Probably the most refined synthetic intelligence fashions out there right this moment produce severely dangerous scientific suggestions in as much as 22.2% of medical instances, elevating pressing questions on affected person security as these techniques turn out to be embedded in healthcare workflows that have an effect on hundreds of thousands of Individuals.
Researchers from Stanford and Harvard released findings on January 2, 2026, demonstrating that even top-performing AI fashions make between 12 and 15 extreme errors per 100 scientific instances, whereas the worst-performing techniques exceed 40 extreme errors throughout the identical variety of affected person encounters. The analysis, titled First, Do NOHARM, evaluated 31 giant language fashions in opposition to 100 actual main care session instances spanning 10 medical specialties.
Subscribe PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one
“Widespread adoption of LLMs in CDS is pushed partially by their spectacular scientific efficiency,” the researchers wrote of their examine. “As LLMs turn out to be an integral a part of routine medical care, understanding and mitigating AI errors is important.”
The findings arrive at a essential juncture for digital well being. Two-thirds of American physicians at the moment use giant language fashions in scientific follow, with one in 5 consulting these techniques for second opinions on affected person care choices. One trade estimate means that greater than 100 million Individuals in 2025 will obtain care from a doctor who has used AI-powered scientific resolution help instruments.
Errors of omission drive most affected person hurt
The analysis reveals a counterintuitive discovering about how AI techniques fail in medical contexts. Throughout all evaluated fashions, errors of omission—failing to advocate essential diagnostic exams or remedies—accounted for 76.6% of severely dangerous errors. Errors of fee, the place fashions inappropriately advocate harmful medicines or procedures, represented a smaller fraction of complete hurt.
“To do no hurt, one should additionally take into account the hurt of sustaining the established order,” the researchers famous when contextualizing their findings in opposition to a baseline “No Intervention” mannequin that advisable no medical actions in any case. That baseline method produced 29 severely dangerous errors—a quantity exceeded by each evaluated AI system.
The examine measured hurt utilizing a framework known as NOHARM (Quite a few Choices Hurt Evaluation for Danger in Drugs), developed particularly to evaluate how regularly and severely AI-generated medical suggestions might injury sufferers. Every of the 100 scientific instances included an in depth menu of potential diagnostic exams, medicines, counseling actions, and follow-up procedures. Twenty-nine board-certified physicians, together with 23 specialists and subspecialists, supplied 12,747 skilled annotations score whether or not every potential motion would profit or hurt sufferers.
Fashions had been evaluated on a number of dimensions past easy hurt counts. The researchers measured Security (avoidance of hurt burden), Completeness (whether or not all extremely acceptable actions had been advisable), and Restraint (tendency to keep away from equivocal care). Security efficiency ranged from 46.1% for the worst mannequin to 69.5% for the perfect, whereas Completeness scores different from 28.2% to 67.1%.
The quantity wanted to hurt—a scientific metric indicating what number of instances a mannequin would deal with earlier than producing not less than one severely dangerous suggestion—ranged from 4.5 for the worst-performing techniques to 11.5 for the perfect. This implies even the strongest fashions produced extreme hurt potential in roughly one out of each 11 affected person instances evaluated.
Purchase adverts on PPC Land. PPC Land has commonplace and native advert codecs through main DSPs and advert platforms like Google Advertisements. By way of an public sale CPM, you may attain trade professionals.
Mannequin measurement and reasoning modes do not predict security
The analysis challenges widespread assumptions about which AI capabilities translate to scientific security. Neither mannequin measurement, recency of launch, reasoning functionality, nor efficiency on well-liked benchmarks reliably predicted how safely a system would carry out in actual medical situations.
Security efficiency confirmed solely average correlation with current benchmarks. The strongest relationships emerged between Security and GPQA-Diamond scores (Pearson’s r = 0.61) and between Security and LMArena rankings (r = 0.64), however the majority of variance remained unexplained. No exterior benchmark correlated with Completeness, the measure of whether or not fashions advisable all essential scientific actions.
“It stays unclear whether or not information positive aspects function a proxy for protected and efficient scientific administration,” the researchers wrote. Their linear regression evaluation discovered that solely Restraint—not Security or Completeness—was positively predicted by reasoning capability and bigger mannequin measurement after a number of testing correction.
These findings carry specific significance as healthcare organizations consider which AI techniques to deploy. The analysis signifies that medical advertising and AI integration continues accelerating throughout well being techniques, but the instruments trade professionals have used to evaluate common AI functionality don’t adequately predict scientific security efficiency.
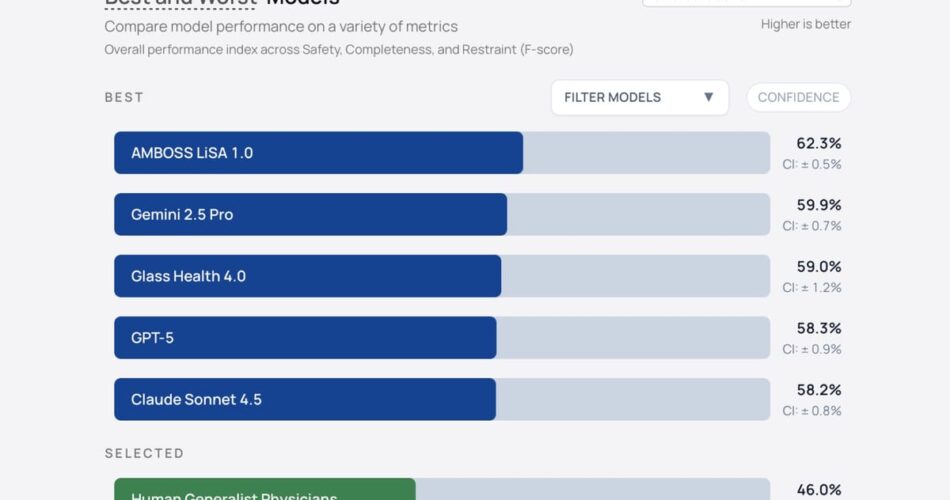
Gemini 2.5 Flash emerged because the top-performing solo mannequin with 11.8 extreme errors per 100 instances, adopted by AMBOSS LiSA 1.0 with 11.9 extreme errors. Claude Sonnet 4.5 produced 13.1 extreme errors, whereas GPT-5 generated 14.5 extreme errors. On the backside of the efficiency spectrum, GPT-4o mini made 40.1 extreme errors per 100 instances, whereas o4 mini produced 39.9 extreme errors.
The specialised medical retrieval-augmented era techniques—AMBOSS LiSA 1.0 and Glass Well being 4.0—demonstrated sturdy efficiency, rating second and third respectively on general scores. These techniques floor their suggestions in scientific information bases moderately than relying solely on common language mannequin coaching.

AI techniques outperform generalist physicians on security
Ten board-certified inner medication physicians accomplished a consultant subset of the benchmark instances utilizing typical assets together with web search, UpToDate, and PubMed, with out entry to AI help. The strongest AI mannequin outperformed these physicians on Security by 9.7 share factors (95% CI 7.0-12.5%), whereas physicians outperformed the weakest fashions by 19.2 share factors (95% CI 16.5-21.8%).
The common AI mannequin additionally exceeded human doctor efficiency on Completeness by 15.6 share factors (95% CI 11.4-19.9%), although no statistical distinction appeared between AI and human efficiency on Restraint. These outcomes recommend that rigorously chosen AI techniques might doubtlessly increase generalist doctor decision-making, significantly in conditions the place specialist session is delayed or unavailable.
Nevertheless, the researchers emphasised essential caveats. The benchmark instances represented main care-to-specialist consultations—situations the place physicians had been actively searching for extra experience. Actual-world deployment would require strong oversight mechanisms to forestall automation bias, the documented tendency for clinicians to simply accept believable AI suggestions with out ample scrutiny.
“When fashions are usually correct, their errors usually tend to be accepted with out detection attributable to automation bias,” the examine warned, citing analysis displaying how automation bias has affected scientific decision-making with different AI instruments.
Multi-agent techniques cut back hurt considerably
The analysis recognized a promising method to mitigating AI scientific errors by way of multi-agent orchestration. Fairly than deploying a single AI mannequin, the researchers examined configurations the place an preliminary “Advisor” mannequin generates suggestions which might be then reviewed and revised by one or two “Guardian” fashions prompted to determine and cut back dangerous recommendations.
Multi-agent configurations achieved 5.9-fold greater odds of reaching top-quartile Security efficiency in comparison with solo fashions. The variety of fashions utilized in these ensembles proved significantly essential. Configurations combining completely different fashions from completely different organizations persistently outperformed these utilizing a number of cases of the identical mannequin.
The best-performing multi-agent configuration mixed three distinct approaches: an open-source mannequin (Llama 4 Scout), a proprietary mannequin (Gemini 2.5 Professional), and a retrieval-augmented era system (LiSA 1.0). This heterogeneous method improved Security by a imply distinction of 8.0 share factors (95% CI 4.0-12.1%) in comparison with solo mannequin deployment.
“These outcomes show that multi-agent orchestration, significantly when combining heterogeneous fashions and retrieval-augmented capabilities, can mitigate scientific hurt with out extra fine-tuning or mannequin retraining,” the researchers concluded.
The discovering has speedy sensible implications for healthcare techniques evaluating AI deployment methods. Fairly than searching for a single “greatest” mannequin, organizations would possibly obtain higher affected person outcomes by implementing various AI techniques that test one another’s suggestions.
Efficiency trade-offs reveal security paradox
Evaluation of 176 solo fashions and multi-agent configurations revealed an sudden relationship between precision and security. Fashions tuned for top Restraint—that means they advisable fewer actions general to maximise precision—truly demonstrated lowered Security efficiency in comparison with fashions with average Restraint ranges.
The connection between Security and Restraint adopted an inverted-U sample, the place Security peaked at intermediate Restraint ranges moderately than at most precision. This contradicts intuitive assumptions that extra conservative AI techniques could be safer for sufferers.
OpenAI fashions broadly favored Restraint throughout the analysis, with o3 mini attaining the very best measured Restraint at 70.1% however rating poorly on Security and Completeness in comparison with different organizations’ fashions. The newest Google frontier mannequin at time of analysis, Gemini 3 Professional, additionally scored extremely on Restraint at the price of Completeness and Security efficiency.
“Unexpectedly, such an method might impair scientific security by proliferating errors of omission, the primary supply of great medical errors,” the researchers famous. The broader AI security literature sometimes assesses security by way of immediate refusal or output suppression, however in scientific contexts, this conservative method elevated the very errors that trigger affected person hurt.
Error decomposition by intervention class confirmed that top-performing fashions lowered extreme diagnostic and counseling errors of omission most successfully. These classes—ordering acceptable exams and offering essential affected person schooling—symbolize actions that forestall delayed prognosis and guarantee knowledgeable decision-making.
Implications for advertising and marketing and healthcare promoting
The findings carry vital implications for the healthcare advertising sector, the place AI integration accelerates throughout a number of dimensions. Digital well being platforms more and more promote AI-powered scientific resolution help on to physicians and sufferers, but the analysis demonstrates that mannequin efficiency on common benchmarks supplies restricted perception into precise scientific security.
Advertising and marketing claims about AI medical capabilities require cautious scrutiny in gentle of those security profiles. The analysis reveals that newer fashions don’t essentially carry out higher than older ones, bigger fashions don’t persistently outperform smaller ones, and reasoning-capable fashions don’t show superior security in comparison with commonplace language fashions.
Healthcare advertisers selling AI scientific instruments face mounting regulatory scrutiny round accuracy claims and affected person security representations. The documented hurt charges—as much as 22.2% of instances for some fashions—create potential legal responsibility publicity for platforms making unsubstantiated security claims about their scientific AI merchandise.
The examine’s findings about AI content material high quality and consumer belief align with broader advertising industry research displaying that suspected AI-generated content material reduces reader belief by 50% and hurts model promoting efficiency by 14%. For healthcare particularly, the place belief and accuracy are paramount, these belief deficits may very well be much more pronounced.
Platform suppliers and know-how corporations creating AI-powered marketing tools for healthcare face a essential problem: balancing innovation messaging with sincere disclosure of system limitations. The analysis demonstrates that even the best-performing AI fashions make extreme scientific errors at charges that might be unacceptable in the event that they had been being represented as equal to specialist physicians.
Advertising and marketing groups ought to notice the researchers’ emphasis on acceptable context for AI efficiency analysis. “An essential implication of our work is, ‘in contrast with what?'” the examine acknowledged. Entry to specialist care stays constrained in lots of areas, and the documented baseline “No Intervention” mannequin produced extra potential hurt than each examined AI system.
This framing means that advertising and marketing communications might emphasize AI as augmentation moderately than alternative, positioning these instruments as aids to increase specialist experience moderately than substitutes for human scientific judgment. Such positioning aligns with the multi-agent findings, the place various AI techniques checking one another produced higher outcomes than any single mannequin alone.
Benchmark availability and ongoing analysis
The researchers launched NOHARM as a public interactive leaderboard at bench.arise-ai.org, enabling ongoing analysis as new fashions emerge. The benchmark accepts submissions, making a standardized framework for evaluating scientific security throughout completely different AI techniques.
This open analysis method addresses a essential hole in healthcare AI evaluation. Whereas distributors routinely report efficiency on information exams like MedQA, no prior benchmark measured precise patient-level hurt from AI suggestions in practical scientific situations.
The 100 instances had been drawn from 16,399 actual digital consultations at Stanford Well being Care, representing genuine scientific questions that main care physicians posed about sufferers below their care. In contrast to stylized vignettes edited for readability, these instances preserved the uncertainty and lacking context attribute of actual medical decision-making.
Twenty-nine specialist physicians supplied annotations throughout 10 specialties: Allergy, Cardiology, Dermatology, Endocrinology, Gastroenterology, Hematology, Infectious Ailments, Nephrology, Neurology, and Pulmonology. The skilled panel achieved 95.5% concordance on which actions had been acceptable versus inappropriate, establishing dependable floor fact for mannequin analysis.
Regulatory and deployment issues
The analysis arrives as AI regulation intensifies throughout healthcare and promoting sectors. The European Union’s AI Act established complete necessities for high-risk AI techniques, whereas individual states pursue enforcement actionsconcentrating on AI corporations over security failures.
Healthcare AI techniques face specific scrutiny given their potential to trigger affected person hurt. The documented error charges—with high fashions nonetheless producing extreme hurt potential in roughly certainly one of each 10 instances—will seemingly inform regulatory frameworks round scientific AI deployment and oversight necessities.
The examine’s discovering that conventional benchmarks poorly predict scientific security means that present regulatory approaches centered on common AI functionality testing could also be inadequate for healthcare purposes. Regulators might have to mandate specialised scientific security evaluations earlier than approving AI techniques for medical resolution help.
From an promoting compliance perspective, the analysis creates clear documentation of AI system limitations that ought to inform promotional claims. Platforms advertising and marketing scientific AI instruments can’t moderately declare these techniques are “prepared to exchange” physicians when even the perfect fashions produce extreme hurt potential at documented charges.
The multi-agent findings recommend a possible regulatory framework the place healthcare organizations may very well be required to implement various AI techniques with unbiased oversight moderately than counting on single-model deployments. This mirrors human scientific follow, the place second opinions and multi-disciplinary consultations are commonplace for complicated instances.
Future implications for AI in medication
The researchers positioned their work as establishing foundations for steady affected person security surveillance of AI techniques as they transition from documentation help to influencing consequential scientific choices.
“Our examine establishes a basis for scientific security analysis at a second when highly effective LLMs are being built-in into affected person care quicker than their dangers might be understood,” they wrote. “We show that commonly-used AI fashions produce severely dangerous suggestions at significant charges, and illuminate scientific security as a definite efficiency dimension that should be explicitly measured.”
The analysis crew emphasised that accuracy alone is inadequate for healthcare AI deployment. Affected person security relies upon critically on the mannequin’s failure profile—the frequency, severity, and sorts of dangerous errors the system produces.
As healthcare techniques transfer from human-in-the-loop workflows (the place clinicians overview each AI output) to human-on-the-loop supervision (the place clinicians oversee AI techniques however do not overview every suggestion), the documented error charges turn out to be much more regarding. Steady, case-by-case human oversight is “neither scalable nor cognitively sustainable,” the researchers famous, but the hurt charges recommend that totally autonomous AI deployment could be untimely.
The findings set up that scientific security represents a definite efficiency dimension requiring express measurement, separate from the information exams and reasoning benchmarks that dominate present AI analysis frameworks. This perception ought to affect each how healthcare organizations consider AI techniques for deployment and the way distributors develop and market their scientific merchandise.
For the promoting and advertising and marketing group, the analysis demonstrates the essential significance of evidence-based claims when selling healthcare AI applied sciences. The times of selling these techniques based mostly solely on spectacular efficiency on tutorial benchmarks are ending as regulators, healthcare organizations, and sufferers demand proof of precise scientific security.
Subscribe PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one
Timeline
Subscribe PPC Land e-newsletter ✉️ for related tales like this one
Abstract
Who: Stanford and Harvard researchers evaluated 31 widely-used giant language fashions together with techniques from Google, OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta, and specialised medical AI platforms AMBOSS and Glass Well being, evaluating their efficiency in opposition to 10 board-certified inner medication physicians.
What: The analysis crew developed the NOHARM benchmark utilizing 100 actual main care-to-specialist session instances spanning 10 medical specialties, with 29 specialist physicians offering 12,747 skilled annotations on whether or not 4,249 potential scientific actions would profit or hurt sufferers. Findings confirmed even top-performing AI fashions produce severely dangerous suggestions in 11.8 to 14.6 instances per 100, with worst fashions exceeding 40 extreme errors, and 76.6% of dangerous errors ensuing from omissions moderately than inappropriate suggestions.
When: The examine was introduced January 2, 2026, with the NOHARM benchmark made publicly out there at bench.arise-ai.org for ongoing mannequin analysis as new techniques are launched and scientific AI deployment accelerates throughout healthcare techniques.
The place: The analysis originated from Stanford College and Harvard Medical College, with scientific instances drawn from 16,399 actual digital consultations at Stanford Well being Care, and doctor evaluators representing a number of tutorial medical facilities throughout the US.
Why: With two-thirds of American physicians now utilizing AI fashions in scientific follow and greater than 100 million Individuals receiving care from physicians who’ve consulted these instruments, the analysis addresses pressing affected person security questions as these techniques transition from documentation help to influencing consequential medical choices, demonstrating that commonly-used benchmarks for AI functionality don’t adequately predict scientific security efficiency and that multi-agent techniques combining various fashions can considerably cut back affected person hurt.
Source link