In response to OECD analysis published in March 2023, privacy-enhancing applied sciences allow assortment, processing, evaluation and sharing of knowledge whereas defending information confidentiality. The group emphasizes these digital applied sciences allow comparatively excessive utility from information whereas minimizing assortment and processing necessities.
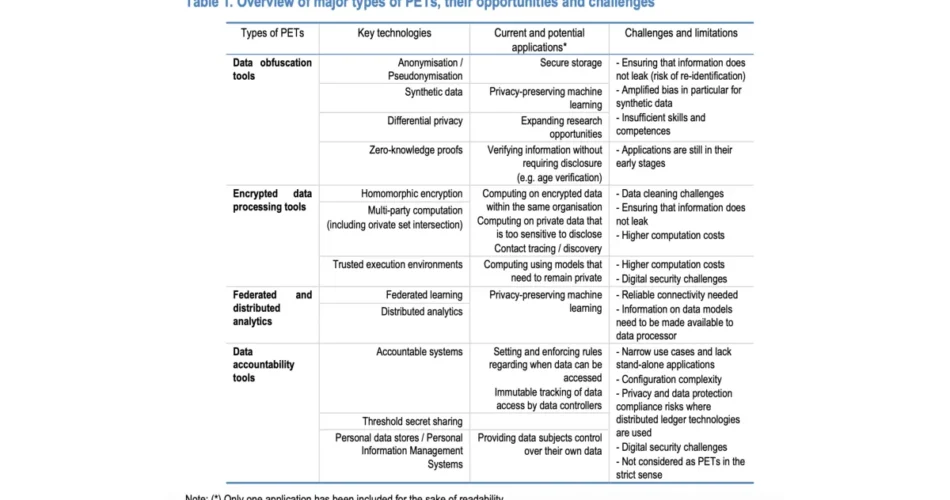
OECD evaluation identifies 4 classes of privacy-enhancing applied sciences: information obfuscation instruments, encrypted information processing instruments, federated and distributed analytics, and information accountability instruments. Every class addresses particular features of the OECD Privateness Pointers’ fundamental ideas.
Subscribe the PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one. Obtain the information day by day in your inbox. Freed from adverts. 10 USD per 12 months.
Information obfuscation instruments embody anonymization, pseudonymization, artificial information technology, differential privateness, and zero-knowledge proofs. These applied sciences alter information by including noise or eradicating figuring out particulars. In response to the analysis, these instruments allow privacy-preserving machine studying and knowledge verification with out requiring delicate information disclosure.
The findings reveal encrypted information processing instruments, together with homomorphic encryption and multi-party computation, symbolize probably the most important development in personal information processing. These applied sciences enable computations over information that stay encrypted, addressing conventional vulnerabilities when information require decryption for processing.
Federated and distributed analytics allow executing analytical duties on information not seen to processors. OECD analysis signifies federated studying reduces the necessity for delicate information to go away gadgets, with solely abstract statistics transferred to information controllers.
The evaluation highlights information accountability instruments present controls over information gathering and utilization. These programs handle information use, observe compliance, and set up guidelines for information entry. OECD researchers be aware these instruments historically fall outdoors strict privacy-enhancing expertise definitions however improve privateness by means of management mechanisms.
Technical limitations current important challenges. The analysis identifies computation prices as considerably greater for encrypted information processing in comparison with commonplace database operations. Organizations keep away from these methods when easier processing stays out there.
Information cleansing challenges emerge with encrypted processing instruments. OECD findings point out analysts can not look at encrypted information for high quality management, requiring pre-processing checks on the information supply stage earlier than submission.
Info leakage dangers persist throughout a number of expertise classes. In response to the evaluation, obfuscation measures can unintentionally expose info regardless of protecting mechanisms. The analysis emphasizes no agreed-upon requirements exist for required noise ranges throughout totally different situations.
Regulatory frameworks more and more acknowledge privacy-enhancing applied sciences. OECD analysis paperwork authorized necessities for information safety by design throughout a number of jurisdictions. The European Union’s Basic Information Safety Regulation Article 25 mandates applicable technical measures for information safety by default.
Implementation approaches range considerably between nations. In response to OECD findings, some jurisdictions depend on finest practices and steerage relatively than necessary necessities. Canada’s federal Privateness Act lacks particular privacy-enhancing expertise provisions however applies privacy-by-design ideas by means of institutional finest practices.
De-identification necessities create regulatory pathways for expertise adoption. OECD evaluation reveals various requirements between anonymization and pseudonymization throughout authorized frameworks. The analysis signifies anonymized information falls outdoors privateness regulation scope in lots of jurisdictions whereas pseudonymized information stays topic to safety necessities.
Innovation initiatives proliferate throughout OECD nations. The evaluation paperwork analysis funding applications, safe processing platforms, certification schemes, innovation contests, and regulatory sandboxes. These initiatives purpose to foster expertise improvement whereas addressing implementation boundaries.
The UK’s Info Commissioner’s Workplace published comprehensive guidance on privacy-enhancing technologies in September 2022. This steerage examines homomorphic encryption, safe multi-party computation, federated studying, trusted execution environments, and zero-knowledge proofs throughout a number of sectors.
Singapore launched a privacy-enhancing expertise sandbox by means of the InfoComm Media Improvement Authority and Private Information Safety Fee in July 2022. The sandbox offers testing environments for piloting expertise initiatives whereas figuring out applicable options for data-sharing aims.
Cross-border information switch functions current each alternatives and constraints. OECD analysis signifies privacy-enhancing applied sciences can facilitate transfers the place conventional strategies show inadequate. Nevertheless, regulatory uncertainty persists relating to expertise acceptance for compliance functions.
Present deployment stays restricted regardless of technological advances. In response to the findings, most functions function at small scales with slender use circumstances. The analysis attributes restricted adoption to excessive prices, inadequate technical experience, and unclear regulatory acceptance.
Abilities and competence gaps hinder broader implementation. OECD evaluation reveals advanced anonymization processes require educated information scientists to stop unintentional info leakage. Many organizations lack needed assets for correct implementation.
Enterprise adoption faces a number of boundaries past technical limitations. The analysis identifies organizational resistance to altering established information processing paradigms. Privateness-enhancing applied sciences require important upfront investments with out assured returns.
Regulatory coordination challenges emerge throughout a number of jurisdictions. OECD findings point out various implementation approaches create compliance complexities for organizations working internationally. Harmonized requirements stay elusive regardless of widespread underlying ideas.
Future improvement depends upon addressing present limitations whereas constructing stakeholder confidence. The analysis emphasizes want for standardized analysis frameworks, improved cost-effectiveness, and clearer regulatory steerage. Technical advances should align with sensible deployment necessities.
Privateness-enhancing applied sciences symbolize basic shifts in information processing paradigms relatively than incremental enhancements. OECD evaluation positions these applied sciences as foundations for privateness by design implementation whereas acknowledging substantial improvement necessities stay.
Subscribe the PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one. Obtain the information day by day in your inbox. Freed from adverts. 10 USD per 12 months.
Timeline
Subscribe the PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one. Obtain the information day by day in your inbox. Freed from adverts. 10 USD per 12 months.
Abstract
Who: The OECD (Group for Financial Cooperation and Improvement), privateness enforcement authorities, expertise firms, and advertising and marketing organizations worldwide are concerned in growing and implementing privacy-enhancing applied sciences.
What: Privateness-enhancing applied sciences (PETs) are digital options that allow information assortment, processing, evaluation and sharing whereas defending confidentiality. These embody information obfuscation instruments, encrypted information processing, federated analytics, and information accountability programs.
When: The OECD revealed its complete evaluation in March 2023, constructing on expertise developments that accelerated following privateness regulation implementation over the previous decade.
The place: Implementation spans a number of jurisdictions globally, with various regulatory approaches throughout OECD member nations together with the USA, European Union, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Japan, and Singapore.
Why: Organizations require privacy-enhancing applied sciences to adjust to evolving information safety laws whereas sustaining analytical capabilities for enterprise operations. These applied sciences deal with the basic pressure between information utility and privateness safety in an more and more regulated setting.
Subscribe the PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one. Obtain the information day by day in your inbox. Freed from adverts. 10 USD per 12 months.
PPC Land explains
Privateness-Enhancing Applied sciences (PETs): Digital options that allow organizations to gather, course of, analyze and share info whereas defending the confidentiality of non-public information. In response to the OECD definition, these applied sciences allow comparatively excessive utility from information whereas minimizing the necessity for information assortment and processing. PETs symbolize a basic shift from conventional information safety approaches that rely totally on authorized and procedural safeguards.
Information Obfuscation: Strategies that alter information by including “noise” or eradicating figuring out particulars to guard particular person privateness whereas sustaining analytical worth. This class contains anonymization, pseudonymization, artificial information technology, and differential privateness. Information obfuscation permits privacy-preserving machine studying and permits info verification with out requiring disclosure of delicate private info.
Encrypted Information Processing: Superior cryptographic strategies that enable computations to run over information that stay encrypted all through the method. This contains homomorphic encryption, multi-party computation, and trusted execution environments. These instruments symbolize probably the most important development in personal information processing, eliminating conventional vulnerabilities that happen when information should be decrypted for evaluation.
Federated Studying: A distributed strategy that allows analytical duties to be executed on information with out requiring the information to go away their unique location. Solely abstract statistics or mannequin parameters are shared relatively than uncooked information. This method reduces privateness dangers by protecting delicate info at its supply whereas nonetheless enabling collaborative evaluation and machine studying throughout a number of organizations.
Cross-Border Information Transfers: The motion of non-public information throughout worldwide boundaries, which faces rising regulatory scrutiny beneath varied privateness legal guidelines. Privateness-enhancing applied sciences supply potential options for enabling compliant worldwide information flows by offering technical safeguards that shield particular person privateness whereas sustaining information utility for legit enterprise functions.
GDPR (Basic Information Safety Regulation): The European Union’s complete information safety legislation that established the precept of “information safety by design and by default” in Article 25. This regulation requires organizations to implement applicable technical and organizational measures to make sure privateness safety, making it a key driver for privacy-enhancing expertise adoption throughout a number of industries.
Regulatory Frameworks: The evolving authorized constructions governing information safety and privateness throughout totally different jurisdictions. These frameworks more and more acknowledge privacy-enhancing applied sciences as legitimate compliance mechanisms, although implementation approaches range considerably between nations. Harmonization stays difficult as a consequence of totally different authorized traditions and coverage priorities.
Information Accountability: Techniques and processes that handle how information could be gathered, used, and shared whereas monitoring compliance with relevant laws. These instruments management and monitor information entry, set up utilization guidelines, and supply immutable information of information processing actions. Although not strictly privacy-enhancing applied sciences, they improve privateness by means of improved governance and management mechanisms.
Anonymization: The method of eradicating figuring out components from information to stop re-identification of people, theoretically rendering the information outdoors the scope of privateness laws. Nevertheless, the OECD analysis highlights important challenges in reaching true anonymization, as researchers proceed to efficiently re-identify supposedly anonymized datasets by means of varied analytical methods and auxiliary information sources.
Technical Implementation: The sensible deployment of privacy-enhancing applied sciences inside present organizational programs and workflows. This encompasses the technical structure, integration challenges, computational overhead, and operational necessities wanted to efficiently deploy these applied sciences. Implementation complexity usually serves as a big barrier to adoption, notably for organizations with restricted technical assets or experience.
Source link