There are lots of methods to seek out and retrieve knowledge from a desk or vary primarily based on a lookup worth. In truth, as a result of Microsoft typically comes up with new, modernized options, there are too some ways! So, listed here are the three I exploit probably the most.
All of the examples on this article lookup values in a formatted Excel desk, as structuring knowledge on this approach has many benefits. In consequence, the formulation use structured table references. In case you use the next features to lookup values in common ranges, use direct cell references as a substitute.
XLOOKUP: A Fashionable Tackle VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP
XLOOKUP is arguably the mom of all lookup features in Excel, which is shocking given it took Microsoft over 30 years to give you it!
It returns a number of gadgets from a spread or array in keeping with the primary or final match it finds. As a result of it really works vertically and horizontally, seems to be up issues to the left, proper, above, or beneath, and might return an entire column or row, it completely replaces its predecessors, VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP. It’s also possible to specify what worth the components returns if there is not any match.
That stated, in case you’re utilizing a model of Excel launched earlier than 2021, you will not be capable to use the XLOOKUP operate.
The XLOOKUP Syntax
XLOOKUP has six arguments:
=XLOOKUP(a,b,c,d,e,f)
the place
- a (required) is the lookup worth,
- b (required) is the lookup array,
- c (required) is the return array,
- d (optionally available) is the textual content to return if the lookup worth (a) is just not discovered within the lookup array (b),
- e (optionally available) is the match mode (0 = actual match (default), -1 = actual match or subsequent smaller merchandise, 1 = actual match or subsequent bigger merchandise, 2 = wildcard match), and
- f (optionally available) is the search mode (1 = first to final (default), -1 = final to first, 2 = binary search the place b is in ascending order, -2 = binary search the place b is in descending order).
Arguments a and c have to be the identical top for vertical lookups or the identical width for horizontal lookups.
The XLOOKUP Operate in Motion
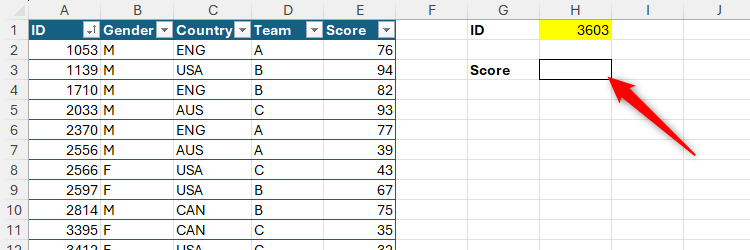
XLOOKUP can return a single worth primarily based on a single criterion. Right here, the components in cell H3 returns the participant’s rating in keeping with the ID in cell H1:
=XLOOKUP(H1,Gamers[ID],Gamers[Score],"No ID")
On this case, there is not any must enter arguments e (match mode) or f (search mode), because the default choices (actual match and a top-to-bottom search) are what you want.
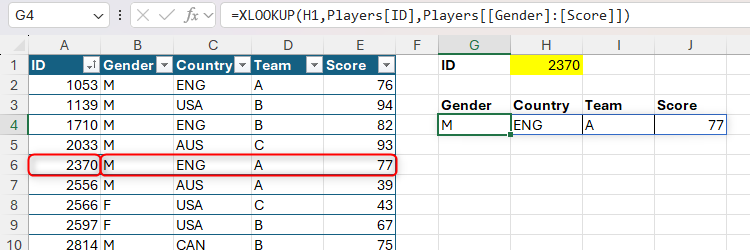
XLOOKUP can be used to return outcomes from a number of adjoining cells. Right here, the components in cell G4 returns a participant’s gender, nation, staff, and rating if you enter the ID, with the lookup worth (argument c) comprising the primary column, then a colon, then the final column:
=XLOOKUP(H1,Gamers[ID],Gamers[[Gender]:[Score]])
When the return array (argument c) is a couple of cell, as within the instance above, this turns XLOOKUP right into a dynamic array function. Which means the consequence spills over from the cell the place you typed the components to the neighboring cells, so you should make certain they’re clear beforehand. In any other case, you may see a #SPILL! error.
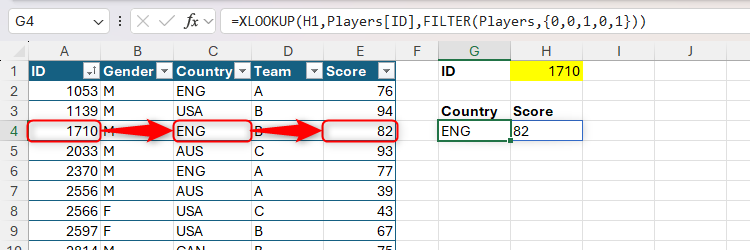
To make use of the XLOOKUP operate to return values from non-adjacent columns or rows, you should nest the FILTER operate within the return array argument, with 0s and 1s in curly braces telling Excel which columns to return. This components seems to be up the ID in cell H1, and returns the corresponding Nation (third column) and Rating (fifth column):
=XLOOKUP(H1,Gamers[ID],FILTER(Gamers,{0,0,1,0,1}))
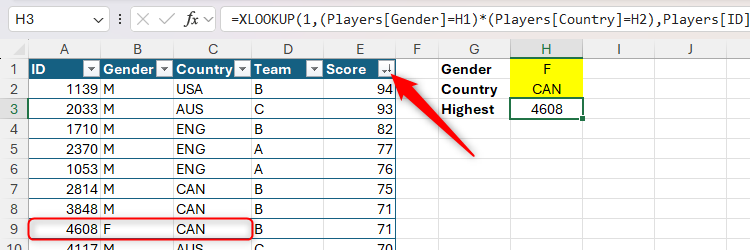
Lastly, you possibly can mix XLOOKUP with logical operators to return a worth primarily based on a number of standards. This components exams whether or not every criterion within the lookup array (argument b) is true, returning 1 whether it is or 0 if it is not. The primary match is returned if all standards are true (in different phrases, the results of the lookup array calculation equals the lookup worth (1):
=XLOOKUP(1,(Gamers[Gender]=H1)*(Gamers[Country]=H2),Gamers[ID])
Because the Rating column is sorted in descending order, the result’s the ID of the highest-scoring feminine Canadian.
To seek out the lowest-scoring feminine Canadian, reverse the sort order of the Rating column or sort -1 for the search mode (argument f).
Abstract: The Professionals and Cons of XLOOKUP
Listed below are the advantages and downsides of this convenient operate:
|
XLOOKUP Advantages |
XLOOKUP Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
Works with vertical and horizontal datasets. |
Lacks backward compatibility with variations of Excel launched earlier than 2021. |
|
The return array could be to the left, proper, above, or beneath the lookup array. |
Solely returns a single match (first or final). |
|
Can return a single consequence or a dynamic array. |
Can not return non-adjacent columns or rows except used with the FILTER operate. |
|
Works with single or a number of lookup values. |
Cannot be utilized in a formatted Excel desk if returning a dynamic array. |
|
Versatile match sorts and search modes. |
|
|
Helps you to deal with errors natively. |
|
|
Helps wildcard searches for partial matches. |
|
|
May be nested to execute two-way lookups. |
INDEX With XMATCH: A Extra Highly effective Various to INDEX With MATCH
Many individuals who’ve used Excel for years nonetheless carry out lookups utilizing the old-school INDEX-MATCH combo, primarily as a result of it is extra versatile than VLOOKUP and XLOOKUP. Nonetheless, combining INDEX with XMATCH, the up to date model of MATCH, offers you extra choices.
INDEX with XMATCH returns an merchandise from a spread or array in keeping with the primary or final match it finds. Like XLOOKUP, it really works with vertical and horizontal datasets, can search in any route, and can be utilized to return complete columns or rows.
Nonetheless, as a result of XMATCH is newer than MATCH, it is solely out there to these utilizing Excel for the web or desktop variations of Excel launched in 2021 or later.
These two features are generally used collectively as a result of the INDEX identifies the lookup column, and XMATCH identifies the lookup row.
The INDEX-MATCH Syntax
Since I will present you mix these features in your lookup, here is the mixed syntax for vertical (the most typical) lookups:
=INDEX(a,XMATCH(b,c,d,e),f)
- a (required) is the array or identify of the desk the place the return worth is positioned.
- b (required) is the lookup worth,
- c (required) is the column containing the lookup worth,
- d (optionally available) is the match mode (0 = actual match (default), -1 = actual match or subsequent smallest merchandise, 1 = actual match or subsequent largest merchandise, 2 = wildcard match, 3 = regex match),
- e (optionally available) is the search mode (1 = first to final (default), -1 = final to first, 2 = binary search the place b is in ascending order, -2 = binary search the place b is in descending order), and
- f (required) is the column variety of the return worth.
In different phrases, the XMATCH arguments (b, c, d, and e) inform the INDEX operate which row within the array or desk to look in, and the ultimate argument of the INDEX operate (f) identifies a column. Collectively, they inform Excel which cell to look in to return the right worth.
For horizontal lookups, you should enter the row quantity earlier than utilizing XMATCH to establish a column.
The INDEX-XMATCH Operate Mixture in Motion
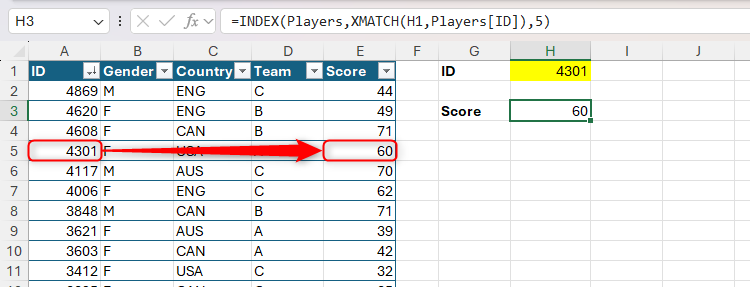
You should utilize INDEX with XMATCH to return a single worth primarily based on a single criterion. On this instance, the pairing is used to return the rating (column 5 within the Gamers desk) of a participant whose ID is in cell H1:
=INDEX(Gamers,XMATCH(H1,Gamers[ID]),5)
Discover how, though the syntax is initially fairly sophisticated, if you wish to return a precise match in a search that appears from high to backside, you possibly can omit two of the arguments.
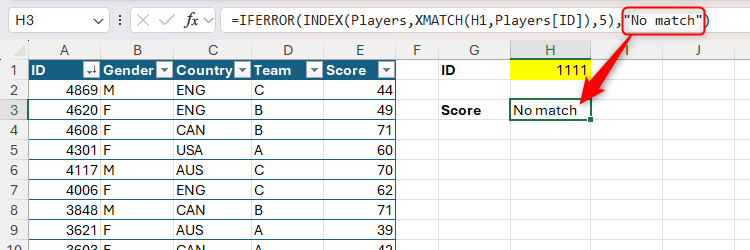
If there is not any match, Excel returns an #N/A error. To keep away from this, use Information Validation to create a drop-down listing of choices for the lookup worth. Alternatively, embed the entire components inside an IFERROR formula:
=IFERROR(INDEX(Gamers,XMATCH(H1,Gamers[ID]),5),"No match")
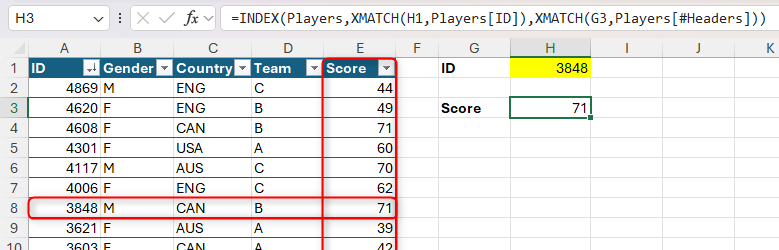
The problem with the above examples is that the column quantity is hard-coded into the components. As an alternative, you possibly can embed a second XMATCH set of arguments to return this worth by a two-way lookup:
=INDEX(Gamers,XMATCH(H1,Gamers[ID]),XMATCH(G3,Gamers[#Headers]))
Right here, the column quantity is recognized by matching the variable in G3 to the column headers within the Gamers desk.
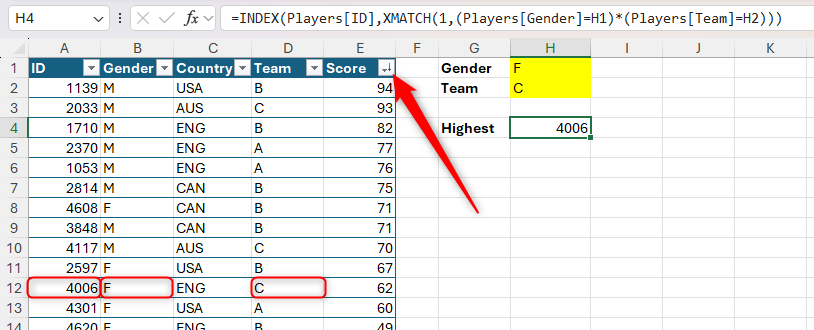
It’s also possible to use INDEX with XMATCH to return a worth primarily based on a couple of criterion by combining them with logical operators. Having sorted column E in descending order, I can use this components to return the ID of the highest-scoring feminine in staff C:
=INDEX(Gamers[ID],XMATCH(1,(Gamers[Gender]=H1)*(Gamers[Team]=H2)))
To seek out the lowest-scoring feminine in staff C, reverse the type order of column E or sort -1 for the search mode (argument e).
Abstract: The Professionals and Cons of INDEX With XMATCH
In case you’re nonetheless unsure whether or not these features are those for you, here is a abstract of their professionals and cons:
|
INDEX/XMATCH Advantages |
INDEX/XMATCH Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
Works with vertical and horizontal datasets. |
Lacks backward compatibility with variations of Excel launched earlier than 2021 and is not out there on the Excel cell app. |
|
The return array could be to the left, proper, above, or beneath the lookup array. |
Solely returns a single consequence. |
|
Works with single or a number of lookup values. |
Solely returns a single match (first or final). |
|
Versatile match sorts and search modes. |
Does not allow you to specify an alternate worth if no matches are discovered except used with the IFERROR operate. |
|
XMATCH could be nested to carry out two-way lookups. |
Utilizing two features concurrently is a steeper studying curve than single-function lookups. |
|
The defaults for optionally available arguments are extra logical in XMATCH than in MATCH. |
|
|
Does not return a dynamic array so can be utilized in Excel tables. |
|
|
Helps wildcard searches for partial matches. |
FILTER: A Easy Operate That Returns All Matching Values
Whereas XLOOKUP and INDEX with XMATCH return a single match, Excel’s FILTER function returns all matches—an excellent motive to decide on it over the others. Nonetheless, solely these utilizing Excel 2021 or later, Excel for the net, or the Excel cell app can use this operate.
The FILTER Syntax
This is how the FILTER operate works:
=FILTER(a,b,c)
the place
- a (required) is the array containing the values you need to return,
- b (required) is the inclusion criterion that determines the filter, and
- c (optionally available) is the textual content to return if no values match the inclusion standards (b).
Arguments a and b should reference arrays which are the identical measurement as one another.
The FILTER Operate in Motion
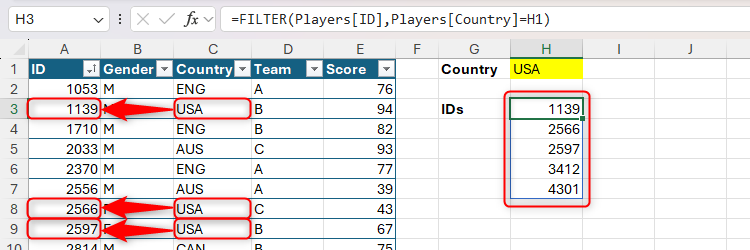
You should utilize the FILTER operate to return an array from a column primarily based on a single criterion. This components, typed into cell H3, returns the IDs of all gamers whose nation matches the worth in cell H1, returning “No match” as a substitute of an error if there aren’t any matches:
=FILTER(Gamers[ID],Gamers[Country]=H1,"No match")
The filtered values are returned within the order they seem within the supply knowledge.
FILTER is a dynamic array operate. This implies the consequence spills over from the cell containing the components to the neighboring cells. In consequence, you should make certain these cells are clear—in any other case, you may see a #SPILL! error.
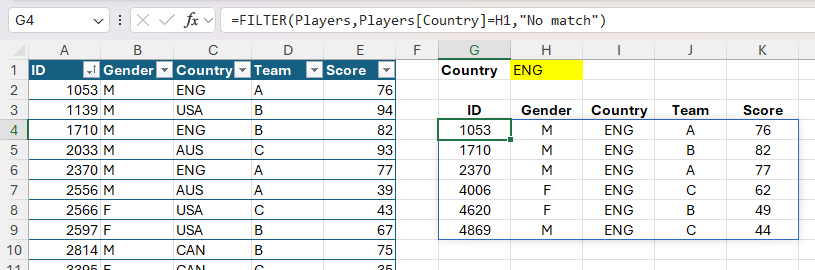
Within the instance above, solely the ID column of the Gamers desk was chosen because the return array. Nonetheless, you may as well use the FILTER operate to return corresponding knowledge from all columns. After typing the column headers manually in cells G3 to K3, in cell G4 I typed:
=FILTER(Gamers,Gamers[Country]=H1,"No match")
the place Gamers (argument a) is the desk identify, which means all columns are returned within the filtered consequence.
There are a number of methods to return knowledge from non-adjacent columns, however the easiest way is to repeat the FILTER operate for every column you need to return.
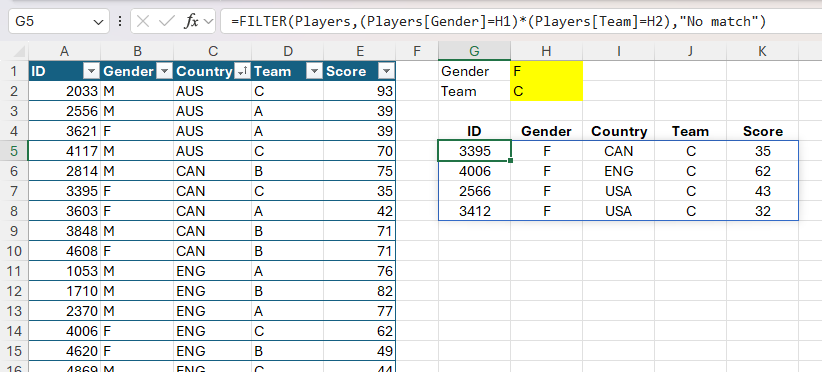
Lastly, you should use FILTER to return values that match a couple of situation through the use of logical operators. This components returns the information for all females in staff C:
=FILTER(Gamers,(Gamers[Gender]=H1)*(Gamers[Team]=H2),"No match")
Use Excel’s Information Validation software to create a drop-down listing of choices for the filters. Then, you will not must enter a no-match time period for argument c.
Abstract: The Professionals and Cons of FILTER
This is an outline of the advantages and downsides of Excel’s FILTER operate:
|
FILTER Advantages |
FILTER Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
Returns all matching values. |
Lacks backward compatibility with variations of Excel launched earlier than 2021. |
|
The return array could be to the left, proper, above, or beneath the filtered array. |
Returns a dynamic array, which means it may well’t be utilized in an Excel desk. |
|
Works with single or a number of filtering standards. |
Returns a zero if a supply cell is clean or null. |
|
Has an easy syntax because it does not require search or match sorts or modes. |
|
|
Works with vertical and horizontal datasets. |
|
|
Helps you to specify a no-match worth. |
Though not strictly lookup features, Excel’s CHOOSECOLS and CHOOSEROWS functions are superb if you wish to shortly extract particular columns or rows out of your knowledge.
Source link