- Researchers create a type of carbon with an unimaginable floor space
- This might enable the fabric to lure extra substance together with varied chemical compounds
- Hypergolics are broadly use in jet propulsion
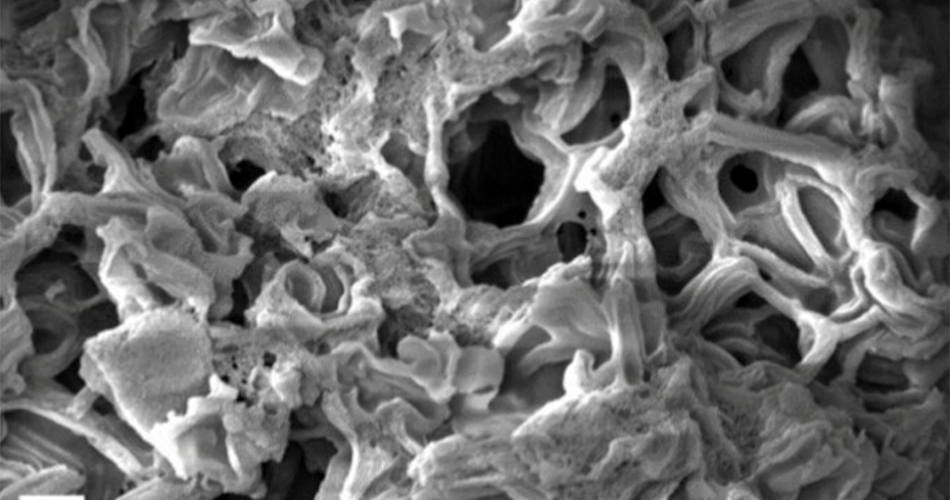
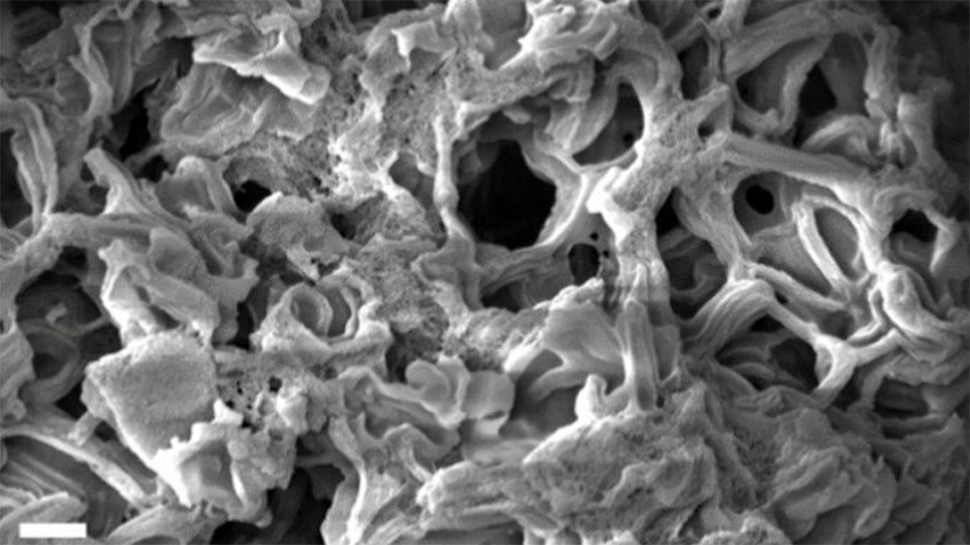
Researchers at Cornell College have developed a nanoporous carbon materials with the very best floor space ever reported.
The breakthrough makes use of a chemical response akin to rocket gasoline ignition and may very well be used to enhance carbon-dioxide seize and vitality storage applied sciences, probably advancing the subsequent technology of batteries.
Growing the porosity of carbon is essential to enhancing its efficiency in purposes resembling pollutant adsorption (the place pollution stick with the floor of the fabric) and vitality storage. The brand new materials boasts a floor space of 4,800 sq. meters per gram – akin to the dimensions of an American soccer area, or 11 basketball courts, condensed right into a single teaspoon.
A vivid future for batteries
“Having extra floor per mass is essential, however you will get to a degree the place there isn’t a materials left. It’s simply air,” stated senior writer Emmanuel Giannelis from the Division of Supplies Science and Engineering, in Cornell Engineering. “So the problem is how a lot of that porosity you’ll be able to introduce and nonetheless have construction left behind, together with sufficient yield to do one thing sensible with it.”
Giannelis collaborated with postdoctoral researcher Nikolaos Chalmpes, who tailored hypergolic reactions – high-energy chemical reactions usually utilized in rocket propulsion – to synthesize this carbon.
Chalmpes defined that by fine-tuning the method, they had been capable of obtain ultra-high porosity. Beforehand, such reactions had been used solely in aerospace purposes, however their fast and intense nature proved excellent for creating novel nanostructures.
The method, detailed in ACS Nano, begins with sucrose and a template materials, which guides the formation of the carbon construction. When mixed with particular chemical compounds, the hypergolic response produces carbon tubes containing extremely reactive five-membered molecular rings. A subsequent remedy with potassium hydroxide removes much less steady buildings, abandoning a community of microscopic pores.
The researchers say the fabric adsorbs carbon dioxide almost twice as successfully as standard activated carbons, attaining 99% of its whole capability in below two minutes. It additionally demonstrated a volumetric vitality density of 60 watt-hours per liter – 4 instances that of business options. This makes it notably promising for batteries and small energy cells, the place environment friendly vitality storage in compact areas is vital, and opens pathways for designing electrocatalysts and nanoparticle alloys.
You may additionally like
Source link