Microsoft Excel’s UNIQUE perform does precisely as its title suggests—it extracts distinctive values from an array. In different phrases, you will solely see every worth as soon as within the end result, even when it seems a number of occasions within the supply. Let’s take a look at the way it works, tips on how to use it, and tips on how to keep away from sure pitfalls.
The UNIQUE perform is accessible to these utilizing Excel for Microsoft 365, Excel for the online, the Excel cell and pill apps, and one-off variations of Excel launched in 2021 or later.

- OS
-
Home windows, macOS, iPhone, iPad, Android
- Model
-
Microsoft
Microsoft 365 contains entry to Workplace apps like Phrase, Excel, and PowerPoint on as much as 5 units, 1 TB of OneDrive storage, and extra.
The UNIQUE Operate Syntax
Excel’s UNIQUE perform has three arguments—one required and two elective:
=UNIQUE(a,b,c)
the place
- a is the array from which you need to return distinctive values,
- b is a Boolean value that determines whether or not distinctive rows (FALSE) or columns (TRUE) are returned, and
- c can be a Boolean worth, however this time, it defines whether or not all distinctive values (FALSE) or solely those who happen precisely as soon as (TRUE) are returned.
Should you omit arguments b and/or c, FALSE is assumed because the default. Because of this inputting solely argument a signifies that all distinctive rows within the array will likely be returned.
The default habits of the UNIQUE perform in Excel is to extract an array whereas eradicating duplicates within the course of. In different phrases, even when a price seems greater than as soon as within the supply information, it’s going to solely seem as soon as within the end result. You should utilize this performance on a one-dimensional array (a single column or row) or a two-dimensional array (two or extra columns or rows). This is how.
To observe alongside as you learn this information, download a free copy of the Excel workbook used within the examples. After you click on the hyperlink, you will discover the obtain button within the top-right nook of your display, and if you open the file, you possibly can entry every instance on a separate worksheet tab.
The UNIQUE perform is mostly used to wash up a one-dimensional array that accommodates repeated entries.
On this spreadsheet, the desk named T_PLWinners lists all Premier League champions since 2010.
The UNIQUE perform is case-insensitive. Because of this it might deal with Geek, geek, and GEEK as the identical textual content string.
Provided that the supply information accommodates repeated values as some groups have received the title greater than as soon as, your goal is to create a cleaner listing that solely lists every winner as soon as. In different phrases, you need to apply the UNIQUE perform to the Winner column of the T_PLWinners desk. To do that, in cell D2, kind:
=UNIQUE(T_PLWinners[Winner])
and press Enter.
Moderately than typing the structured reference to the column header manually, hover your cursor over the column header till you see a small, black down arrow, and click on as soon as to pick the entire column.
On this case, there isn’t any want to supply arguments b and c since you need to return all distinctive rows within the array, which is the default habits. That mentioned, if the listing of groups ran throughout row 2 as an alternative of column B, you would wish to kind TRUE for argument b.
Excel’s UNIQUE perform is a dynamic array perform, that means the result spills from the cell the place you typed the method. It additionally signifies that if you add extra rows of knowledge to the supply desk, the end result updates to replicate the adjustments.
Extracting Distinctive Values From Two or Extra Columns or Rows
The UNIQUE perform in Excel will also be utilized to 2 or extra columns or rows concurrently to return distinctive combos.
For instance you need to extract the primary and final names of all prize winners from this desk, named T_Prizes, however solely as soon as if they’ve received a number of prizes.
The precept is pleasantly just like extracting distinctive values from a one-dimensional array—the one change being the cells referenced in argument a:
=UNIQUE(T_Prizes[[First]:[Last]])
Discover how the method references each the column headed First and the column headed Final. Additionally, although there are two Tims within the supply information, they’re each listed as distinctive names, as they’re paired with totally different surnames.
If you choose all columns in a formatted desk for argument a, the structured reference accommodates the desk title solely, not the column headers.
If, after extracting the distinct values, you need to flip the end result from a dynamic array to a hard and fast array, choose the cells, press Ctrl+C to repeat them, after which press Ctrl+Shift+V to stick them as values. This removes the method whereas retaining the cell contents.
Use the identical methodology to extract distinctive column-based combos, however keep in mind to kind TRUE for argument b.
Utilizing the UNIQUE Operate to Return Values Showing Solely As soon as
Once you omit argument c within the UNIQUE perform, the end result contains all distinct values, whether or not they seem as soon as or a number of occasions within the supply information. Nonetheless, typing TRUE for argument c forces Excel to return a listing of values that seem solely as soon as.
The desk under is known as T_Transactions, and also you need to contact all the shoppers who’ve solely had one transaction with you.
That is the place the ultimate argument of the UNIQUE perform comes into play:
=UNIQUE(T_Transactions[Customer],,TRUE)
Typing TRUE for arguments b and c in the identical method returns columns whose distinctive values seem solely as soon as.
Utilizing the UNIQUE Operate Alongside Different Excel Capabilities
The ability of Excel’s UNIQUE perform really turns into evident when it is mixed with others.
All of the examples under solely use argument a of the UNIQUE method, although you possibly can apply the identical rules to UNIQUE formulation whose arguments b and/or c are the non-default Boolean worth, TRUE.
COUNTA and UNIQUE: Counting Distinctive Values
Nesting UNIQUE in COUNTA counts the variety of distinctive values within the array.
This desk, named T_PremChamp, lists the winner of the Premier League in every season since 2010. You need to use this information to find out what number of totally different groups have received the Premier League in that interval.
Within the following method, the UNIQUE perform produces a theoretical listing of all of the groups with none duplicates, and the COUNTA perform counts the variety of cells that this theoretical listing would occupy:
=COUNTA(UNIQUE(T_PremChamp[Winner]))
As a result of UNIQUE is a dynamic array perform, the resultant worth will enhance if a brand new staff is added to the desk.
SORT and UNIQUE: Extracting and Sorting Distinctive Values
When used by itself, the UNIQUE perform returns the values within the order during which they seem within the unique dataset. For instance, utilizing UNIQUE to return all distinctive values from the Winner column of the T_PremW desk right here returns Chelsea because the third worth, although it is the closest to A alphabetically.
To repair this, it’s essential nest the above UNIQUE method inside SORT. This forces Excel to generate a theoretical listing of distinctive values, and the SORT perform manifests this listing in alphabetical order:
=SORT(UNIQUE(T_PremW[Winner]))
UNIQUE and FILTER: Extracting Distinctive Values Primarily based on Standards
Excel’s FILTER function helps you to extract values from a dataset primarily based on sure standards you set. Nesting it inside UNIQUE signifies that if a sure worth matches the standards greater than as soon as, it isn’t duplicated within the end result.
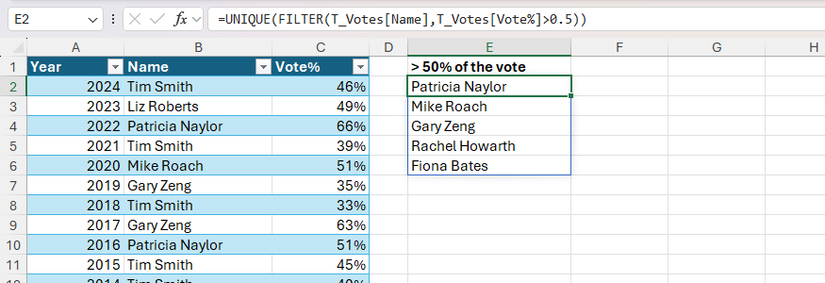
On this instance, the names of all winners who’ve gained greater than 50% of the vote in a given yr are extracted from the T_Votes desk utilizing the FILTER perform.
=FILTER(T_Votes[Name],T_Votes[Vote%]>0.5)
Nonetheless, Patricia Naylor seems greater than as soon as within the information supply, that means she seems greater than as soon as within the end result. So, to repair this, and return every title solely as soon as, nest the method inside UNIQUE:
=UNIQUE(FILTER(T_Votes[Name],T_Votes[Vote%]>0.5))
If you would like the results of the distinctive, filtered listing to be alphabetical, nest the entire method inside SORT.
UNIQUE, FILTER, and COUNTIF: Extracting Values That Happen Extra Than As soon as
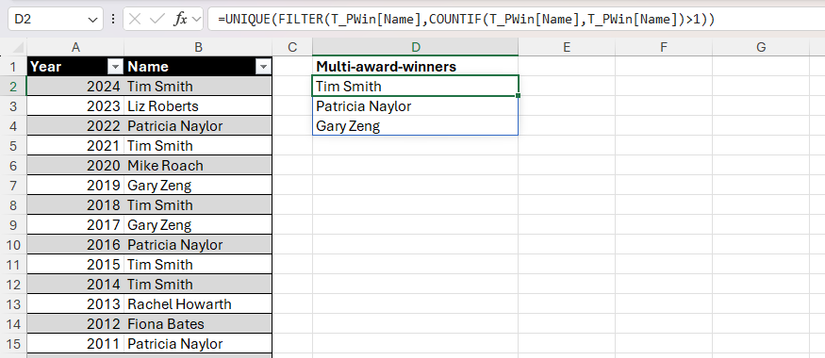
In a last instance, the UNIQUE perform can be utilized alongside FILTER and COUNTIF to extract values that happen greater than as soon as.
Right here, the names of people whose names seem not less than twice are extracted utilizing this method:
=UNIQUE(FILTER(T_PWin[Name],COUNTIF(T_PWin[Name],T_PWin[Name])>1))
Utilizing solely FILTER and COUNTIF would additionally embody solely these names that seem not less than twice, however they’d be repeated within the end result.
So, the UNIQUE perform removes these duplicates to make sure every title seems solely as soon as.
Use >2 within the last argument of the method to extract values that happen greater than twice, >3 for those who happen greater than thrice, and so forth.
Issues You May Encounter When Utilizing UNIQUE in Excel
As with all features in Excel, sure eventualities and environments cease them from working as you’d anticipate. Listed here are some hurdles you would encounter, and what you are able to do to leap them:
|
Drawback |
What This Means |
What to Do |
|---|---|---|
|
You see the #NAME? error. |
The model of Excel you are utilizing would not assist the UNIQUE perform. |
Swap to Excel for Microsoft 365, Excel for the web, the Excel cell and pill apps, or one-off variations of Excel launched in 2021 or later, and check out once more. |
|
You see the #SPILL! error. |
The world the place the UNIQUE perform’s dynamic array of outcomes needs to spill is blocked. |
Clear the cells the place the result’s making an attempt to spill, and check out once more. Then again, for those who’ve typed the method into the cell of a formatted Excel desk, convert the table to a regular range, and check out once more. |
|
You see the #REF! error. |
The UNIQUE method references an array in one other workbook, however that workbook is closed. |
Open the workbook containing the referenced array, and check out once more. |
|
An alert seems to let you know that there is a downside with the method. |
You may need mistyped a part of the method. |
Once you click on “OK,” the primary a part of the method inflicting the issue is highlighted within the method bar. Double-check and amend that part of the formula, and check out once more. Repeat this course of till the method is accepted. Alternatively, click on “Assist” for extra assist. |
The UNIQUE perform is not the one one in Excel that can be utilized to extract information. For instance, the CHOOSECOLS and CHOSOEROWS functions allow you to extract particular columns or rows, the GETPIVOTDATA function lets you extract particular data from a PivotTable, and utilizing the DROP function, you possibly can take away a specified variety of rows or columns from the beginning or finish of an array.
Source link