In short: Safety researchers found a very alarming type of malware that methods customers into downloading an contaminated app to propagate. Whereas the assault vector is widespread, the insidious nature of the malicious code makes it distinctive. It targets and steals crypto pockets safety codes utilizing OCR to scan pictures for mnemonic passphrases.
A complicated new pressure of Android malware has emerged from Korea. It targets cryptocurrency wallets by exploiting customers’ mnemonic keys. McAfee Labs researcher SangRyol Ryu got here throughout the malware after tracing knowledge stolen by malicious apps to rogue servers and gaining entry.
The malicious software program, dubbed SpyAgent, makes use of crafty ways to infiltrate gadgets and exfiltrate delicate data, together with photographs which will comprise pockets restoration phrases. SpyAgent disguises itself as legit apps, starting from banking and authorities companies to streaming platforms and utility software program. To date, McAfee has recognized over 280 of those faux functions.
As soon as the sufferer downloads a SpyAgent-infected app, the malware springs into motion, establishing a reference to a command and management (C2) server that permits attackers to challenge directions remotely. It then harvests textual content messages, contact lists, and saved pictures from the contaminated gadget.
What units this malware aside is its use of optical character recognition (OCR) know-how to scan pictures for mnemonic keys – the 12-word phrases used to get well cryptocurrency wallets. Utilizing mnemonic phrases is rising in crypto-wallet safety, as they’re simpler to recollect than a protracted string of random characters.
SpyAgent has additionally proved to be wily with its efforts to keep away from detection. It diverts the sufferer’s consideration from a doable drawback with the cellphone utilizing infinite loading screens or temporary clean shows.
The malware’s creators have confirmed adept at increasing SpyAgent’s attain. It initially focused customers in Korea. Nonetheless, the malware just lately unfold to the UK. It has additionally transitioned from easy HTTP requests to WebSocket connections, enabling real-time, two-way communication with the C2 server. It has intelligent strategies to keep away from detection from safety researchers, together with string encoding and performance renaming.
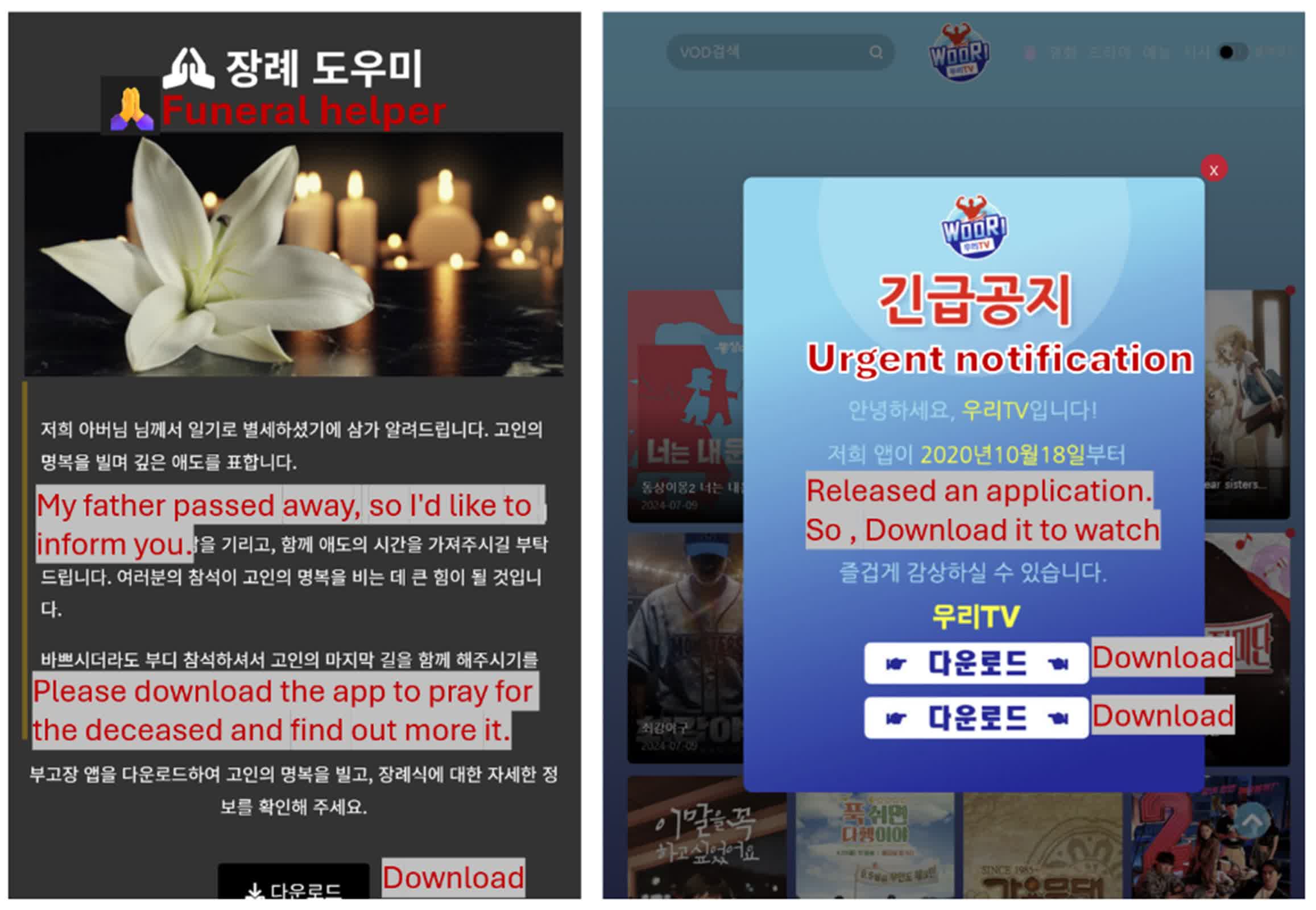
SpyAgent makes its approach onto victims’ gadgets largely by way of phishing campaigns. Attackers use social engineering ways to lure victims into clicking malicious hyperlinks. These hyperlinks direct customers to convincing faux web sites that immediate downloading the malware-laden APK file. The campaigns are proving notably profitable when mixed with stolen contact knowledge.
“These phishing messages, seemingly despatched by a well-known contact, usually tend to be trusted and acted upon by recipients,” Ryu wrote. “As an illustration, an obituary discover showing to return from a pal’s quantity might be perceived as genuine, drastically elevating the probability of the recipient partaking with the rip-off, particularly in comparison with phishing makes an attempt from unknown sources.”
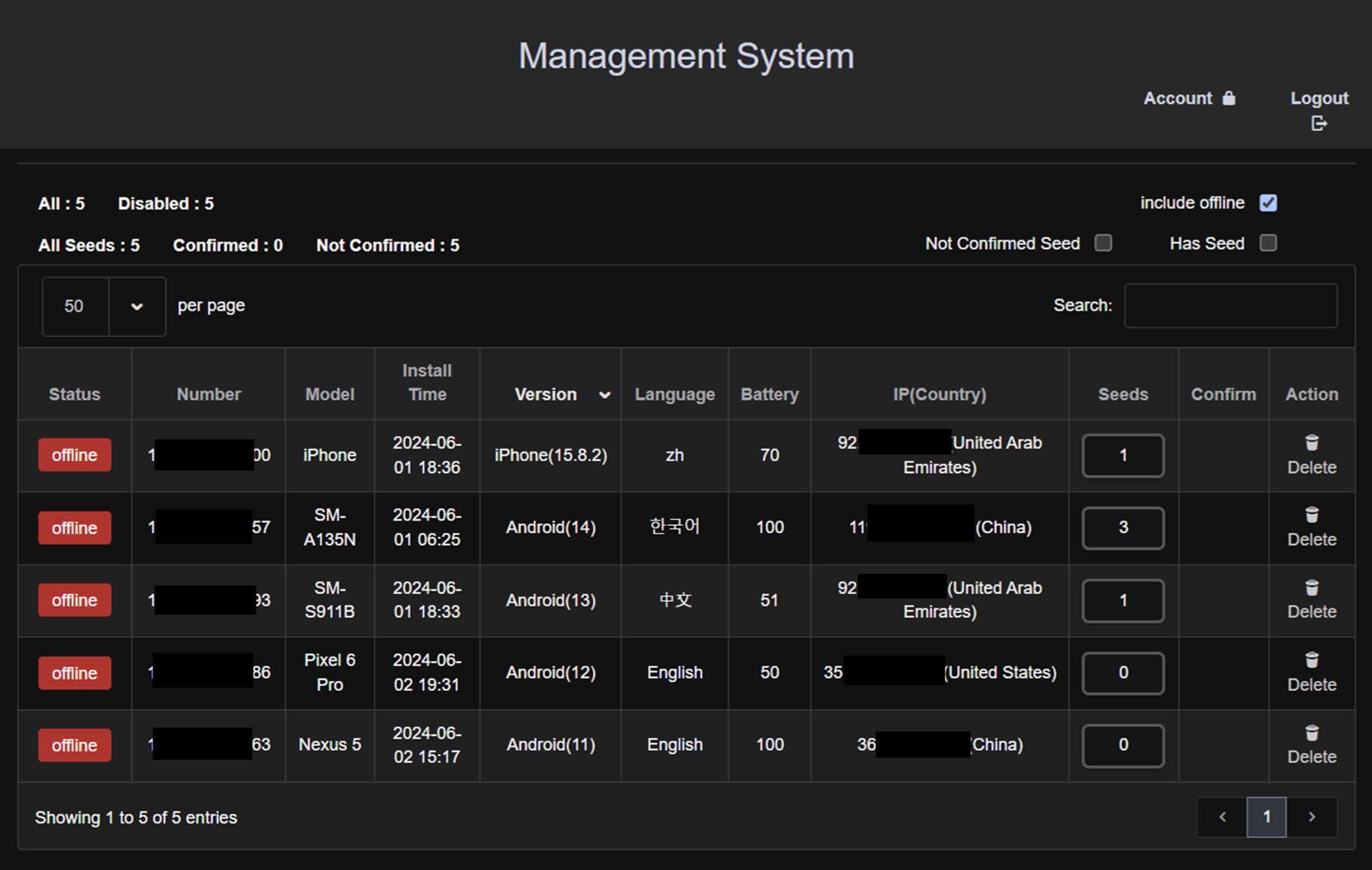
SpyAgent’s backend operations are very subtle, because the malware’s scale signifies. As an illustration, researchers found admin pages designed for managing compromised gadgets. It additionally makes use of Python and Javascript on the server aspect to course of the stolen knowledge, which is then organized and managed by way of an administrative panel.
One other indication of its sophistication is how shortly it developed legs. The primary sighting of SpyAgent was solely earlier this yr and solely in Korea. It has already unfold to UK customers.
Safety researchers hope to stamp out SpyAgent, or no less than comprise it, now that they know the way it works. Nonetheless, its creators proceed refining their strategies, and McAfee believes they’re at the moment growing an iOS model.
Source link


