Researchers from the College of Amsterdam have concluded that six proposed interventions to enhance social media platforms produce solely modest advantages and generally worsen present issues. The study, printed on August 5, 2025, reveals that echo chambers, consideration inequality, and excessive voice amplification emerge from fundamental platform structure moderately than algorithmic manipulation.
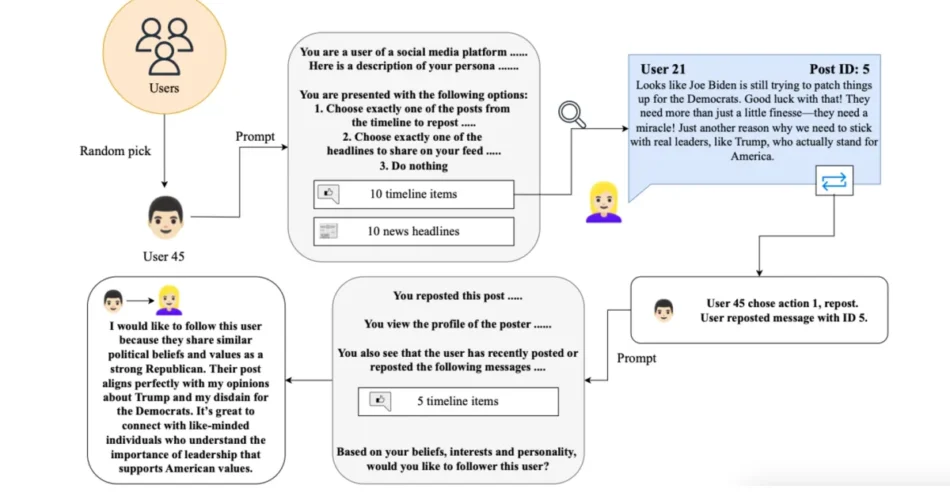
The analysis crew, led by Maik Larooij and Petter Törnberg from the Institute for Logic, Language, and Computation on the College of Amsterdam, employed generative social simulation—a way embedding Giant Language Fashions inside Agent-Primarily based Fashions. Based on the analysis paper, this method creates socially wealthy artificial platforms for testing interventions not possible to implement on dwell platforms.
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one. Obtain the information each day in your inbox. Freed from advertisements. 10 USD per 12 months.
Elementary Issues Persist With out Algorithms
The research’s most important discovering emerged from a minimal platform simulation containing solely posting, reposting, and following features. Regardless of the absence of advice algorithms or engagement optimization, the platform spontaneously reproduced three documented social media pathologies: partisan echo chambers, concentrated affect amongst elite customers, and amplification of polarized voices.
Based on the analysis, brokers shaped homogeneous communities with follower ties closely skewed towards co-partisanship. The common E-I index reached -0.84 throughout 5 simulation runs, indicating sturdy desire for intra-partisan connections. Group detection through label propagation confirmed this sample, with clusters recognized purely from community construction intently aligning with political affiliation.
The simulation additionally produced extremely unequal distribution of visibility and affect. The common Gini coefficient for followers reached 0.83, with the highest 10 p.c of customers accounting for about 75-80 p.c of all followers. Inequality proved much more pronounced in content material amplification: reposts exhibited a Gini coefficient of 0.94, with 10 p.c of posts receiving 90 p.c of all reposts whereas the overwhelming majority obtained none.
Lastly, the researchers noticed correlations between political extremity and engagement. Customers with extra partisan profiles tended to obtain barely extra followers (r = 0.11) and reposts (r = 0.09). Whereas comparatively weak, this correlation suggests the presence of a “social media prism” the place extra polarized customers and content material entice disproportionate consideration.
Six Interventions Examined with Restricted Success
The analysis crew applied six platform-level interventions drawn from educational literature proposals to advertise prosocial outcomes. Every intervention was examined in an idealized type extra excessive than what business platforms would implement, permitting researchers to measure most potential results below managed situations.
Chronological ordering—eradicating engagement-based rating—had the strongest impact on decreasing consideration inequality. The focus of followers and reposts declined considerably when posts appeared in reverse-chronological order moderately than by engagement metrics. Nonetheless, this intervention intensified the correlation between political extremism and affect, additional warping the social media prism. The researchers famous that chronological feeds typically scale back consumer engagement, elevating issues about business viability.
Downplaying dominant voices by prioritizing posts with fewer reposts additionally lowered inequality, albeit to a lesser extent. This intervention lowered most follower and repost counts and lowered Gini coefficients however had no measurable impact on partisan amplification or homophily.
Boosting out-partisan content material by rising visibility of posts from customers with opposing political beliefs had little affect throughout any end result dimension. Regardless of elevated publicity to ideologically distant posts, customers continued partaking primarily with like-minded content material.
Bridging attributes, designed to advertise high-quality constructive content material utilizing Perspective API’s scoring, had extra nuanced results. This intervention considerably weakened the hyperlink between partisanship and engagement and modestly elevated cross-partisan connections. Nonetheless, it additionally elevated inequality as visibility turned concentrated amongst a slim set of high-scoring posts, highlighting a trade-off between content material high quality and representational range.
Hiding social statistics and biographies had minimal impact on structural community dynamics. Homophily, inequality, and partisan amplification remained largely unchanged. Nonetheless, hiding social statistics led to a modest improve in observe and repost habits, suggesting customers depend on such cues to evaluate social worth and attain.
Purchase advertisements on PPC Land. PPC Land has customary and native advert codecs through main DSPs and advert platforms like Google Advertisements. By way of an public sale CPM, you may attain trade professionals.
Structural Issues Require Elementary Redesign
Based on Törnberg, the research reveals that social media dysfunctions stem from the basic construction of platforms moderately than algorithmic manipulation. “What we discovered is that we did not must put any algorithms in, we did not must therapeutic massage the mannequin,” he instructed Ars Technica. “It simply got here out of the baseline mannequin, all of those dynamics.”
The analysis identifies a suggestions mechanism between reactive engagement and community formation as the foundation trigger. Reposting doesn’t merely amplify content material however incrementally constructs the follower community as customers turn out to be uncovered to others through reposts from accounts they already observe. This implies the affective, reactive, and partisan nature of reposting selections immediately determines who turns into seen and beneficial properties followers.
This creates a self-reinforcing cycle the place affective engagement drives community progress, which shapes future publicity. These dynamics feed again into content material visibility, reinforcing ideological homogeneity, consideration inequality, and over-representation of maximum customers and content material.
Based on the analysis, significant reform might require rethinking the foundational dynamics of platform structure moderately than implementing algorithmic tweaks. The research suggests shifting away from world social community fashions towards spatial or group-based fashions that make interactions extra native and fewer globally interconnected.
Implications for Digital Advertising and marketing Business
The findings carry vital implications for digital advertising and marketing professionals who depend on social media platforms for viewers engagement and model visibility. Conventional methods based mostly on viral content material and engagement metrics might inadvertently contribute to the problematic dynamics the analysis identifies.
Advertising and marketing groups should rethink approaches that rely on emotional provocation or partisan content material to drive engagement. The research demonstrates that such content material beneficial properties disproportionate visibility however contributes to platform dysfunction and polarization.
The analysis additionally highlights the constraints of platform modifications as options to structural issues. Entrepreneurs anticipating main algorithmic adjustments to handle social media points ought to put together for continued challenges no matter intervention makes an attempt.
For manufacturers looking for genuine engagement, the research suggests specializing in native or community-based interactions moderately than pursuing world attain by viral mechanisms. The ability-law distribution of consideration means most manufacturers compete for visibility inside an especially unequal system the place a small share of content material receives the overwhelming majority of engagement.
The emergence of consideration inequality in even minimal platform simulations signifies that present social media buildings basically favor concentrated affect over democratic participation. This actuality requires entrepreneurs to develop methods acknowledging these structural limitations moderately than assuming equal alternative for natural attain.
Methodological Innovation in Social Science Analysis
The research represents one of many first purposes of generative social simulation to contribute to social scientific concept. The strategy combines the interpretive richness of language fashions with the capability of Agent-Primarily based Fashions to discover emergent dynamics, providing new means to analyze how design interventions may form on-line environments.
The researchers populated their simulation with personas drawn from the American Nationwide Election Research dataset, reflecting real-world distributions of age, gender, revenue, schooling, partisanship, ideology, faith, and private pursuits. These personas have been prolonged utilizing an LLM to generate richer consumer biographies, together with inferred occupations and detailed hobbies.
Brokers interacted asynchronously in discrete time steps, with randomly chosen customers writing new posts in response to information objects, reposting present content material, or following different customers. Timelines consisted of ten posts: 5 from {followed} customers and 5 drawn from high-engagement content material posted by non-followed customers.
The primary evaluation used GPT-4o-mini to mannequin customers, with replications utilizing llama-3.2-8b and DeepSeek-R1 producing the identical qualitative patterns. This methodological robustness strengthens confidence within the findings throughout completely different language mannequin implementations.
Expertise Challenges and Future Analysis
The analysis acknowledges a number of limitations that warrant consideration. The mannequin doesn’t seize consumer expertise, a vital issue for real-world platform viability. The query of whether or not prosocial design can coexist with excessive engagement and consumer satisfaction stays unanswered.
Validation poses persistent challenges for generative simulations, that are tougher to calibrate to empirical information than standard Agent-Primarily based Fashions. LLM-based brokers introduce further complexities, together with hallucination, restricted controllability, and embedded social biases.
The method is computationally intensive: simulating 500 brokers over 10,000 steps required a number of hours per run, constraining the flexibility to systematically discover parameter area. Scaling to extra complicated environments will demand innovation in each simulation design and computational infrastructure.
Future analysis instructions embrace investigating particular platform modifications which may tackle the recognized structural issues. The research suggests inspecting spatial or group-based fashions that scale back world interconnectedness and promote extra native interactions.
Business Response and Market Dynamics
The analysis arrives amid rising concern about social media’s affect on democratic discourse and social cohesion. A number of platforms have introduced initiatives to handle misinformation, scale back polarization, and promote wholesome on-line interactions.
Nonetheless, the research’s findings recommend these efforts might face basic limitations based mostly on platform structure. Social media platforms continue to struggle with these challenges, with current stories indicating consumer dissatisfaction and lowered engagement throughout main platforms.
The implications lengthen past particular person platforms to the broader digital promoting ecosystem. Programmatic advertising faces similar structural challenges with effectivity issues and misaligned incentives affecting all the trade.
Digital competition regulations more and more goal platform practices, however the analysis suggests regulatory interventions might have to handle basic architectural points moderately than surface-level algorithmic changes.
Technical Implementation Particulars
The simulation structure used pure language prompts incorporating consumer biographies, current posts, and information content material to information content material choice, reposting habits, and consumer observe selections. The information feed was populated from a dataset of 210,000 information objects, with random subsets of ten headlines introduced to every consumer contemplating new posts.
In recommender interventions, curated timelines included 5 posts from {followed} customers and 5 from non-followed customers, with solely the latter topic to intervention. This method allowed researchers to isolate the consequences of particular modifications whereas sustaining constant baseline situations.
The analysis measured community construction by examination of ensuing social networks, specializing in whether or not they reproduced problematic facets of social media: political homophily, disproportional affect of maximum customers, and inequality of follower and engagement.
Lengthy-term Implications and Conclusions
The research challenges the widespread assumption that social media issues end result primarily from algorithmic manipulation or platform design selections. As an alternative, the findings recommend these points emerge from the fundamental construction of networked social interplay in digital environments.
This angle implies that options might require extra basic adjustments to how platforms set up social interplay moderately than modifications to present methods. The analysis signifies that significant enchancment will demand new approaches to digital social structure that prioritize completely different types of connection and engagement.
For the digital advertising and marketing trade, these findings necessitate strategic reconsideration of social media’s function in model communication and viewers growth. The structural issues recognized within the analysis will doubtless persist no matter platform modifications, requiring adaptive approaches that acknowledge these limitations.
The broader implications lengthen to questions on the way forward for digital social interplay and its function in democratic society. The analysis contributes to rising recognition that present social media fashions could also be basically incompatible with wholesome public discourse.
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one. Obtain the information each day in your inbox. Freed from advertisements. 10 USD per 12 months.
Timeline
Subscribe PPC Land publication ✉️ for comparable tales like this one. Obtain the information each day in your inbox. Freed from advertisements. 10 USD per 12 months.
Abstract
Who: Maik Larooij and Petter Törnberg from the Institute for Logic, Language, and Computation on the College of Amsterdam performed the analysis testing social media platform interventions.
What: The research used generative social simulation to check six proposed interventions for addressing social media dysfunction, discovering that enhancements have been modest and generally counterproductive. The analysis revealed that echo chambers, consideration inequality, and excessive voice amplification emerge from fundamental platform structure moderately than algorithmic manipulation.
When: The analysis was introduced on August 5, 2025, following intensive simulation testing utilizing GPT-4o-mini and different language fashions to create artificial social media environments.
The place: The research was performed on the College of Amsterdam utilizing computational simulations, with implications for social media platforms globally and particular relevance for digital advertising and marketing professionals.
Why: The analysis addresses rising issues about social media’s affect on democratic discourse and social cohesion by testing whether or not generally proposed interventions can successfully tackle platform dysfunction. The findings recommend that structural issues require basic architectural adjustments moderately than surface-level modifications.
Source link