Have you ever ever seen once you go into Home windows to optimize your storage drives, it says retrim for SSDs? Simply what precisely is getting trimmed and why is it wanted? Is it the identical as defragmenting or one thing solely completely different? (it’s completely different).
Such good questions all deserve thorough solutions, so on this article we’ll cowl all of that.
What’s SSD trimming?
SSD trimming is a course of that helps to keep up the efficiency of a solid-state drive over time. Trim works by periodically erasing blocks of information which might be not in use. The trimmed information is not at all times eliminated immediately, as a posh course of decides precisely when this takes place. However when it does, not solely does it liberate area on the drive, it helps the SSD carry out higher and last more, too.
Easy, sure? What truly goes on, although, is kind of a bit extra advanced — learn on to seek out out!
Digging into the heart of your SSD
To know why SSDs do not simply delete information once you press the button, we have to take a fast have a look at how they work. We have taken apart SSDs earlier than and you may see that there is not a lot inside them.
The pattern under is of a comparatively previous SATA mannequin (Samsung 850 Professional), however even the newest SSDs aren’t a lot completely different when it comes to the elements that make up the drive.
The chip within the center is a processor that manages all of the directions, information stream, encryption, and different algorithms. Above it’s a small quantity of DRAM, which acts as an instruction and information cache, plus it shops a desk of information areas on the drive.
To the fitting and under the processor are two NAND flash modules — these are the chips that retailer all the information and it is them that we have to delve into.
Deep inside these chips are billions of tiny elements, known as charge-trapping floating-gate steel oxide semiconductor area impact transistors. Since that title does not precisely roll off the tongue, the expertise is often known as cost entice flash (CTF) and is essentially the most generally used system to retailer information in in the present day’s SSDs.
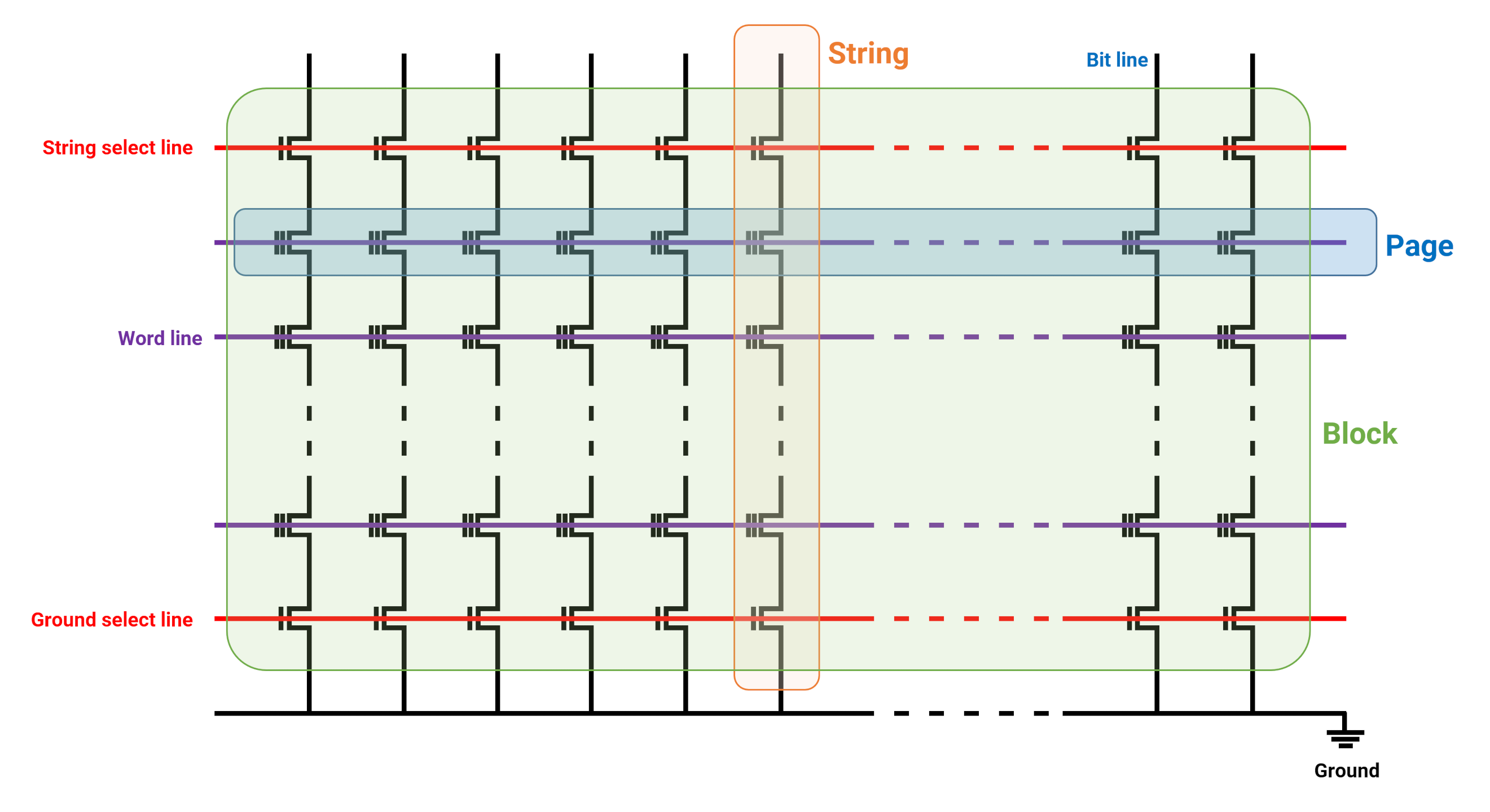
Every CTF acts as a single unit of storage, often known as a reminiscence or bit cell, that has three electrical traces related to it. The CTFs are grouped collectively, first as a protracted column (a string), with anyplace between 32 and 128 cells.
The cells in a string share a typical hint (a bit line), which is used to learn the information saved in them. These which might be on the identical row as one another (often known as a web page) are all hooked as much as one other frequent hint (phrase line). The string and floor choose traces are utilized in mixture with the phrase traces to find out whether or not a learn, write, or erase course of takes place.
An array of strings and pages varieties what known as a block. Pages and block sizes fluctuate enormously, with the previous being as small as 4 kB in dimension, and the latter as massive as 512 kB, though so much is dependent upon the producer and mannequin.
A single NAND flash die will comprise hundreds of blocks, and flash modules themselves might comprise a number of dies. These huge, advanced grids of traces and transistors make up each flash storage machine, from USB reminiscence sticks price a couple of {dollars}, to enterprise-level multi-terabyte SSDs.
NAND flash is bizarre
Pages and blocks are necessary as a result of all the reminiscence cells on this construction share the identical substrate — the slice of semiconducting materials, reminiscent of silicon or gallium arsenide, that all the transistors are constructed upon.
To erase information from any cell includes the usage of a excessive destructive voltage, forcing any electrons saved within the CFT to stream into the substrate. Sadly, because of this the erase course of wipes clear each cell within the block, not simply one in all them.
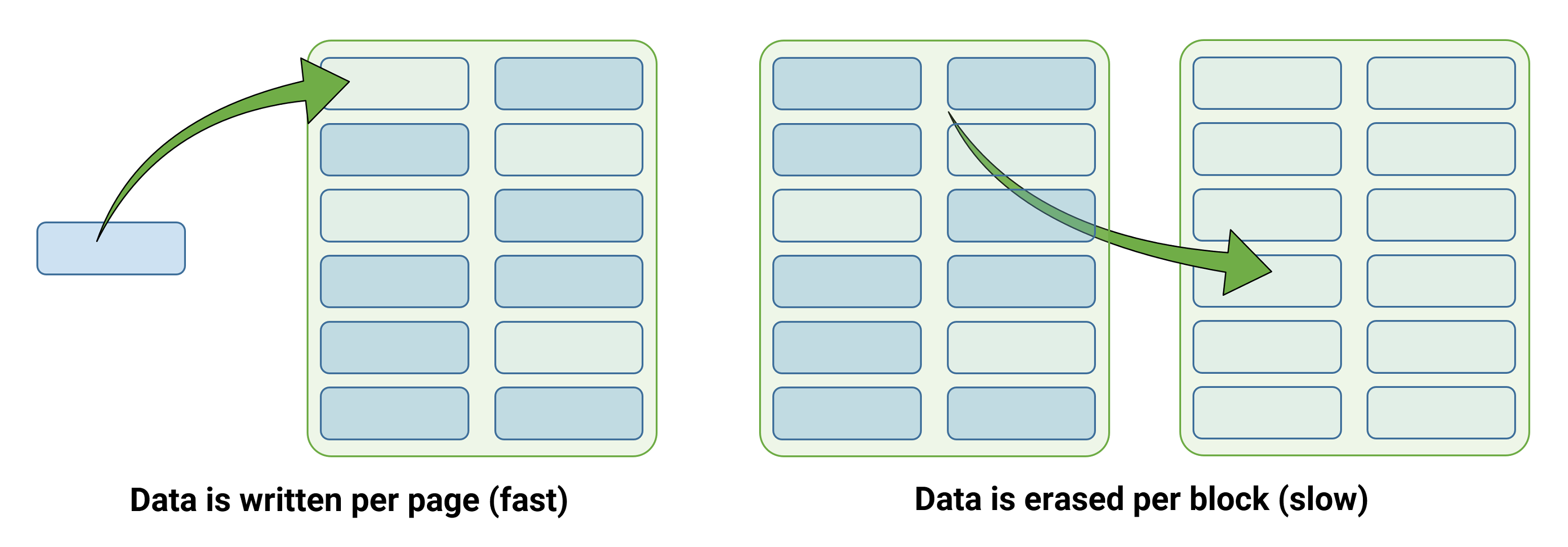
One other oddity with NAND flash is that the reminiscence cells can’t be programmed with new information till all the cells have been cleaned — in different phrases, SSDs by no means immediately write new information over previous stuff, which conventional onerous drives do. And the place erasing must be executed on the block stage, writing to them is finished on the web page stage, which implies that programming an SSD is far quicker than erasing one.
The method of programming and erasing additionally damages the reminiscence cells every time, carrying away the layer contained in the transistor that shops the cost. To enhance the longevity of the chips, the processor managing them cycles via all the blocks, till every one has been used as soon as, earlier than going again to the beginning (so to talk).
So sure, NAND flash is unquestionably bizarre — quick writes, gradual erases, damages itself doing both operation!
Throwing across the rubbish
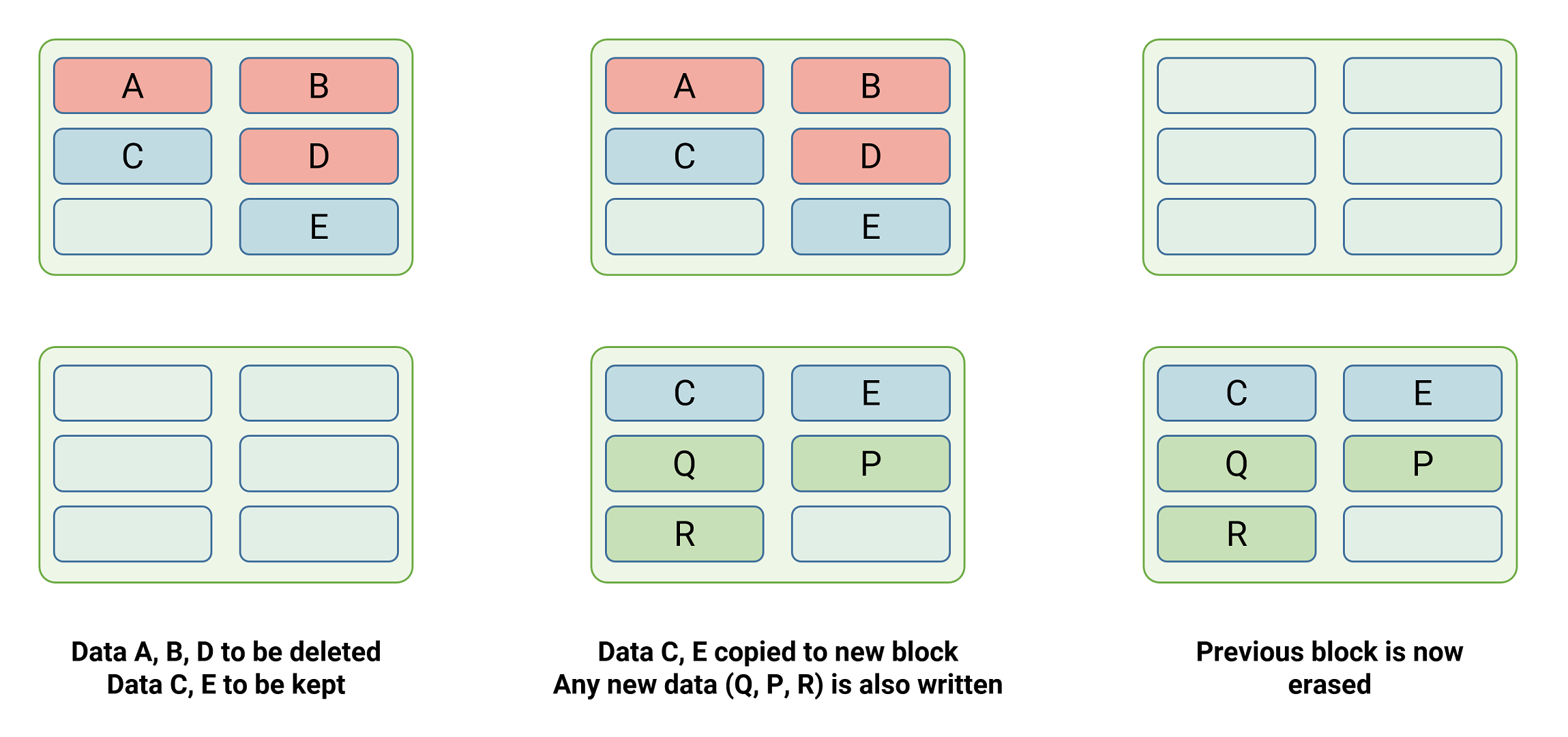
Now, let’s get again to understanding what SSD trimming is all about. To do that, we’ll take an imaginary SSD that has 4 kB pages and 256 kB blocks, so 64 pages per block. What would occur when you needed to delete a single file that takes up 3056 kB in your SSD?
This file will likely be taking over 764 pages — 11 full blocks and one with 60 out of the 64 pages used. How will we delete this file with out risking affecting these final 4 pages, as they might be containing information for one more file? Looks as if we’re utterly caught!
Rescue initially comes within the type of the TRIM command. All information stays on the storage drive till it’s explicitly instructed to do one thing about it. Information and folders which were deleted by the working system are flagged as not being required, and when the TRIM command is issued, the desk saved within the SSD’s DRAM (or the NAND flash itself, if the drive does not have any DRAM) is then up to date to replicate this.
Be aware that not each SSD producer makes use of the time period TRIM however Home windows does, so we’ll stick with utilizing this time period. Information is not erased instantly after the TRIM command has been despatched — it both takes place when the drive is idle or when it subsequent writes some information to a block. Which methodology will get used is dependent upon the producer, with consumer-grade fashions dealing with erases when idle, and enterprise-level ones typically doing it when writing.
Information which might be flagged for removing are erased when the NAND flash’s firmware commences a course of known as rubbish assortment. This includes studying a block and any pages that must be saved are copied to the cache, then written to a totally empty block. The earlier one, together with the pages flagged for deletion, is then erased.
In some methods, this course of is to SSDs what disk defragmentation is to conventional onerous drives, but it surely’s not the identical factor.
Is trim the identical as defragmenting?
SSD trimming and defragmenting are not the identical factor. Defragmenting is a course of that’s used to optimize the efficiency of onerous disk drives (HDDs) by rearranging the information on the disk in order that it’s saved in a contiguous method. This improves the effectivity of the drive by lowering the period of time it takes to learn and write information.
Alternatively, Trimming is restricted to SSDs and is used to keep up the efficiency of the drive over time. SSDs use of flash reminiscence means they’ve a restricted variety of write cycles. When information is deleted from an SSD, the area that it occupied is just not instantly made out there for reuse. As an alternative, the drive’s firmware marks the area as “invalid” and it isn’t overwritten till the Trimming course of is carried out. This course of helps to stop the drive from turning into fragmented and slowing down.
Rubbish assortment is helpful to the lifespan of the SSD and its general efficiency, and TRIM simply makes it higher (generally the 2 phrases are used interchangeably). It’s because with out that command, rubbish assortment will simply always transfer all pages about, condensing partially stuffed blocks, to maintain freshly erased blocks out there for programming — however this implies undesirable pages will get moved about too, losing time and growing the damage on the reminiscence cells. As a result of TRIM explicitly factors out which pages are actually junk, they are often left alone throughout rubbish assortment and erased as required.
Sending out the clippers
TRIM is routinely issued by Home windows once you completely delete a file (i.e. take away it from the Recycling Bin) but it surely does not immediately happen. It is added to a queue and will get processed when the SSD is prepared for it.
Nevertheless, this queue has a most dimension to it, and if it will get stuffed up, a few of these TRIM requests will get dropped. By default, Home windows schedules a re-issue of TRIM instructions frequently (calling it a retrim).
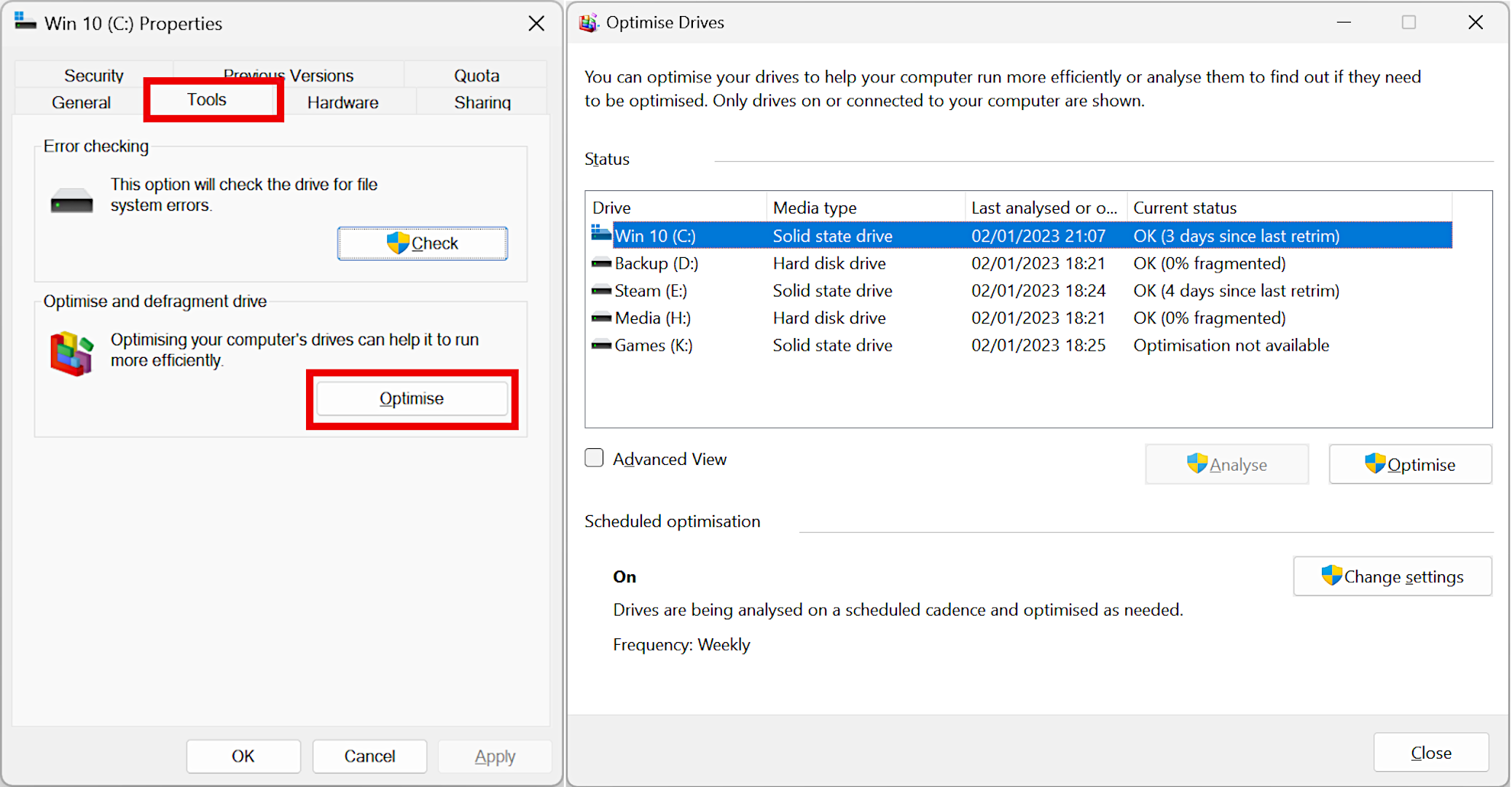
You may power this to happen however we do not advocate you accomplish that. However when you insist, go to File Explorer, right-click on a drive, click on on Properties, after which on the Instrument tab. Lastly, click on on the button that claims Optimize. If you haven’t any SSDs in your PC, optimizing simply runs regular disk defragmentation, however for NAND flash gadgets, clicking this re-issues a TRIM command. You may’t truly make the drive to do something, so don’t be concerned about operating it too ceaselessly; the drive will take care of itself completely effectively!
See how one of many SSDs above cannot be optimized? That is as a result of it is utilizing a dynamic volume, which does not assist the usage of trimming. Primary volumes do acknowledge the TRIM command and for many customers, it is best to make use of that sort of drive quantity anyway.
In case your working system or SSD configuration does not assist TRIM, it is not likely unhealthy information — rubbish assortment nonetheless takes place, however the course of is not anyplace close to as efficient. Outdated information finally will get eliminated just because the drive will finally overwrite undesirable pages, sooner or later in time.
For PCs utilizing Home windows 7, TRIM is simply supported on SATA SSDs; for machines with NVMe ones, the command is simply out there in Home windows 8, 10, and 11. TRIM was added to MacOS within the final replace to Snow Leopard again in 2011. Most Linux distributions additionally assist the operation, however not each file system is appropriate — talking of which, RAID programs typically do not assist TRIM, though that state of affairs is slowly bettering.
Now you understand what TRIM is and the way it’s helpful to your SSD.
Maintain Studying. Explainers at TechSpot
Source link