Abstract
- AI detectors are at the moment unreliable as a result of false positives and negatives.
- Google’s SynthID Detector scans for digital watermarks in AI-generated content material.
- SynthID Detector won’t be a 100% dependable silver bullet, but it surely’s in all probability as dependable as a detector can get for AI.
AI detectors, whereas a doubtlessly helpful function, are at the moment a multitude. Instruments like ZeroGPT love to do a number of false positives and false negatives. Nonetheless, the necessity for an truly dependable AI detector is actual, and that is why efforts proceed to be made in that route. Google has its personal, although you may’t use it but.
Google has simply introduced SynthID Detector, a brand new verification portal designed to determine content material created utilizing its synthetic intelligence instruments, corresponding to Gemini, the Imagen picture era mannequin, or the Veo video era mannequin. The SynthID Detector works by scanning uploaded media for an imperceptible digital watermark, additionally named SynthID. Google has been growing this watermarking know-how to embed immediately into content material generated by its AI fashions, together with Gemini (textual content and multimodal), Imagen (photographs), Lyria (audio), and Veo (video). In keeping with the corporate, over 10 billion items of content material have already been watermarked utilizing this technique. That is, then, a Google-made device that appears for that watermark and tells you whether or not one thing is AI-generated or not.
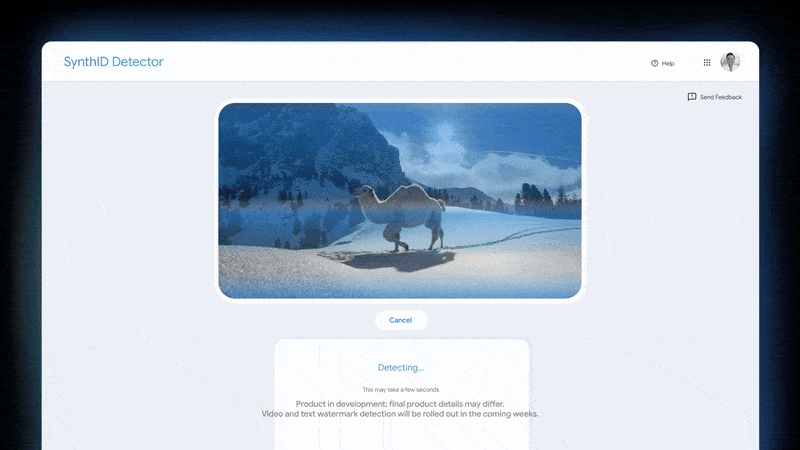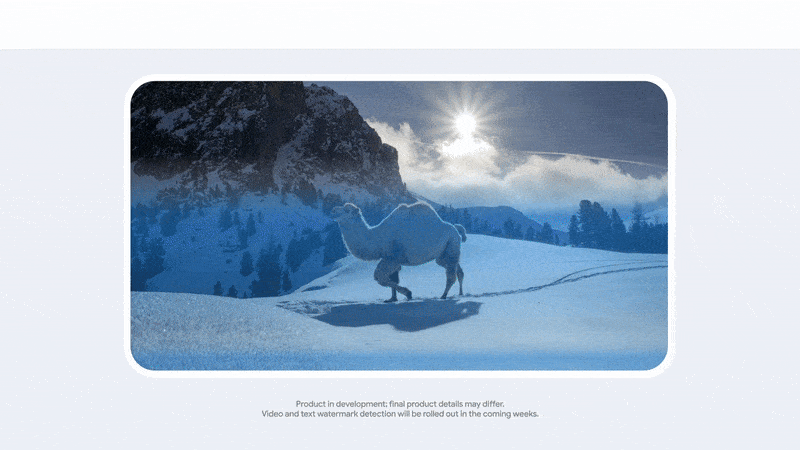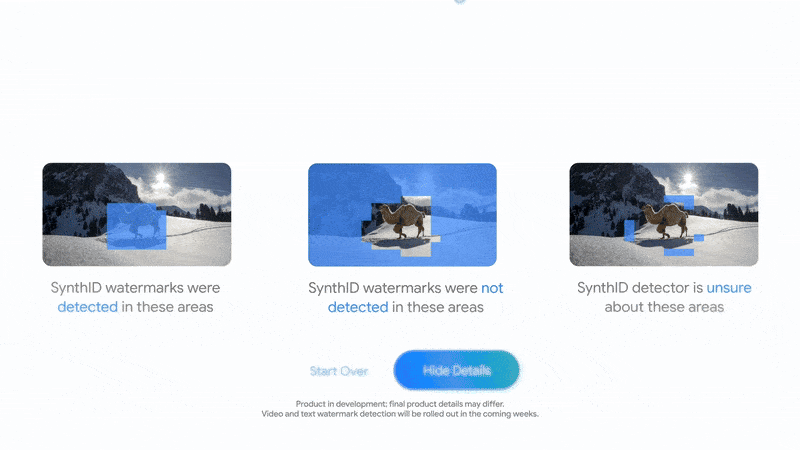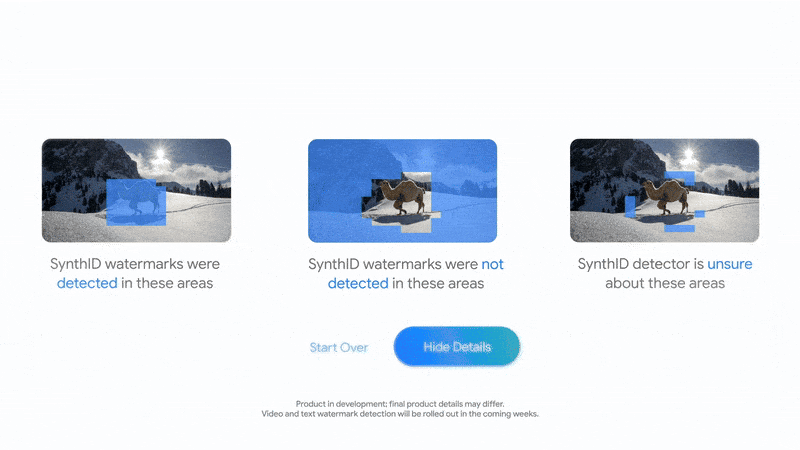
While you add a file—be it a picture, audio monitor, video, or textual content doc—to the SynthID Detector portal, it appears round to see whether or not this embedded watermark is current. And whether it is, the portal will point out that the content material is probably going AI-generated and, in some instances, spotlight particular parts the place the watermark is most prominently detected. For one, in audio information, it might probably level out segments containing the watermark, and for photographs, it might probably point out areas the place the digital signature is more than likely current.
What I nonetheless do not love about that is that it nonetheless appears to do a number of guesswork. The detector may be “not sure” about sure components, which isn’t omen for a supposedly dependable watermarking technique that may stand up to alterations and modifications. Identical to it may be not sure about some bits, it might detect a watermark the place there is not one, or it might fail to detect one thing AI-generated. I would say it might be extra liable to false positives than false negatives, however false positives can nonetheless be an issue. I am certain it’s going to proceed to be improved upon, although. A primary-party device like this is perhaps probably the most dependable approach proper now to search out out if one thing was AI-generated, however I would not say that there is nonetheless a 100% dependable, bulletproof technique to catch all of them.
This detector is at the moment rolling out to some people in an early entry method, and it will likely be adopted by a restricted rollout for journalists, media professionals, and researchers through a waitlist.
Supply: Google
Source link