Researchers analyzing 4 million Claude AI conversations found a putting focus sample: solely 5% of occupational duties account for 59% of all synthetic intelligence interactions, in keeping with a analysis paper printed October 29, 2025, on arXiv. The research, authored by Peeyush Agarwal, Harsh Agarwal, and Akshat Rana, supplies the primary systematic proof linking real-world generative AI utilization to complete activity traits throughout the financial system.
The evaluation used Anthropic’s Financial Index dataset, which mapped tens of millions of anonymized person interactions with the Claude AI assistant to standardized occupational duties from the U.S. Division of Labor’s O*NET database. Duties requiring excessive creativity, complexity, and cognitive demand attracted probably the most AI engagement, whereas extremely routine duties noticed minimal adoption. The findings problem assumptions about which work actions profit from AI augmentation.
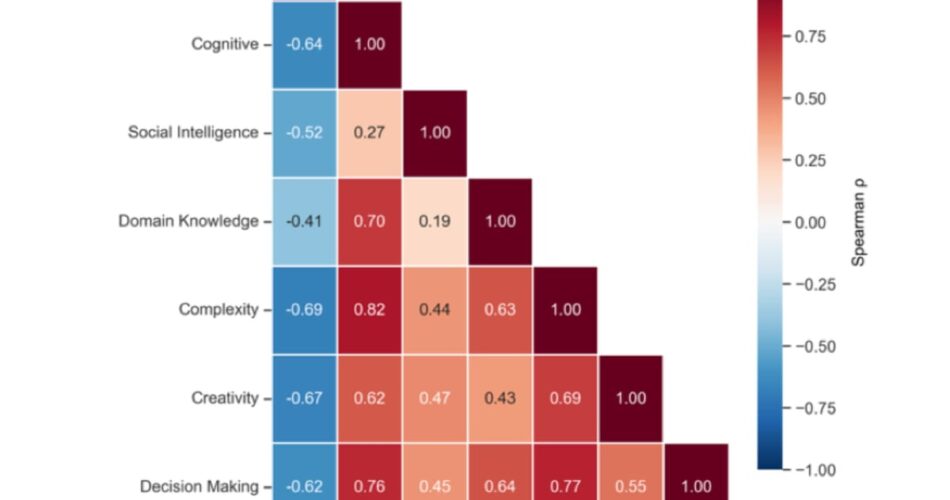
The researchers developed a scoring framework that evaluated every activity throughout seven key dimensions: Routine, Cognitive, Social Intelligence, Creativity, Area Information, Complexity, and Choice Making. Every dimension comprised 5 particular parameters, creating 35 measurable traits that had been scored utilizing massive language fashions. This technique enabled quantitative evaluation of what drives AI adoption on the activity stage quite than the occupation stage.
Duties demanding thought era confirmed the strongest correlation with AI utilization, with a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.173. Data processing duties adopted at 0.157, whereas originality necessities reached 0.151. Conversely, duties characterised by predictable outcomes correlated negatively at -0.135, with frequency of repetition at -0.131. The sample suggests AI at present serves as a brainstorming and synthesis instrument quite than an execution system for well-defined procedures.
The focus of AI utilization extends past particular person activity traits. The distribution of AI interactions throughout O*NET duties proved sharply right-skewed, with the median activity accounting for less than 0.006% of AI conversations. Three-quarters of all duties fell beneath 0.017% utilization. This excessive “lengthy tail” distribution signifies present AI deployment stays extremely selective quite than representing broad-based software throughout work actions.
Three distinct activity archetypes emerged from multivariate evaluation utilizing principal part evaluation and Okay-means clustering. The researchers labeled these classes as “Dynamic Downside Fixing,” “Procedural & Analytical Work,” and “Standardized Operational Duties.” Every archetype exhibited statistically distinct profiles throughout the seven traits and confirmed considerably totally different charges of AI adoption.
Dynamic Downside Fixing duties, comprising 2,100 duties or the most important group, attracted the very best imply AI utilization at 3.31%. These duties scored lowest on routineness at 3.36 and highest on cognitive calls for at 8.53, creativity at 6.43, complexity at 8.43, and choice making at 8.25. The archetype represents work requiring substantial mental flexibility and unique pondering.
Procedural & Analytical Work, consisting of 1,017 duties, confirmed average AI utilization at 2.45%. These duties demonstrated average routineness at 5.8, low social intelligence at 4.51, and low creativity at 3.39. The profile suggests structured analytical actions that comply with established frameworks however require cognitive effort. Standardized Operational Duties, the smallest group with 397 duties, exhibited the bottom AI utilization at 0.014%. These duties scored highest on routineness at 7.08 and lowest throughout all different dimensions, together with cognitive calls for at 4.6, social intelligence at 3.1, and creativity at 1.53.
The evaluation revealed a putting attribute: social intelligence confirmed near-zero correlation with AI utilization throughout all 5 of its constituent parameters. Duties requiring interpersonal interplay, emotional administration, collaboration, or social perceptiveness demonstrated no statistical relationship with AI adoption patterns. This discovering positions social intelligence as probably sturdy human comparative benefit in an AI-augmented financial system.
Inside the Creativity dimension, vital variation appeared throughout parameters. Thought era correlated way more strongly with AI utilization than innovation necessities, suggesting present AI software focuses on divergent pondering phases quite than convergent implementation. Duties requiring inventive or aesthetic parts confirmed decrease correlation than pure conceptual work.
Excessive-usage duties, outlined as the highest tenth percentile, exhibited a definite signature in comparison with low-usage duties within the backside tenth percentile. Excessive-usage duties scored considerably larger on Cognitive (8.8 versus 6.8), Complexity (8.7 versus 6.5), Creativity (7.1 versus 2.8), and Choice Making (8.3 versus 6.6) dimensions. They scored considerably decrease on Routine (2.9 versus 6.2). Social Intelligence confirmed minimal distinction between teams at 6.1 versus 5.7.
The researchers acknowledged a number of limitations. The utilization information derives from a single AI mannequin household, Claude, whose person base might not characterize your entire workforce. The LLM-based scoring technique for activity traits, whereas systematically utilized, serves as a proxy for human judgment and should carry inherent biases. The evaluation supplies a cross-sectional snapshot quite than capturing dynamic evolution of AI use as know-how advances and adoption patterns change.
Anthropic released its Economic Index on February 10, 2025, revealing that roughly 36% of occupations use AI for at the least 1 / 4 of their related duties, whereas solely 4% of occupations make the most of AI throughout three-quarters of their duties. Laptop-related duties noticed the most important AI utilization at 37.2% of all queries, adopted by writing duties in academic and communication contexts at 10.3%.
The focus sample has vital implications for advertising professionals. Duties involving content material era, strategic planning, and marketing campaign conceptualization align with the high-usage archetype traits. Routine execution duties like customary reporting or repetitive media shopping for operations present traits related to low AI adoption.
Research from IAB Europe in September 2025 discovered that 85% of firms already deploy AI-based instruments for advertising functions, with concentrating on and content material era main adoption at 64% and 61% respectively. Nevertheless, the concentrated utilization patterns revealed within the Adobe paper recommend substantial variation wherein particular advertising duties profit from AI help.
The findings problem assumptions about AI changing routine work. Whereas earlier automation applied sciences primarily focused repetitive duties, present generative AI adoption exhibits reverse patterns. Duties with excessive routineness and predictable outcomes correlate negatively with utilization, whereas cognitively demanding artistic work correlates positively.
Advertising and marketing measurement challenges documented all through 2025 might clarify some adoption patterns. Research released December 2, 2025, by Funnel and Ravn Research discovered that 86% of in-house entrepreneurs wrestle to find out the impression of every advertising channel on total efficiency regardless of unprecedented entry to analytics instruments. AI instruments that synthesize data and generate insights deal with these data processing challenges that characterize high-usage duties.
The paper identifies cognitive offloading because the central psychological dimension of present AI adoption. People leverage AI to beat preliminary high-friction phases of data work, significantly brainstorming, outlining, and synthesizing data. The sample seems throughout all activity classes however manifests most strongly in advanced cognitive work.
Area data necessities confirmed average optimistic correlation with AI utilization at 0.084, suggesting specialised experience neither strongly attracts nor repels AI adoption. Duties requiring specialised data nonetheless see substantial AI software once they contain excessive cognitive calls for and complexity. This sample challenges assumptions that knowledgeable domains would resist AI integration.
The researchers scored duties utilizing Gemini 2.5 Professional with temperature set to zero, offering every O*NET activity description and requesting scores on a 1-10 scale for every particular parameter. The seven main attribute scores characterize the arithmetic imply of their 5 constituent parameter scores. This method aligns with the rising “LLM-as-a-Decide” paradigm, the place language fashions function scalable alternate options to human specialists for advanced analysis duties.
Principal part evaluation revealed that the primary two parts defined 82.3% of variance throughout the seven traits. The inter-correlation matrix confirmed that Cognitive, Complexity, and Choice Making traits correlated strongly and positively with one another, all above 0.75, whereas correlating strongly negatively with Routine, all beneath -0.61. Social Intelligence exhibited weaker correlations with all different traits.
The research utilized the Clio system developed by Anthropic, which permits privacy-preserving evaluation of conversations whereas sustaining person privateness. The analysis analyzed roughly a million conversations on Claude.ai Free and Professional plans throughout December 2024 and January 2025. The methodology maintains enterprise-grade confidentiality requirements whereas extracting combination patterns.
Enterprise AI adoption faces persistent scaling problems despite widespread deployment. McKinsey launched analysis on November 9, 2025, revealing that whereas 88% of respondents report common AI use in at the least one enterprise perform, solely roughly one-third report their firms have begun scaling AI applications throughout the enterprise. The concentrated utilization patterns revealed within the Adobe paper present potential rationalization: most duties might not but exhibit traits that entice heavy AI adoption.
Advertising and marketing organizations face selections about which particular actions warrant AI funding. The analysis framework supplies evidence-based steerage. Duties combining excessive creativity necessities with substantial cognitive complexity however low routineness characterize the highest-probability AI adoption candidates. Customary operational actions might require totally different automation approaches than conversational AI interfaces.
The paper introduces three key contributions to understanding AI’s impression on work. First, systematic proof linking real-world AI utilization patterns to intrinsic activity traits. Second, a complete multi-dimensional framework for characterizing occupational duties that captures the multifaceted nature of recent AI capabilities. Third, distinct activity archetypes revealing deeper patterns in AI adoption than particular person traits alone.
Future implications span a number of domains. Labor markets might expertise elementary transformation as data work shifts from data processing towards activity delegation, choice making, and high quality analysis. Academic priorities require reorientation towards vital pondering, activity delegation capabilities, and analytical abilities to tell apart between helpful AI contributions and potential errors.
Enterprise technique implications recommend organizations ought to systematically analyze jobs requiring excessive cognitive complexity and creativity for AI-powered product growth. These characterize duties the info exhibits folks readily offload and characterize clear market indicators for accelerating adoption. Organizations ought to examine low adoption charges for routine duties to find out whether or not these have been optimized by different applied sciences or whether or not organizational limitations forestall utilization.
Coverage issues deal with facilitating labor market transitions by equipping staff with abilities to function inside high-complementarity archetypes. Policymakers would possibly think about monetary incentives to speed up workforce adaptation to AI-augmented work environments. Tax rebates or exemptions on AI abilities coaching for firms may facilitate smoother labor market transitions.
The researchers acknowledge that O*NET activity descriptions, whereas complete, might not seize all nuances of recent work or might group distinct actions collectively. The cross-sectional evaluation supplies a snapshot in time quite than capturing dynamic evolution. The one AI mannequin household information supply might not characterize your entire workforce person base.
Claude Code demonstrations have revealed significant productivity gains for specific engineering tasks. A Google principal engineer acknowledged on January 3, 2026, that Claude Code reproduced advanced distributed methods structure in a single hour that her staff spent a full 12 months constructing. Such instances exemplify the acute focus patterns recognized within the analysis, the place particular high-complexity duties entice disproportionate AI utilization.
The concentrated adoption sample raises questions on return on funding for AI infrastructure. If solely 5% of duties drive 59% of utilization, organizations might obtain most advantages by figuring out and optimizing these high-value functions quite than pursuing common deployment throughout all actions.
Advertising and marketing functions that align with high-usage traits embody strategic temporary growth, artistic idea era, multi-channel marketing campaign planning, aggressive evaluation synthesis, and efficiency report narrative creation. Actions aligned with low-usage traits embody media shopping for execution, customary efficiency reporting, routine asset trafficking, and established workflow procedures.
The sturdy human worth emerges not in direct competitors with AI’s cognitive capabilities, however in complementary domains. Whereas the info demonstrates widespread willingness to delegate advanced cognitive duties to AI methods, human benefit focuses on oversight and contextual software of AI outputs. Social intelligence maintains its distinct place, remaining statistically decoupled from AI adoption patterns and suggesting interpersonal capabilities proceed representing human comparative benefit.
The implications lengthen to advertising know-how growth. Platforms specializing in data synthesis, conceptual exploration, and strategic evaluation align with high-adoption activity traits. Instruments emphasizing course of automation for well-defined workflows might require totally different technological approaches than conversational AI interfaces optimized for exploratory work.
Timeline
Abstract
Who: Researchers Peeyush Agarwal from Netaji Subhas College of Expertise, Harsh Agarwal from Adobe Inc., and Akshat Rana from Netaji Subhas College of Expertise performed the evaluation, using Anthropic’s Financial Index dataset of Claude AI interactions.
What: The analysis paper reveals excessive focus in AI utilization patterns, with simply 5% of occupational duties accounting for 59% of all interactions with Claude AI, demonstrating that duties requiring excessive creativity, complexity, and cognitive demand however low routineness entice probably the most engagement whereas extremely routine work stays largely untouched.
When: The paper was printed on arXiv on October 29, 2025 (model 2), analyzing dialog information from December 2024 and January 2025, following preliminary submission on October 26, 2025.
The place: The research analyzed roughly a million conversations on Claude.ai Free and Professional plans, mapping them to O*NET occupational activity classes representing the U.S. workforce, although implications lengthen globally to data work throughout all markets.
Why: The analysis addresses a vital hole in understanding which intrinsic activity traits drive customers’ selections to delegate work to AI methods, transferring past occupation-level evaluation to task-level insights that inform workforce growth, enterprise technique, and coverage selections as generative AI transforms the character of data work.
Share this text