Ahead-looking: A brand new growth in versatile thermoelectric movie know-how may pave the way in which for a brand new era of wearable units and cooling options. Researchers at Queensland College of Know-how (QUT) have created a versatile movie that addresses the longstanding challenges of flexibility, manufacturability, and efficiency.
Australian researchers have engineered an ultra-thin, versatile movie able to harnessing body heat to power wearable units, probably eliminating the necessity for batteries. This know-how, which may additionally cool digital chips in smartphones and computer systems, marks a major development in a area that has been steadily progressing for years. The breakthrough builds upon foundational work by analysis groups worldwide specializing in vitality harvesting and thermal administration.
Thermoelectric units that may convert temperature variations into electrical energy have lengthy been wanted for wearable electronics. Nevertheless, creating versatile, environment friendly, and commercially viable variations has confirmed to be tough. Restricted flexibility, complicated manufacturing processes, excessive prices, and inadequate efficiency have been among the many roadblocks in scaling up and commercializing versatile inorganic thermoelectrics for wearable electronics and high-end cooling functions.
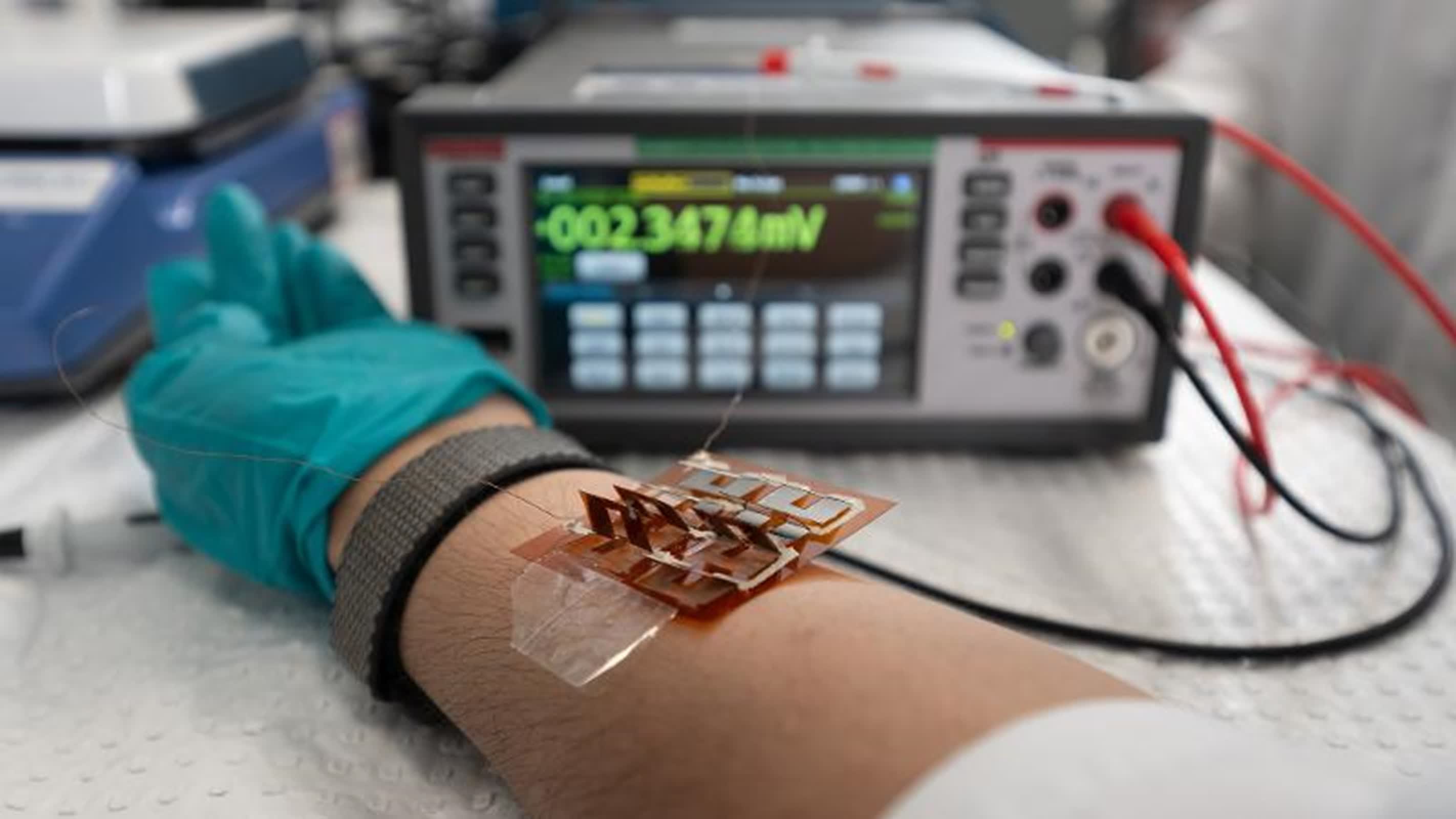
Professor Zhi-Gang Chen and his crew at QUT seem to have addressed these challenges. Their analysis, printed within the journal Science, introduces an economical know-how for producing versatile thermoelectric movies. The important thing innovation lies in the usage of tiny crystals, or “nanobinders,” that type a constant layer of bismuth telluride sheets, enhancing each effectivity and adaptability.
The crew’s methodology integrates solvothermal synthesis, screen-printing, and sintering strategies. Solvothermal synthesis creates nanocrystals in a solvent beneath excessive temperature and strain, whereas screen-printing allows large-scale movie manufacturing. The sintering course of heats the movies to near-melting level, successfully bonding the particles collectively.
The ensuing printable movie consists of Bi₂Te₃-based nanoplates as extremely oriented grains and Te nanorods as nanobinders. When assembled into a versatile thermoelectric gadget, the movie’s energy density ranked among the many highest for screen-printed units.
The QUT crew’s method isn’t restricted to bismuth telluride-based thermoelectrics. Wenyi Chen, the examine’s first creator, famous that their method may additionally work with different techniques, comparable to silver selenide-based thermoelectrics, that are probably cheaper and extra sustainable.
This know-how opens up a variety of potential functions. “Versatile thermoelectric units may be worn comfortably on the pores and skin the place they successfully flip the temperature distinction between the human physique and surrounding air into electrical energy,” Professor Chen stated.
Past powering wearable electronics, the movie could possibly be used for private thermal administration. For instance, the combination of versatile thermoelectric units into textiles opens up new potentialities for smart clothing with these units used to create self-powered heated clothes for chilly environments.
Earlier analysis has proven that versatile thermoelectric units can supply modern options for vitality harvesting and thermal administration throughout numerous sectors.
Within the automotive trade, versatile thermoelectric units could possibly be incorporated into automobiles to energy battery-free distance detection sensors for autonomous driving by using the temperature distinction between a automobile’s inside and exterior. These units may additionally harvest vitality from exhaust pipes and different heat-generating parts, bettering gasoline effectivity and lowering emissions.
The medical area may additionally profit drastically from this know-how. Versatile thermoelectric units may energy implantable medical units utilizing physique warmth, eliminating the necessity for battery replacements and lowering the chance of issues. Moreover, they may allow steady, non-invasive physique temperature monitoring techniques, offering worthwhile knowledge for well being monitoring.
On a bigger scale, versatile thermoelectric units have the potential to reap waste warmth from infrastructure. By conforming to the curved surfaces of pipes, equipment, or constructing parts, these units may generate electrical energy from beforehand untapped warmth sources, contributing to extra energy-efficient buildings and industrial processes.
Source link


