Online visibility is the most crucial factor in the world of modern marketing. It is assessed by the position of a webpage on the topmost search results for a query. Given the importance of search performance for deciding the destiny of a website, Search Engine Optimization(SEO) has become an inseparable part of efforts behind improving this performance.

It requires meticulous planning and staying up to date with the latest SEO trends to stay at the top of Google’s search results and drive more traffic to your website to generate more leads and conversions for your business.
User experience has been the backbone of Google’s metrics determining the ranking of a website for the longest time. Its commitment to offer the best to its users has pushed website developers to consider and implement all factors which determine a seamless user experience.
Google’s user-centric commitment has been visible in many of its decisions over the years like the elimination of keyword stuffing, making mobile-first ranking a metric, making page load time a ranking factor, etc. — the effort to maintain their position as the benefactor of users has been constant.
Core Web Vitals are a step in the same direction: further enhancing the standard of better user experience as the driving force behind search page rankings.
What exactly are Core Web Vitals and why should you care about them? You don’t have to worry, we are here to answer your questions. Keep reading!
In this article, we will be taking a deep dive into Core Web Vitals and their effect on search performance. We will also take a glance at other signals that influence Google’s algorithms and how Core Web Vitals will combine with them to act as a unit of measuring user experience as a whole.
Furthermore, we will also try to learn how to improve scores associated with these metrics to improve the search page rankings of your website and achieve your marketing goals.
Why is User Experience Important?
User experience is a cumulation of various factors decided by Google as the cornerstone of measuring the effectiveness of a web page in terms of CTR(Clickthrough Rate) and time spent on it. It is the sum of a set of user-centric indicators influencing Google’s algorithms for deciding the page rank of website links relevant to user search queries.
SEO is a set of best practices involved in making the user experience palatable enough for algorithms involved in sorting web pages according to queries.
Owing to the say user experience has in deciding the performance of your website in search results ranking, it holds immense importance. Enhancing the user experience is at the top of the agenda while designing a website because everything else — from content to design — revolves around it and gets influenced by it.
SEO best practices are designed keeping in mind the role user experience plays in making or breaking the journey of a website to the top few results of the first page of search results, thereby focusing solely on enhancing user experience.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Google had announced in May of 2020 that it is planning to introduce new indicators for analyzing page experience aimed at measuring overall user experience. Come May 2021 the tech giant rolled out an entirely revamped ranking system. The new ranking algorithm factors in new page experience signals with the inclusion of Core Web Vitals in determining the rank of websites on a search engine.
Core Web Vitals are indicators used to measure the speed and efficiency of a web page — referenced by Google to gauge page experience. Simply put, Core Web Vitals are a set of specific signals considered inherent by Google in determining the overall user experience of a webpage. These are page experience metrics used to analyze the visitor experience when they land on a web page.
Core Web Vitals are an array of three factors that, according to Google, are paramount in quantifying user interaction and helping in improving its quality. These metrics are an addition to the pre-existing web vitals that shall be taken up in a later section. Even though the primary objective of all such metrics is to measure the speed and efficiency of interactiveness, the score they represent is concerned with their specific interactions.
Now that Core Web Vitals have been implemented in their entirety by the end of September 2021, it has become necessary to understand them individually, in detail, for recognizing the extent of their effect on page ranking and search performance.
Core Web Vitals are a measure of three factors viz. Loading, Interactivity, and Visual Stability of a webpage. Here, loading refers to the measure of the speed of loading of a webpage in terms of a numerical value for quantification.
Similarly, interactivity in this context is the measure of time taken by a user to ‘actually’ interact with a web page, such as clicking on a link, choosing menu options, expanding a list, or entering data in forms.
Visual stability is the quantified measure of how much the objects on a webpage move on the screens of users as the content loads; in simpler words, it is the measure of the stability of a web page.
These metrics are calculated in terms of three corresponding values: Largest Contentful Paint(LCP), First Input Delay(FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift(CLS), respectively. Let’s elaborate on what these are and how they impact search performance and SEO.
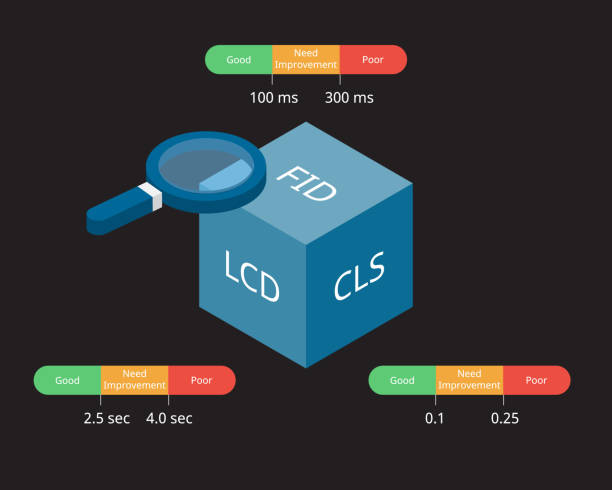
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
It is a measure of time in seconds between the start of page loading and the rendering of every element to the very last image, block of text, or any other media element on a user’s screen. In simpler terms, LCP determines the time it takes till the loading of all contents of a web page has finished.
Quite understandably, the lower the LCP value, the better. In other words, LCP is the measure of a web page’s loading speed. A lower LCP convinces a user about the better usability of a web page.
For interpreting the LCP score, the values are simplified as follows:
-
LCP less than or equal to 2.5 seconds: Good
-
LCP between 2.5 and 4 seconds: Improvement Required
-
LCP greater than 4 seconds: Poor
There can be numerous reasons for below-par LCP scores(higher scores), such as render-blocking JavaScript, slow server response times, creating quality content i.e resources being unusually heavy, etc.
Points to be noted:
It is observed that in the majority of the cases when LCP optimization is considered, most useful LCP elements should be shortlisted on a page — because not all LCP elements are equally important in terms of user experience. The next step is to prioritize among the ones identified as relevant. For example: for a product description page these could be product info, product images, etc.
2. First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay(FID) is a Core Web Vital which computes the time in milliseconds between the first interaction of the user on a website (clicking on a link, pressing a key, tapping a button, etc.) and the response of the browser to that interaction.
FID indicates the first impression on the user of your website’s responsiveness and interactivity. It’s crucial to have this impression be a good one. Yet again, the lower values of FID are an indication of better responsiveness.
For interpreting the FID score, the values are simplified as follows:
-
FID score less than or equal to 100ms: Good
-
FID score between 100ms and 300ms: Improvement Required
-
FID score greater than 300ms: Poor
The main reason for a below-par FID score (higher) is a browser’s main thread being busy executing and parsing JavaScript code. Naturally, a busy main thread can’t simultaneously respond to user interaction.
Points to be noted:
FID may not play as major a role as other web vitals for pages where the extent of user interaction is less, for example, blog content, text pages, etc. The FID score can be improved — for better responsiveness and interactivity — by working on the main thread of a browser. As it’s a complicated process, let’s look at a few easier ways in which FID can be improved:
-
Finding ways to reduce the execution time of JavaScript.
-
The impact of the third-party code needs to be reduced.
-
Make sure to reduce the burden on the main thread by minimizing its work.
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
It is a Core Web Vital that is used for assessing the cumulative score of all unexpected shifts occurring in the layout within the viewport during the entire lifecycle of a page. As mentioned above, CLS is the measure of the ‘visual stability’ of a web page.
Visual stability is a crucial indicator of user experience as it heavily influences their opinion of a web page. Stable web pages increase the quality of a user’s experience significantly because stability makes navigation easier.
Lower CLS scores are considered ideal. Unlike the previous two core web vitals, CLS isn’t measured in seconds. Instead, it is viewed with the viewport size and focuses on the elements moving between two frames — these elements are called unstable elements. It measures the movement of these unstable elements in the viewport. The shift in the layout is a score derived as a product of two components: the impact fraction and the distance fraction.
The Impact Fraction is the area taken by the unstable elements on the viewport in various stages of page navigation.
The Distance Fraction is measured as the greatest distance moved by an unstable element in various stages of page navigation divided by the largest dimension of the viewport.
For interpreting CLS score, the values are simplified as follows:
-
CLS score less than or equal to 0.1: Good
-
CLS score between 0.1 and 0.25: Improvement Required
-
CLS score greater than 0.25: Poor
A poor CLS score is usually a result of images or ads having unidentified dimensions, adding DOM elements dynamically to a page on top of the existing pre-loaded content, or loading of resources sporadically.
Points to remember:
Unexpected layout shifts can be mitigated by paying attention to the inclusion of clear size attributes for images, videos, and other infographics and making sure not to insert any content above already loaded content.
Why are Core Web Vitals Important?
1. For Improving User Experience
User experience is the deciding factor towards improved CTR and better engagement levels. Accessibility of a website has always been an important aspect of impacting signals that impact and decide page ranking as per Google’s algorithms.
Core Web Vitals measure the overall accessibility of a website for users and therefore, directly impact search performance based on user experience. Measures of better visibility and faster loading time can help create a better user experience.
2. Impact on SEO Practices
Now that Google has hinted that optimization of web pages from the perspective of Core Web Vitals can improve user experience, it’s only imperative to recognize its impact on SEO. The inclusion of Core Web Vitals into signals that decide search ranking has presented a unique opportunity for well-planned and executed websites to be more visible than their competition.
A digital agency can be consulted or hired for streamlining website building efforts and improving SEO strategy.
How did Google Measure User Experience Before and What has Changed?
Before Google introduced Core Web Vitals the page ranking and user experience was measured by various other indicators that are as follows:
Mobile-friendly websites are preferred by Google’s algorithm in calculating search performance.
Users tend to avoid visiting unsecured websites. HTTPS pages are known to be secure and provide a better user experience.
Malware on a website is like ticking time-bombs, as a result, Google takes away points from the user experience score of a web page laden with malware. Safe browsing helps improve user experience.
Lack of Unwelcomed Interstitials (Pop-ups)
Users don’t appreciate intrusive pop-ups when they visit a web page as they come in the way of a seamless experience and can be frustrating. Therefore, they hurt Google’s search ranking on that page. Limiting these pop-ups improves search performance.
After the introduction of Core Web Vitals, Google’s algorithm takes into consideration a combined assessment of all of the above factors with the addition of LCP, FID, and CSR signals. Therefore, it’s crucial to strike a balance between all of these factors and Core Web Vitals for planning, designing, and developing a website that passes the test of Google’s search ranking algorithm.
Conclusion
Google has introduced Core Web Vitals to attract more attention towards improving user experience. Search performance can be enhanced massively by tuning a website in a way that increases the scores of these vitals. Therefore, the focus should be on enhancing page speed, visibility, and responsiveness of a page for better search ranking performance.


