Google Search Advocate John Mueller yesterday highlighted a testing capability that permits web site homeowners to confirm whether or not their pages exceed Googlebot’s 2MB HTML fetch restrict. The characteristic addition comes after Google reduced Googlebot’s file size limit from 15MB to just 2MB earlier this yr, marking an 86.7% lower in crawling capability.
Dave Sensible, the developer behind Tame the Bots, applied performance on February 6 to cap text-based information to 2MB in his fetch and render simulator instrument. The addition permits builders to test whether their HTML responses would be truncated when accessed by Google’s crawler. “On the danger of overselling how a lot of an actual world situation that is (it actually is not for 99.99% of web sites I would think about), I added performance to tamethebots.com/instruments/fetch-… to cap textual content based mostly information to 2 MB to simulate this,” Sensible said in his Bluesky announcement.
Mueller’s acknowledgment of the instrument arrived inside hours. “Should you’re curious in regards to the 2MB Googlebot HTML fetch restrict, here is a option to examine,” the Google Switzerland-based search advocate wrote at 12:48 on February 6. His endorsement supplies official validation for a testing methodology addressing technical issues that emerged following Google’s documentation adjustments.
Technical implementation particulars
The Tame the Bots fetch and render simulator operates via a number of configuration choices designed to duplicate Googlebot’s crawling habits. The instrument processes requests utilizing the Google open supply parser for robots.txt information, fetching these information recent for every check to make sure correct compliance checking. In response to the instrument’s documentation, it honors robots.txt directives utilizing the identical parsing logic Google employs.
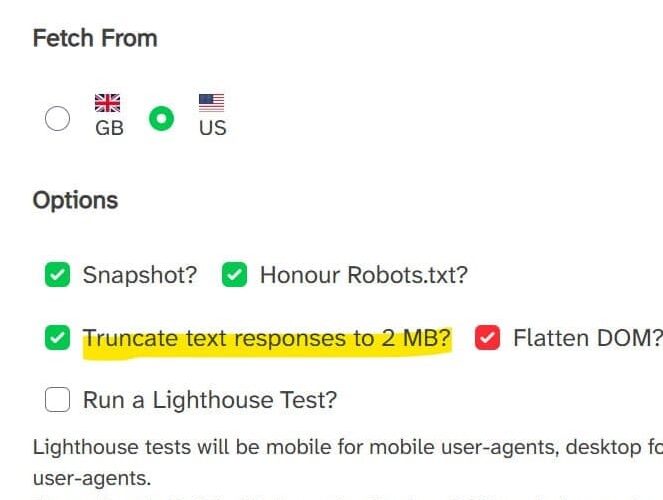
The brand new 2MB truncation characteristic seems as an non-obligatory checkbox inside the instrument’s interface alongside current capabilities together with snapshot era, robots.txt compliance, DOM flattening, and Lighthouse testing. When enabled, the truncation simulates Google’s present most file measurement restrict for preliminary HTML responses. Customers can fetch from both UK or US geographic areas and choose varied person brokers together with Googlebot Cellular to check completely different crawling situations.
The rendering course of employs Puppeteer for JavaScript execution and dom2html for DOM flattening. Snapshot technique choices permit customers to regulate when the instrument captures rendered HTML, with the default ready for 2 community connections to turn into idle earlier than finalizing the snapshot. The instrument returns each rendered HTML and preliminary supply code, together with screenshots exhibiting how pages seem to Googlebot.
Sensible emphasised the instrument’s limitations in reaching excellent parity with Google’s programs. “Though supposed to match, parity with the Google WRS can’t be assured, all the time affirm in both the Wealthy Outcomes Take a look at or URL Inspection instrument in Search Console,” the instrument’s documentation states. Take a look at outcomes get deleted after 5 minutes most and will not be logged, addressing privateness issues for customers testing dwell manufacturing websites.
Actual-world implications assessed
Sensible’s characterization of the 2MB restrict as affecting lower than 0.01% of internet sites aligns with broader business assessments about HTML file sizes. The developer famous in a subsequent publish on February 3 that “2 MB of uncooked HTML is a BIG, like REALLY massive file.” His commentary displays the fact that the majority HTML paperwork measure far beneath this threshold.
The 2MB restrict applies particularly to preliminary HTML responses somewhat than rendered content material after JavaScript execution. This distinction issues for single-page functions and JavaScript-heavy web sites the place vital content material will get generated client-side. As documented in Google’s December JavaScript rendering clarification, pages returning 200 standing codes persistently enter Google’s rendering queue no matter preliminary HTML measurement.
Sensible applied the testing characteristic as what he described as “a enjoyable train” somewhat than an pressing business want. “I might deal with is as steerage in case you are testing one of many few websites that genuinely does get affected by this restrict,” he defined. His pragmatic method acknowledges that whereas the technical constraint exists, its sensible influence stays restricted.
The developer directed customers to depend on Google’s personal verification instruments for definitive solutions. “As ever, what’s really listed (URL inspector) & findable (website: and quote snippet) are the ultimate phrase!” Sensible said. This steerage emphasizes that testing instruments present directional data whereas Search Console’s URL Inspection instrument delivers authoritative information about what Google really crawled and listed.
Context of crawling restrictions
The 2MB restrict emerged as a part of broader adjustments to Google’s crawling infrastructure. Google updated its crawling documentation on November 20, 2025, including HTTP caching help particulars and switch protocol specs. The infrastructure documentation now contains specific details about HTTP/1.1 because the default protocol model and help for gzip, deflate, and Brotli compression strategies.
Chris Lengthy, co-founder at Nectiv, introduced consideration to the 2MB documentation change via social media discussions that unfold throughout LinkedIn. Trade professionals together with Barry Schwartz, Jamie Indigo, and Steve Toth participated in conversations about potential implementation impacts. The widespread dialogue amongst technical web optimization practitioners mirrored uncertainty about how the decreased restrict may have an effect on crawling patterns and indexing habits.
The excellence between compressed and uncompressed information creates implementation complexity. Whereas builders sometimes serve compressed belongings utilizing gzip or brotli encoding, Googlebot applies the 2MB restrict to decompressed content material. This implies pages delivering 500KB of compressed HTML may probably exceed the restrict if uncompressed measurement approaches 2MB, although such compression ratios could be uncommon for text-based content material.
JavaScript and CSS assets face specific scrutiny beneath the file measurement constraints. Single-page functions that compile giant JavaScript bundles danger having execution interrupted if main software code exceeds 2MB when decompressed. Fashionable net growth practices typically produce JavaScript bundles within the 500KB to 1.5MB vary after compression, however uncompressed sizes can attain a number of megabytes for complicated functions.
Integration with rendering infrastructure
The 2MB restrict intersects with Google’s Web Rendering Service operations documented on December 3, 2024. The rendering infrastructure operates via three distinct phases: crawling, rendering, and indexing. When Googlebot fetches a URL from its crawling queue, it first verifies whether or not robots.txt permits entry. Pages passing this verification obtain HTTP requests, and Google parses the HTML response to find extra URLs via hyperlink components.
For JavaScript-heavy websites, the rendering section turns into crucial. Pages returning 200 standing codes persistently enter the rendering queue, the place Google’s headless Chromium executes JavaScript and generates rendered HTML. If main software JavaScript exceeds the 2MB restrict, the rendering course of may match with incomplete code, probably affecting the ultimate listed model.
The Internet Rendering Service implements a 30-day caching system for JavaScript and CSS assets, impartial of HTTP caching directives. This caching method helps protect crawl funds, which represents the variety of URLs Googlebot can and needs to crawl from a web site. The interplay between file measurement limits and useful resource caching creates complexity for builders managing deployment pipelines and cache invalidation methods.
Content material fingerprinting emerges as an vital method for managing JavaScript useful resource caching beneath these constraints. Together with content material hashes in filenames, similar to “foremost.2bb85551.js,” ensures that code updates generate completely different filenames that bypass stale caches whereas conserving particular person file sizes manageable via code splitting strategies.
Crawl funds optimization context
The file measurement discount could mirror Google’s response to operational value pressures. Cloudflare data revealed that Googlebot accesses considerably extra web content material than competing crawlers. Based mostly on sampled distinctive URLs utilizing Cloudflare’s community over two months, Googlebot crawled roughly 8 p.c of noticed pages, accessing 3.2 instances extra distinctive URLs than OpenAI’s GPTBot and 4.8 instances greater than Microsoft’s Bingbot.
Google presently operates Googlebot as a dual-purpose crawler that concurrently gathers content material for conventional search indexing and for AI functions together with AI Overviews and AI Mode. Publishers can not afford to dam Googlebot with out jeopardizing their look in search outcomes, which stay crucial for visitors era and promoting monetization. The crawl restrict discount could allow Google to take care of complete net protection whereas lowering operational prices via stricter effectivity controls.
Google’s crawling infrastructure has undergone steady refinement addressing scale and effectivity issues. The corporate deprecated the Crawl Rate Limiter Tool in Search Console on January 8, 2024, changing it with automated programs that modify crawl charges based mostly on server responses. If servers persistently return HTTP 500 standing codes or response instances improve considerably, Googlebot mechanically slows crawling with out requiring guide intervention.
Crawl rate disruptions affected multiple hosting platforms beginning August 8, 2025, when giant web sites throughout Vercel, WP Engine, and Fastly infrastructures skilled dramatic decreases. Google acknowledged on August 28 that the difficulty stemmed from their programs, with John Mueller confirming the issue concerned “decreased / fluctuating crawling from our facet, for some websites.” The incidents demonstrated Google’s ongoing challenges in balancing complete protection with operational constraints.
Developer testing workflows
The Tame the Bots instrument integrates into current technical web optimization workflows the place builders confirm crawler compatibility earlier than deploying main adjustments. The fetch and render simulator has supplied Chrome extension integration, permitting customers to entry testing capabilities via right-click context menus. The extension, obtainable via the Chrome Retailer, supplies fast entry with out requiring guide URL entry via the online interface.
Testing workflows sometimes contain a number of verification steps. Builders first examine whether or not pages honor robots.txt directives appropriately, then confirm rendered HTML matches expectations, and at last affirm that crucial assets load inside crawler constraints. The 2MB truncation choice provides one other checkpoint to this course of, permitting groups to establish potential points earlier than Google encounters them in manufacturing.
The instrument’s Lighthouse integration presents efficiency testing alongside crawlability verification. Lighthouse exams run as cellular for cellular user-agents and desktop for desktop user-agents, matching the responsive testing method that mirrors precise person experiences. This mixed testing method helps builders establish each crawler-specific points and broader efficiency issues which may have an effect on person engagement metrics.
DOM flattening capabilities show notably invaluable for testing complicated JavaScript functions. The characteristic pierces the Shadow DOM and renders content material from iframes, offering visibility into content material that is likely to be hidden from commonplace HTML parsing. This method, impressed by discussions with Glenn Gabe of G-Squared Interactive, helps establish crawlability points in trendy net frameworks that rely closely on part encapsulation.
Trade response patterns
Mueller’s endorsement of the testing instrument follows his broader sample of partaking with community-developed assets that assist web site homeowners perceive Google’s necessities. The search advocate has warned against various optimization approaches whereas concurrently encouraging builders to construct instruments and check technical implementations. On December 19, 2025, Mueller endorsed criticism of formulaic web optimization content material, sharing an article describing most optimization-focused content material as “digital mulch.”
The testing instrument dialogue happens towards backdrop of broader technical web optimization instrument evolution. Screaming Frog released version 22.0 with semantic similarity evaluation on June 11, 2025, using giant language mannequin embeddings to establish duplicate and off-topic content material. Conventional web optimization instruments are adapting to AI-powered content material evaluation somewhat than turning into out of date as some predicted.
Mueller has persistently emphasised that problematic technical implementations sometimes reveal themselves via regular searching somewhat than requiring specialised detection instruments. On February 3, 2026, Mueller cautioned against excessive redirect chain analysis, stating that points vital sufficient to have an effect on search rankings would manifest as user-facing issues. His method prioritizes fixes for points that influence precise customers over optimization of edge instances that exist primarily in technical audits.
The file measurement testing functionality aligns with Mueller’s framework for helpful technical instruments: people who assist builders establish actual issues somewhat than creating work based mostly on theoretical issues. Sensible’s implementation contains the nuance that the majority websites will not encounter points, avoiding the alarmist framing that typically accompanies technical web optimization instrument releases.
Verification finest practices
Sensible’s steerage emphasizes that the instrument supplies approximations somewhat than ensures. Web site homeowners involved in regards to the 2MB restrict ought to complement testing instrument outcomes with verification via Google’s official channels. Search Console’s URL Inspection instrument stays the authoritative supply for understanding what Google really crawled, rendered, and listed from particular pages.
The URL Inspection instrument reveals whether or not Googlebot efficiently fetched a web page, whether or not it was allowed by robots.txt, what HTTP standing code the server returned, whether or not rendering succeeded, and what the ultimate listed model appears like. For pages approaching the 2MB threshold, evaluating the “View crawled web page” output towards supply HTML can reveal whether or not truncation occurred.
Web site-specific search queries utilizing the location: operator present extra verification of indexing standing. Sensible famous that pages seen solely in focused website: queries will not seem for common customers, suggesting that partial indexing of truncated content material could have minimal sensible influence on search visibility. This commentary aligns with Google’s broader method the place a number of alerts decide whether or not content material deserves distinguished placement in search outcomes.
The testing instrument’s five-minute information retention coverage addresses privateness issues whereas offering enough time for customers to assessment outcomes. For organizations testing delicate pre-production pages or inner functions, this automated deletion ensures that check information does not persist in exterior programs the place it is likely to be accessed inappropriately.
Efficiency optimization methods
Builders managing giant HTML responses have a number of optimization approaches obtainable past easy content material discount. Server-side rendering frameworks can generate minimal preliminary HTML that features solely crucial above-the-fold content material, deferring remaining web page content material to client-side JavaScript execution after preliminary web page load. This sample retains preliminary HTML responses small whereas nonetheless delivering full performance to finish customers.
Progressive enhancement strategies permit web sites to ship useful experiences with minimal HTML, then improve with JavaScript for customers whose browsers help superior options. This method naturally produces smaller preliminary HTML payloads whereas making certain content material stays accessible to crawlers that will execute JavaScript in a different way than trendy browsers.
Code splitting divides JavaScript functions into smaller chunks that load on demand somewhat than delivering whole functions in single bundles. Fashionable construct instruments together with Webpack, Rollup, and Vite present refined code-splitting capabilities that may hold particular person file sizes properly beneath the 2MB threshold whereas sustaining software performance. Dynamic imports allow loading extra code solely when particular options are accessed.
HTTP/2 server push capabilities permit delivering a number of assets in response to single requests, probably working round sure file measurement constraints. Nevertheless, Google’s crawling infrastructure documentation signifies HTTP/1.1 stays the default protocol, suggesting builders should not rely solely on HTTP/2 options for Googlebot optimization.
Regulatory and aggressive context
The crawling restrict discount emerged throughout a interval of heightened regulatory scrutiny over Google’s information gathering practices. The UK’s Competition and Markets Authority opened consultations analyzing conduct necessities for Google following its designation with Strategic Market Standing. The CMA’s investigation focuses on whether or not publishers have practical choices to forestall content material utilization in AI options whereas sustaining search visibility.
Publishers have expressed frustration that blocking AI options via current mechanisms concurrently eliminates visibility in typical search outcomes. The coupling of conventional search entry with AI characteristic participation creates what business observers characterize as compelled participation. Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince said in July 2025 that the corporate would get hold of strategies from Google to dam AI Overviews and Reply Containers whereas preserving conventional search indexing capabilities.
The crawl restrict discount permits Google to take care of complete net protection important for each search and AI functions whereas probably lowering the operational prices that regulatory scrutiny has highlighted. By optimizing crawl effectivity via stricter file measurement limits, Google addresses value issues with out essentially altering its entry to writer content material.
Unbiased publishers filed a proper antitrust criticism with the European Fee on June 30, 2025, alleging abuse of market energy via AI Overviews that show content material summaries with out producing clicks to authentic sources. The criticism argues that Google leverages its search dominance to extract writer content material for AI functions with out truthful compensation.
Future monitoring implications
Sensible plans to deal with the 2MB truncation characteristic as steerage for the small variety of websites which may encounter points somewhat than as a crucial testing requirement for all implementations. “Largely I did this as a enjoyable train, & it’s maybe a bit blunt,” he defined. This framing acknowledges the instrument’s limitations whereas offering helpful performance for edge instances.
The provision of testing instruments permits builders to proactively establish potential points somewhat than discovering issues after Google’s programs encounter them in manufacturing. For organizations deploying content material administration programs, e-commerce platforms, or functions that generate giant HTML responses, periodic testing supplies early warning of crawling compatibility issues.
Monitoring crawl statistics via Search Console helps establish whether or not file measurement points are affecting precise crawling habits. Vital will increase in crawl errors, declining crawl charges, or pages exhibiting “Listed, although blocked by robots.txt” standing could point out underlying technical issues value investigating. The URL Inspection instrument’s detailed crawl data helps diagnose whether or not file measurement constraints contributed to indexing points.
The interplay between file measurement limits, rendering infrastructure, and crawl funds allocation will doubtless proceed evolving as Google refines its programs. Web site homeowners ought to monitor official documentation updates and Search Console notifications for adjustments which may have an effect on their particular implementations. Mueller’s willingness to spotlight neighborhood instruments suggests Google acknowledges worth in third-party verification assets that assist builders perceive crawler habits.
Timeline
- December 3, 2024: Google publishes detailed documentation explaining Googlebot’s crawling process, together with Internet Rendering Service operations and 30-day caching for JavaScript assets
- November 20, 2025: Google updates crawling infrastructure documentation with HTTP caching help particulars and switch protocol specs
- December 18, 2025: Google clarifies JavaScript rendering for error pages, explaining how non-200 standing codes could skip rendering section
- Early 2026: Google reduces Googlebot file size limit from 15MB to 2MB, marking 86.7% lower affecting uncompressed HTML, JavaScript, and CSS information
- February 3, 2026: Dave Sensible posts on Bluesky stating “the max HTML measurement for the preliminary HTML is 2 MB, not 15 MB” and noting that “2 MB of uncooked HTML is a BIG, like REALLY massive file”
- February 6, 2026: Dave Sensible implements 2MB truncation characteristic in Tame the Bots fetch and render simulator at 12:30
- February 6, 2026: John Mueller endorses testing instrument on Bluesky at 12:48, stating “Should you’re curious in regards to the 2MB Googlebot HTML fetch restrict, here is a option to examine”
Abstract
Who: Dave Sensible, developer of Tame the Bots technical web optimization instruments, applied the 2MB testing characteristic with endorsement from John Mueller, Google’s Search Advocate based mostly in Switzerland.
What: Sensible added performance to his fetch and render simulator instrument permitting builders to cap text-based information to 2MB, simulating Google’s present Googlebot HTML fetch restrict. The instrument supplies non-obligatory truncation alongside current options together with robots.txt compliance testing, DOM flattening, and Lighthouse efficiency evaluation.
When: Sensible introduced the characteristic implementation on February 6, 2026, at 12:30, with Mueller highlighting the testing functionality roughly 18 minutes later at 12:48.
The place: The testing instrument operates at tamethebots.com/instruments/fetch-and-render as a part of a broader suite of technical web optimization verification assets. The instrument processes requests from UK or US geographic areas utilizing varied Googlebot person brokers.
Why: The testing functionality addresses uncertainty following Google’s discount of its file measurement restrict from 15MB to 2MB earlier in 2026, an 86.7% lower that raised questions on potential crawling impacts. Sensible characterised the real-world influence as affecting lower than 0.01% of internet sites whereas acknowledging worth in offering verification instruments for edge instances. Mueller’s endorsement validates the testing methodology for builders in search of to confirm compatibility with Google’s present crawling infrastructure.
Share this text