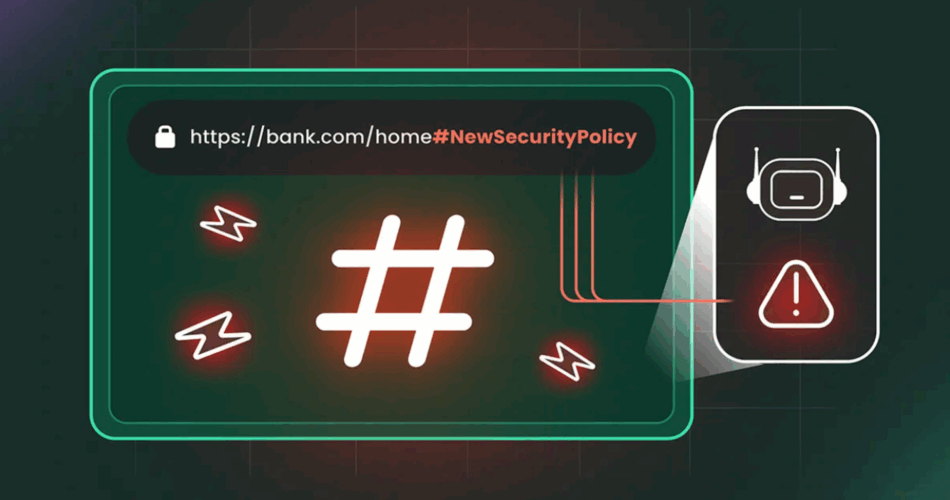
- Hidden URL fragments permit attackers to control AI assistants with out person information
- Some AI assistants transmit delicate information to exterior endpoints robotically
- Deceptive steering and faux hyperlinks can seem on in any other case regular web sites
Many AI browsers are going through scrutiny after researchers detailed how a easy fragment in a URL can be utilized to affect browser assistants.
New analysis from Cato Networks discovered the “HashJack” method permits malicious directions to take a seat quietly after a hashtag in an in any other case legit hyperlink, making a path for covert instructions that stay invisible to conventional monitoring instruments.
The assistant processes the hidden text locally, which means the server never receives it, and the user continues to see a normal page while the browser follows instructions they never typed.
Behaviour of assistants when fragments are processed
Testing showed certain assistants attempt autonomous actions when exposed to these fragments, including actions that transmit data to external locations controlled by an attacker.
Others present misleading guidance or promote links that imitate trusted sources, giving the impression of a normal session while altering the information provided to the user.
The browser continues to display the correct site, which makes the intrusion difficult to detect without close inspection of the assistant’s responses.
Major technology firms have been notified of the issue, but their responses varied significantly.
Some vendors deployed updates to their AI browser features, while others judged the behaviour as expected based on existing design logic.
Companies said defending against indirect prompt manipulation depends on how each AI assistant reads hidden page instructions.
Regular traffic inspection tools can only observe URL fragments that leave the device.
Therefore, conventional security measures provide limited protection in this scenario because the URL fragments never leave the device for inspection.
This forces defenders to move beyond network-level review and examine how AI tools combine with the browser itself.
Stronger oversight requires consideration to native habits, together with how assistants course of hidden context invisible to customers.
Organisations have to make use of stricter endpoint protection and tighter firewall guidelines, however these are solely a layer and don’t repair the visibility hole.
The HashJack methodology illustrates a vulnerability distinctive to AI-assisted looking, the place legit web sites could be weaponised with out leaving standard traces.
Consciousness of this limitation is crucial for organisations deploying AI instruments, as conventional monitoring and defence measures can not totally seize these threats.
How to stay safe
- Limit personal information shared online.
- Monitor financial accounts for unusual activity.
- Use unique, complex passwords for all accounts.
- Verify URLs before logging into websites.
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages or calls claiming to be from financial institutions.
- Deploy antivirus software to guard gadgets from malware.
- Allow firewalls to dam unauthorized entry.
- Use identity theft protection to observe private data.
- Acknowledge that subtle phishing campaigns and AI-driven assaults nonetheless pose dangers.
- Effectiveness is determined by constant implementation throughout gadgets and networks.
Follow TechRadar on Google News and add us as a preferred source to get our professional information, opinions, and opinion in your feeds. Make sure that to click on the Observe button!
And naturally you too can follow TechRadar on TikTok for information, opinions, unboxings in video type, and get common updates from us on WhatsApp too.