortinet defined that for each $4,000 dangerous actors spend on cybercrime, $1 million is returned to them — a 2,500 per cent return on funding.)
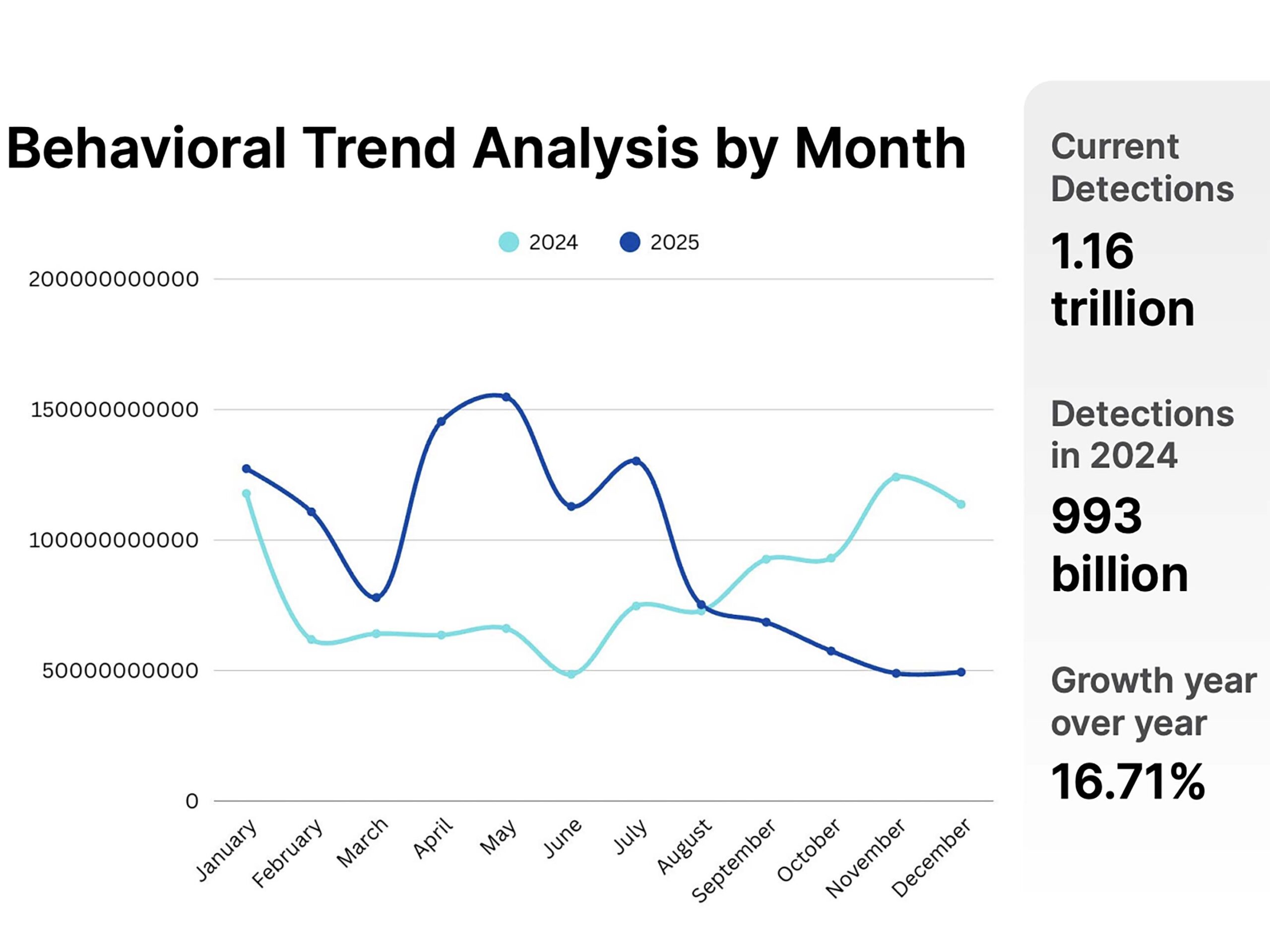
Information from Fortinet’s 2025 Risk Panorama Report.
Subsequently, he requires folks to be extra “usually cyber conscious,” particularly in terms of youthful customers. “They might be simpler to trick as a result of they don’t have the expertise we’ve as adults. After which additionally they take benefit people who find themselves much less cyber conscious or tech conscious; they actually make the most of senior residents […] Hopefully, making it simpler and higher for them to be extra conscious, and cybersecurity consciousness is basically the most important piece of that.”
Naturally, then, that begs the query: what recommendation would he give to assist enhance that consciousness?
“My father and I discuss this rather a lot, as a result of I’ll get the decision saying, ‘Hey, I obtained this message. Ought to I click on on it?’ Don’t click on!” he says. “Actually have a look at it and say, ‘Am I anticipating one thing from my financial institution?’ Or don’t click on and go in your banking app and see if that message is ready there for you. As a result of sometimes, these are simply folks making an attempt to steal your credentials. So don’t click on. Be very assured with what you’re doing. Don’t go to an untrusted website. Simply a few of these instruments are tremendous vital.”
He suggests double-checking to verify supposed considerations are certainly legitimate, be that by opening the corresponding app or, within the case of banking data, logging on by way of your laptop as an alternative. “It’s sometimes simply dangerous data.”
Picture credit score: Fortinet
MobileSyrup might earn a fee from purchases made by way of our hyperlinks, which helps fund the journalism we offer free on our web site. These hyperlinks don’t affect our editorial content material. Help us here.
Source link



